Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Blue skin lesions may be due to melanocytic lesions, vascular lesions or exogenous pigment. Dermoscopy may be useful to distinguish them.
Melanin is normally a brown colour. Melanocytic lesions tend to be blue in colour if the melanin is located within the dermis. They may be congenital (e.g., mongolian spot) or acquired.
For each of the seven cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately 2 minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
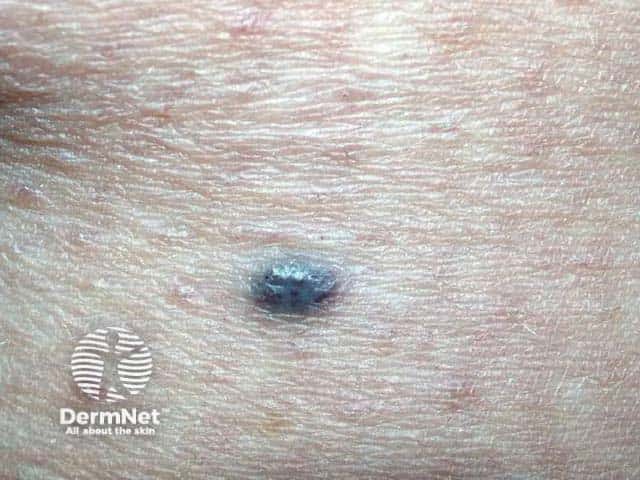
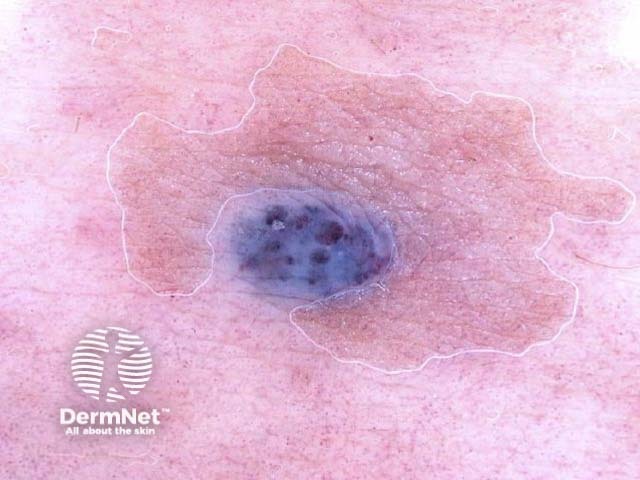
Name this blue-coloured skin lesion.
Angioma
Describe the dermoscopic features
Vascular lesions may also be congenital (e.g. vascular naevi) or acquired. They may be skin coloured, red, purple or blue in colour. They include ectasias, angiomas and purpura.
It is not surprising that vascular lesions are sometimes thought to be melanoma, as they may have a dark blue-black colour. An angioma will lose its colour on compression, unless its thrombosed.
Dermoscopy is nearly always very helpful, revealing typical uniform lacunes separated by fibrous bands. The glassy appearance of an angioma is not classified as ‘blue-grey veil’ because it extends across the entire lesion.