Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
For each of the ten cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately five minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
When you finish the quiz, you can download a certificate.
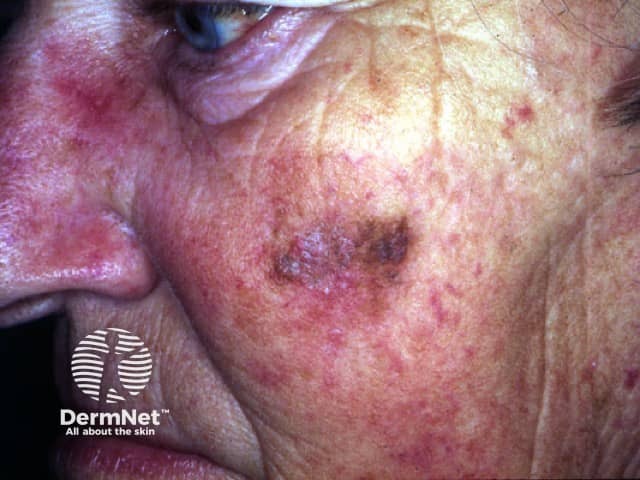
What is the differential diagnosis of the lesion?
The lesion on the left cheek is more than 2cm in diameter and irregular in shape and pigmentation. Possible diagnoses include: lentigo maligna (Hutchinson's melanotic freckle), superficial spreading melanoma, solar lentigo and seborrhoeic keratosis.
What should you advise her?
She should be informed of the possible explanations including melanoma. She should be referred to a dermatologist or plastic surgeon for an opinion. Because the lesion is so large, it would be reasonable to consider a biopsy, perhaps several biopsies, to make the diagnosis. However,'sampling' can result in erroneous results if a melanoma is arising in a benign lentigo. The most likely diagnosis is lentigo maligna. This is a melanoma in-situ (i.e. malignant melanocytic cells confined to the epidermis) and arises in sun damaged skin. The risk of lentigo maligna progressing to invasive melanoma is unknown, but may be less than 10%. Complete excision is however advisable. Because of the need for extensive surgery, sometimes radiotherapy or cryotherapy is preferred or the patient may choose 'observation'. Excision becomes more urgent if a palpable nodule arises within the lesion.