Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
For each of the ten cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately five minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
When you finish the quiz, you can download a certificate.
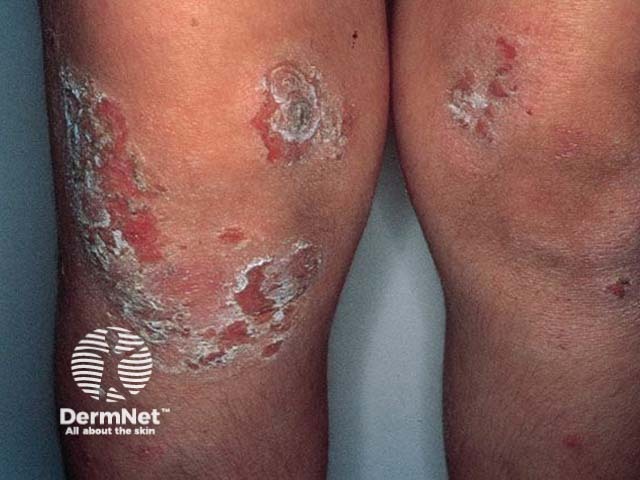
What initial investigations should be performed?
A swab should be taken for gram stain and bacterial culture. The presumptive diagnosis is bullous impetigo. Although most often due to Staphylococcus aureus, many cases have concurrent haemolytic streptococci.
What treatment should be instituted?
Extensive impetigo should be treated with adequate dose of antistaphylococcal and antistreptococcal oral antibiotics. Suitable medications include dicloxacillin, flucloxacillin, and erythromycin. Local treatment may be with wet dressings and topical antiseptics or topical antibiotics. Dilute acetic acid compresses are useful.
Suggest management if the rash fails to clear or later relapses.
Check the sensitivity of the bacteria to the prescribed antibiotic. Ensure it is taken in adequate dose until clinical resolution. Treat carrier sites eg. mupirocin or fusidic acid ointment to nostrils, and use antiseptic cleanser. Examine family members and treat cutaneous infection and nasal staphylococcal carriage. Evaluate patient for underlying skin condition such as atopic dermatitis, or scabies. Refer to a dermatologist to ensure diagnosis is correct.