Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Cutaneous spots and blotches may be yellow because of endogenous or exogenous pigment (xanthochromia), or because of a thick layer of keratin of lipid.
For each of the twelve cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately 2 minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
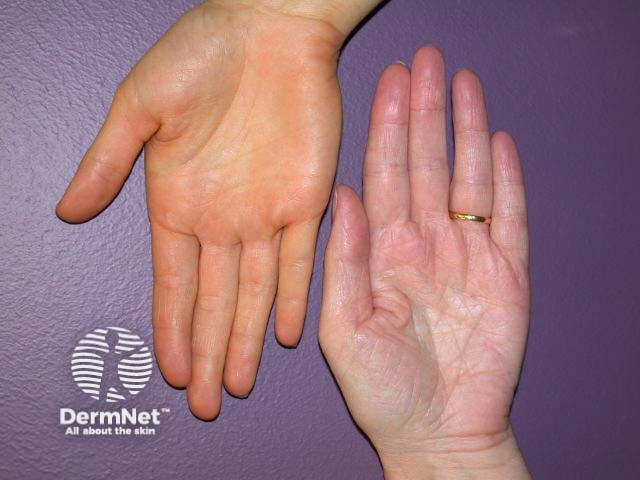
What is the diagnosis?
Carotenaemia (the hand on the left)
What causes the yellow hue in the skin in this condition?
Carotenaemia results in orange-yellow skin discolouration, especially on the nasolabial folds, palms and soles as the lipochrome is excreted through the epidermis via sebum and sweat. The sclerae remain white and the colour is more pronounced under artificial light. The vitamin A level remains normal. Most often observed in infants, carotenaemia is mainly due to dietary carotene in ripe yellow, red and green vegetables and fruit, eggs and milk. Tomatoes also contain lycopenes, which may contribute to skin colour. It may also occur if there is hyperlipidaemai (diabetes) decreased conversion into vitamin A (hypothyroidism, primary liver disease).