Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Necrotising infundibular crystalline folliculitis pathology — extra information
Follicular disorder Diagnosis and testing
Necrotising infundibular crystalline folliculitis pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Necrotising infundibular crystalline folliculitis is characterised clinically by sharply demarcated waxy papules. It is caused by follicular accumulation of a material which is thought to be derived from Malassezia yeasts, bacteria, and/or sebaceous lipids.
Histology of necrotising infundibular crystalline folliculitis
In necrotising infundibular crystalline folliculitis, sections show filamentous deposits, enclosed by parakeratotic columns within partly necrotic follicle ostium (figure 1). There is incidental actinic keratosis in the case illustrated herein. Higher power examination shows crystalline urate-like structures within the filamentous material (figures 2, 3). The material is birefringent with polarised light.
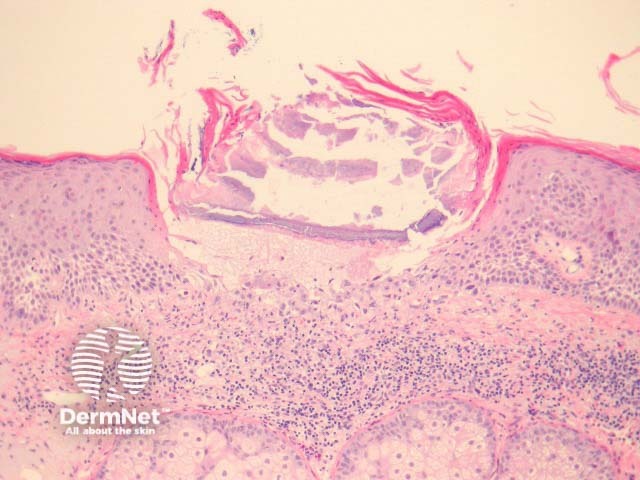
Figure 1
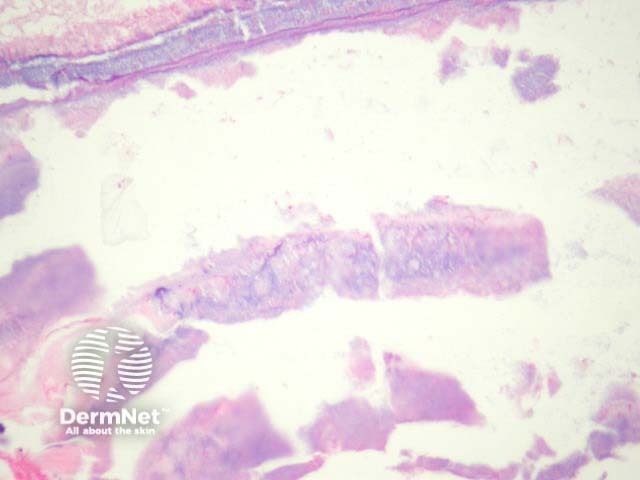
Figure 2
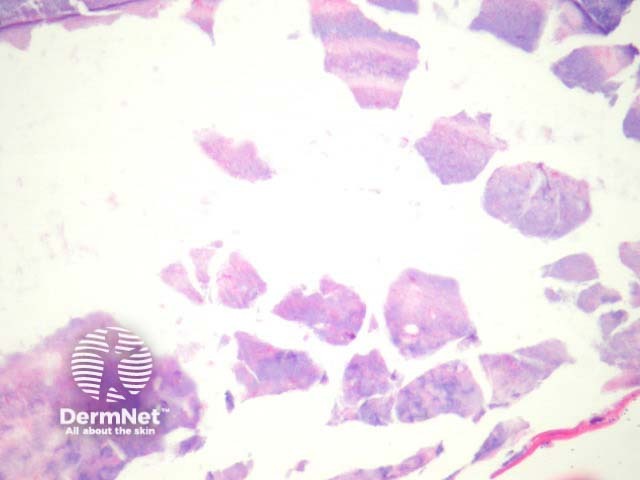
Figure 3
Special studies for necrotising infundibular crystalline folliculitis
None are generally needed. PAS may demonstrate pityrosporum species.
Differential diagnosis of necrotising infundibular crystalline folliculitis pathology
Gout – The distinctive filamentous material resembles gout.
References
- Kossard S, Scurry J, Killingsworth M. Necrotizing infundibular crystalline folliculitis. Br J Dermatol. 2001 Jul;145(1):165–8. PubMed
On DermNet
