Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Connective tissue diseases Metabolic
Author: Harriet Cheng BHB, MBChB, Dermatology Unit, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, New Zealand; Duncan Lamont, Pathologist, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, New Zealand; A/Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Lichen myxoedematosus or papular mucinosis is a rare skin disorder characterised by mucin deposits in the skin. The localised form presents with firm, waxy papules with localised distribution and without systemic features. The generalised form (also known as scleromyxoedema) presents with widespread flesh-coloured papules arranged in lines and progressive skin thickening. It is strongly linked to monoclonal gammopathy.
Early lesions may show deposition of mucin in the superficial dermis which may be difficult to distinguish from focal muconosis.
In more established lesions, the epidermis may be normal, acanthotic or atrophic.
There are deposits of mucin throughout the dermis accompanying by fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition (figure 1, 2).
The fibroblast proliferation may be more overt with generalised scleromyxoedema.
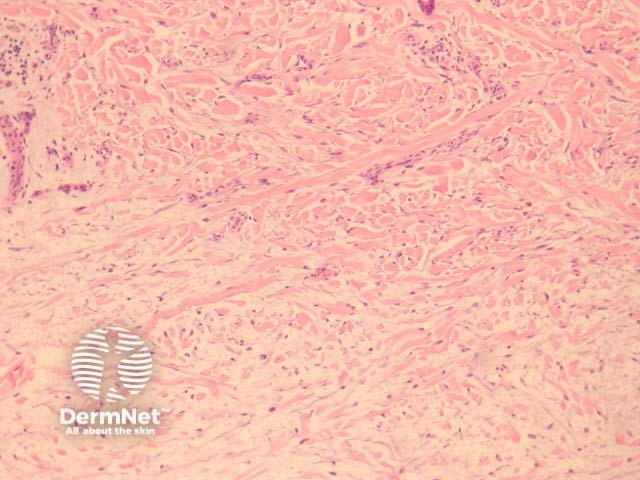
Figure 1
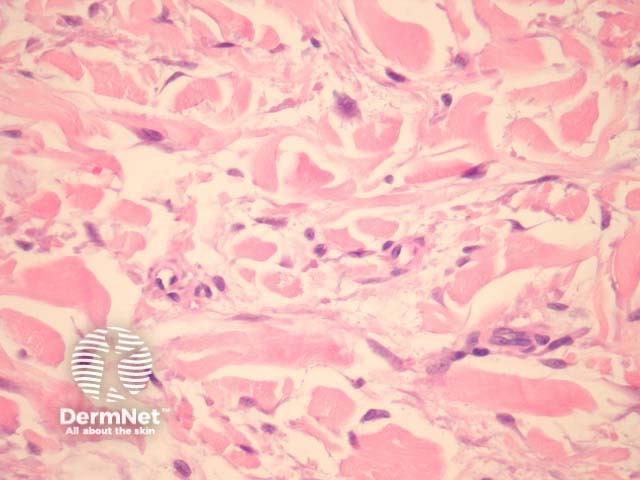
Figure 2
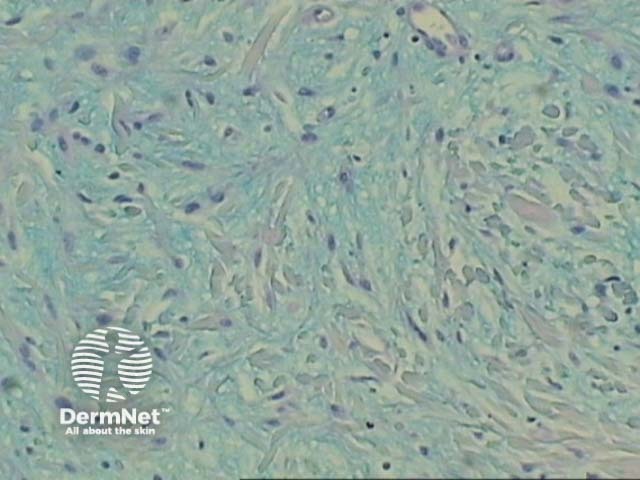
Figure 3
Mucin stains with colloidal iron (blue-green) and Alcian blue at pH 2.5 (blue). Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) is negative. Figures 3 show staining with Alcian blue.
Clinical correlation is very helpful.
Nephrogenic systemic sclerosis: This condition is associated with the use of gadolinium-based contrast agents used during magnetic resonance imaging in people with renal insufficiency. Histological changes are similar to scleromyxoedema although the subcutis is more often involved. Sclerotic bodies have been described in this condition.
Focal mucinosis: May be indistinguishable from localized papular mucinosis. Lacks fibroblastic change and collagen deposition in superficial dermis. Clinically, this is a solitary lesion
Generalised and pretibial myxoedema: These conditions are associated with thyroid disease. There is mucin deposition in the dermis without fibroblast proliferation. Epidermal changes may include hyperkeratosis and follicular plugging.