Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Diagnosis and testing Connective tissue diseases
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand. January 2015.
Sclerema neonatorum usually affects gravely ill, preterm neonates in the first week of life. It is characterised by hardening of the skin that gets bound down to the underlying structures.
In sclerema neonatorum, needle-shaped crystals are arranged radially in adipocytes. There is little or no associated inflammatory infiltrate and no fat necrosis (figures 1, 2).
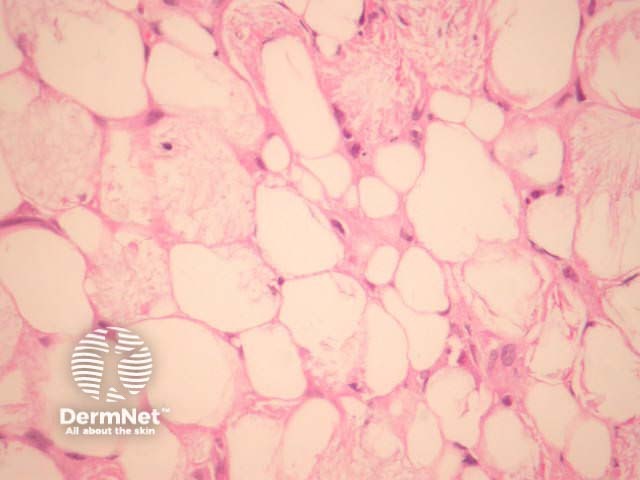
Figure 1
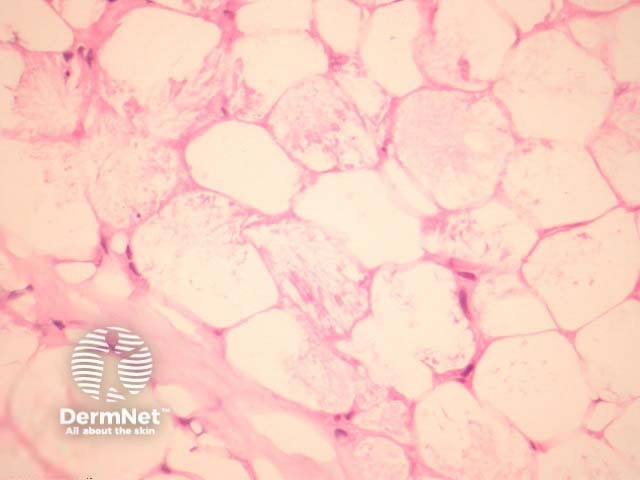
Figure 2
None are generally needed.
Poststeroid panniculitis and subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn: These show identical crystals but there is associated inflammatory and foreign body response.