Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
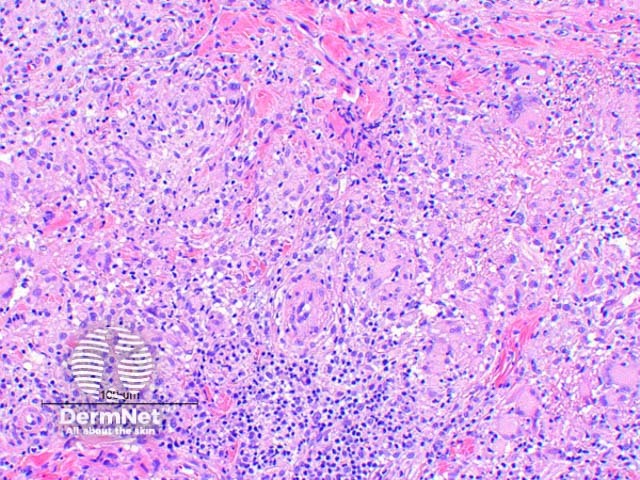
Figure 3
Keywords: Mycobacterium marinum skin infection, Histopathology-image, Pathology
The histologic findings of Mycobacterium marinum infection vary by the age of the lesion. Scanning power view of well developed lesions demonstrate a granulomatous dermatitis (Figure 1), forming an extensive inflammatory nodular infiltrate within the dermis. Early lesions may show an acute suppurative inflammatory process with little granuloma formation. The epidermis may show prominent pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with or without ulceration. There are tuberculoid granulomas with varying degrees of abscess formation (Figure 2). The infiltrate is mixed lymphohistiocytic with multinucleated giant cells and scattered neutrophils (Figures 3 and 4).
© DermNet
You can use or share this image if you comply with our image licence. Please provide a link back to this page.
For a high resolution, unwatermarked copy contact us here. Fees apply.
Source: dermnetnz.org