Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant inherited condition characterised by the development of benign tumours on the head, face and upper body. The benign skin tumours involved in this condition are:
People with Birt-Dogg-Dubé syndrome are at increased risk of developing colon or kidney cancer (in 15%) as well as spontaneous pneumothorax (lung collapse) due to pulmonary (lung) cysts.
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome is also known as fibrofolliculoma with trichodiscoma and acrochordon. Canadian physicians Birt, Hogg and Dubé first described it in 1977.
Painless, small, papular skin lesions develop gradually over the scalp, face, neck, chest and back. Lesions usually develop at around age 30 or 40 years, although they have been found in younger patients, and they are not always present in people with the abnormal BHD gene.
Oral mucosal polyps, collagenomas, angiolipomas, and deforming lipomas may also form.
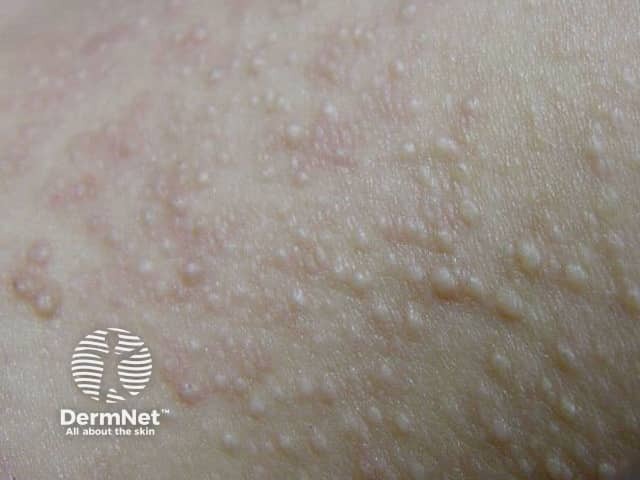
Fibrofolliculomas
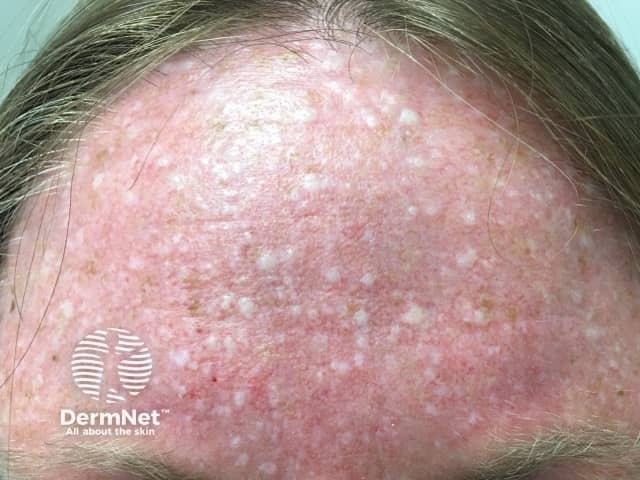
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome
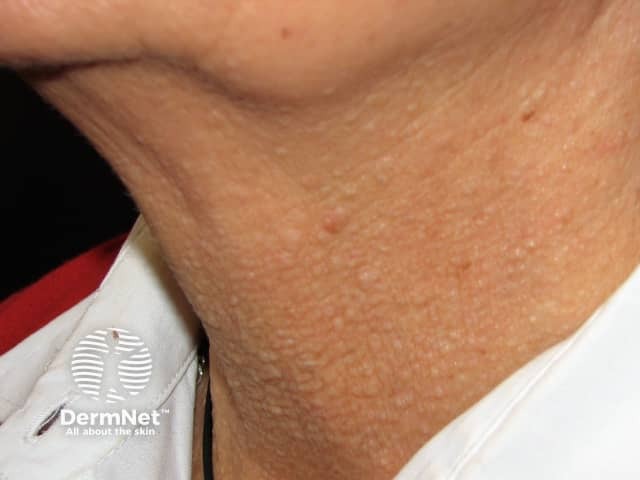
Fibrofolliculomas in Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome
See more images of Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome.
Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome is due to a mutation in the BHD or FLCN gene on chromosome 17p12-q11.2 encoding a protein called folliculin. It is not known why this mutation occurs. The syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition meaning half of an affected person's children have a risk of inheriting the mutation.
As the BHD gene had been identified, a gene test is the best definitive method of diagnosis for BHDS. This test is available in the main centres.
Skin biopsy of a lesion may also be performed to identify the nature of the lesion; facial papules are fibrofolliculomas or trichodiscomas. Adults with a positive gene test result for Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome should also undergo a renal ultrasound and abdominal CT/ MRI to determine if there are any associated problems or malignancies. They may also undergo chest x-ray and colonoscopy.
Patients with Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome should undergo medical and physical examinations and appropriate laboratory and radiographic tests regularly to check for internal complications such as kidney carcinoma, pulmonary cysts, and pneumothorax.
No specific medical treatment exists for the skin lesions of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Although the skin tumours are benign, they may become disfiguring if multiple lesions occur. The following skin procedures may help remove lesions, although recurrence is frequent.