Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
For each of the ten cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately five minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
When you finish the quiz, you can download a certificate.
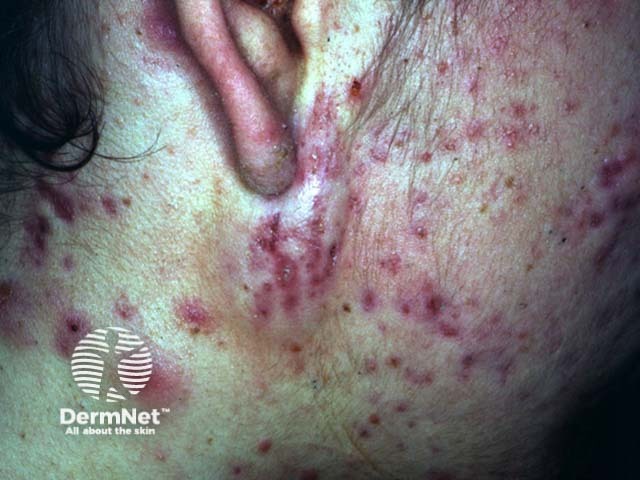
How would you manage his acne?
This young man has severe nodulocystic acne. It is resulting in pain, unsightliness and scarring. Prompt effective treatment is required. He should be referred to a dermatologist. While waiting for the appointment, initial treatment should be with oral tetracycline 1g/day or one of its derivatives (minocycline or doxycycline at least 100mg/day) and continuation of topical benzoyl peroxide. Antidepressant medication should be considered if there is significant mood disturbance. The most effective treatment of nodulocystic acne is oral isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/day for five or six months (occasionally longer). Isotretinoin is often curative. It is subsidised only when prescribed by a vocationally registered dermatologist. The dermatologist will review the patient regularly to monitor and manage inevitable side effects. These include mucocutaneous dryness, staphylococcal infections, tiredness, myalgia and hyperlipidaemia. Isotretinoin is a teratogen so must not be taken in pregnancy. Some patients treated with isotretinoin suffer from depression so multidisciplinary care may be appropriate. Some patients with severe nodulocystic acne will also receive oral erythromycin for a month or two - tetracycline is contraindicated when isotretinoin is prescribed because of an increased risk of raised intracranial pressure. Oral vitamin-A is contraindicated for the same reason.