Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
For each of the ten cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately five minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
When you finish the quiz, you can download a certificate.
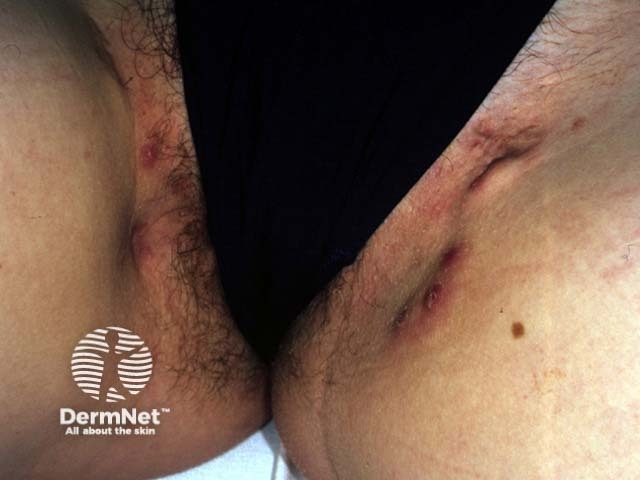
What is the diagnosis?
She has hidradenitis suppurativa. This is a chronic suppurative skin disease affecting the axillae, submammary and genitocrural areas of men and, more commonly, women. It is due to occlusion, secondary bacterial infection and inflammation of the apocrine glands. Hidradenitis is occasionally familial. Onset is generally at puberty and it improves at menopause. It is associated with other diseases due to follicular occlusion, such as conglobate acne and pilonidal sinus. Hidradenitis results in comedones, painful red nodules, induration, scarring, destruction of skin appendages and sinus formation.
What treatments are available?
Acute exacerbations should be treated as bacterial infections with antibiotic choice depending on isolated pathogens (most commonly Staphyococcus aureus, Stretpoccus milleri and Bacteroides). Fluctuant nodules (abscesses) should be drained. Long term the following may be useful: topical antiseptic washes; oral tetracycline, erythromycin or clindamycin; the oral contraceptive pill; antiandrogens (cyproterone); a prolonged course of oral isotretinoin. A surgical opinion should be sought in severe cases. Excision of nodules, marsupialisation of cysts and removal of sinus tracts may be necessary. Complete excision of all affected skin and healing by secondary intention is sometimes necessary for very severely affected individuals and is curative.