Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
This quiz will test how good you are at diagnosing skin conditions due to fungi, bacteria and viruses.
For each of the ten cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately 2 minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
When you finish the quiz, you can download a certificate.
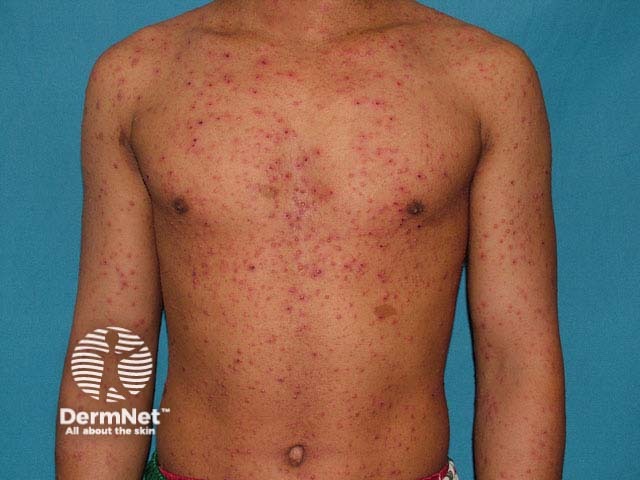
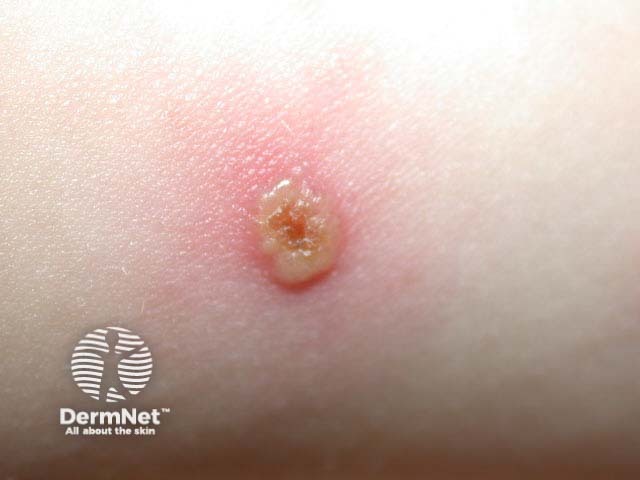
What is the diagnosis?
Chickenpox, a common primary infection with varicella-zoster or human herpes virus type 3 (VZV)
What are the clinical features of this condition?
More than 90% of children with chickenpox are infected before they are 10 years old. It is highly contagious, acquired by inhalation of airborne respiratory droplets or by direct contact with vesicle fluid. There may be a prodrome of fever, nausea, myalgia, anorexia and headache, with widespread vesicles appearing 10 days to 3 weeks after initial infection. Chickenpox tends to be more extensive and prolonged in adults and immunocompromised children, with secondary bacterial infection, viral pneumonia, encephalitis, thrombocytopenia and leucocytoclastic vasculitis causing the majority of complications. Chickenpox during pregnancy may result in fetal death or congenital varicella syndrome.
Several crops of macules rapidly progress to very itchy papules, vesicles and pustules over a few hours, with subsequent umbilication and crusting resolving in 7 to 10 days. The characteristic dew drop on a rose petal
describes a vesicle with surrounding erythematous halo. Few or many lesions at various stages of development may be seen at one time. The majority are found on the scalp, face, trunk and proximal limbs. However vesicles may also arise inside the mouth or on distal limbs. Larger blisters (bullae) may be seen occasionally. There may be more lesions in areas that have been sun exposed or overheated during the incubation period.
How is the diagnosis confirmed?
If required, the diagnosis may be confirmed by isolation of VZV by culture, direct immunofluorescence or increasingly, by polymerase chain reaction techniques.
What is the treatment?
Oatmeal baths, calamine lotion and oral antihistamines may reduce itching. In most cases, this is all that is required.
Oral aciclovir 800mg 5 times daily for 7 days should be prescribed for children with risk factors for complications such as severe atopic dermatitis or who are taking systemic steroids. It should be routinely prescribed for adults, preferably commenced within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms. Intravenous acyclovir is recommended in immunosuppressed patients.
Can the condition be prevented?
Live attenuated vaccine based on Oka strain of VZV is effective as a single dose in children and two doses in adults. It is available for healthy children, susceptible adolescents and adults on demand. It is recommended for at risk health care workers, especially those on obstetric, paediatric and neonatal units. It should only be used in immune suppressed children, under the direction and care of a paediatric oncologist. It may result in a mild vesicular rash a month after vaccination (2-10%) but this is rarely transmitted to others. The vaccine can be followed by clinical zoster but it is thought likely the risk is lower than after natural VZV infection [Varicella. Ministry of Health Immunisation Handbook 2002, section 17].