Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma pathology — extra information
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma pathology
Author: A/Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Introduction
Histology
Special studies
Differential diagnoses
Introduction
Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma is a histiocytic/granulomatous dermal infiltrate that results in phagocytosis and destruction of elastic fibres. Atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica is probably best considered a form of this disorder and because of this there is confusion in nomenclature.
Histology of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma
Sections show a granulomatous and lymphocytic infiltrate involving the dermis (figures 1, 3). The giant cells often contain asteroid bodies (figure 2, arrows). There is an associated infiltrate containing histiocytes, lymphocytes and some plasma cells (figures 1, 2).
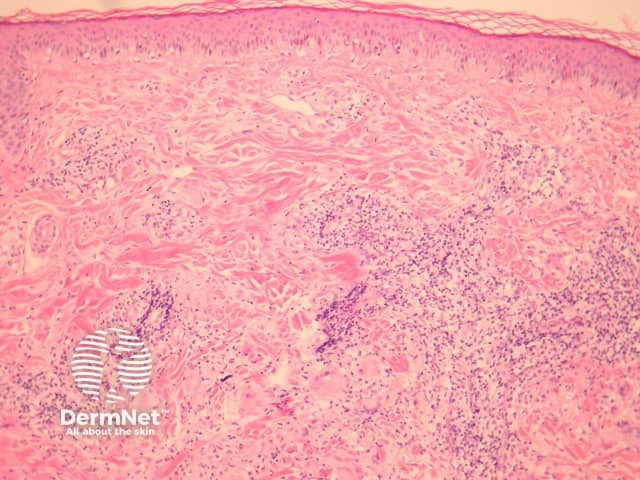
Figure 1
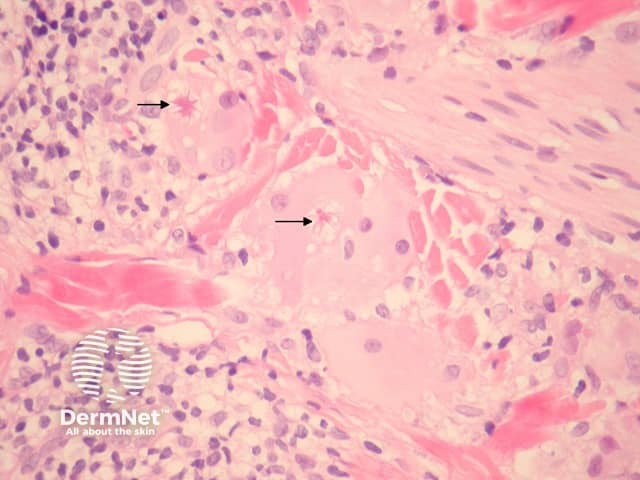
Figure 2
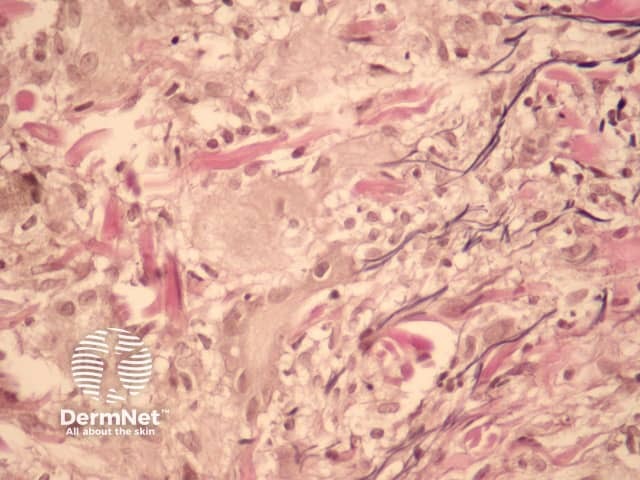
Figure 3
Special studies of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma
Elastic stains show a disruption of the elastic architecture (Figure 3, notice the reduced density of elastic fibres on the left side of the image).
Differential diagnosis of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma
Conditions to consider in the differential diagnosis of annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma are:
- Actinic granuloma (O’Brien) — this shows dense dermal elastosis which is thought to be responsible for the granulomatous reaction. There may also be elastolysis and phagocytosis of degenerate actinically damaged elastin by giant cell histiocytes. Some of these cases have been considered synonymous with annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma which has caused some confusion with nomenclature.
- Atypical facial necrobiosis lipoidica — this is thought by many authors to be annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma and seems to have no association with usual necrobiosis lipoidica.
- Sarcoidosis — this shows less associated inflammation and generally shows well-defined epithelioid granulomas.
References
- Pathology of the Skin (Fourth edition, 2012). McKee PH, J. Calonje JE, Granter SR
