Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Facial rashes — extra information
Facial rashes
Author: Hon A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, May 2016.
Erosions and crusting Dry or scaly rash Papulopustular rash Erythema Brown macules and patches Pale or white macules and papules Skin lesions
Facial rashes
Patients often present with quite mild signs when they have a facial lesion or rash — due to embarrassment — and the diagnosis may be tricky.
Significant itch suggests atopic dermatitis or contact dermatitis.
Face: erosions/crusting
Herpes simplex
- Monomorphic clustered vesicles or crusted papules
- Often locally recurrent in the same site
- Swabs: Herpes simplex
Herpes zoster
- Acute dermatomal eruption
- Painful: pain may precede the rash
- Erythema may precede vesicles
- Swabs: Herpes zoster
Impetigo
- Irregular enlarging plaque
- Honey-coloured crusts
- Swabs for impetigo: Staphylococcus aureus +/- Streptococcus pyogenes
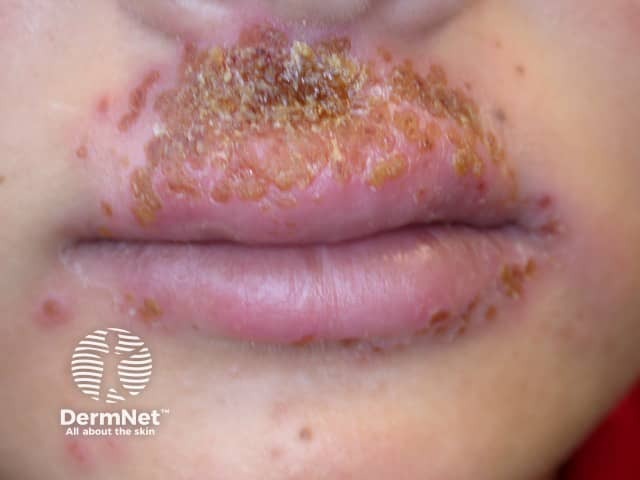
Herpes simplex
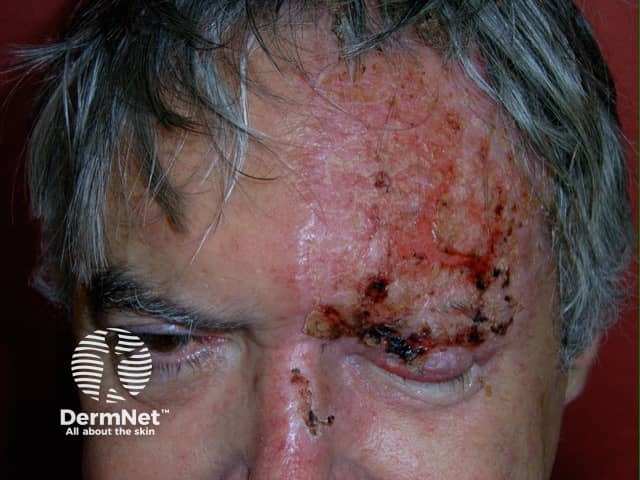
Herpes zoster
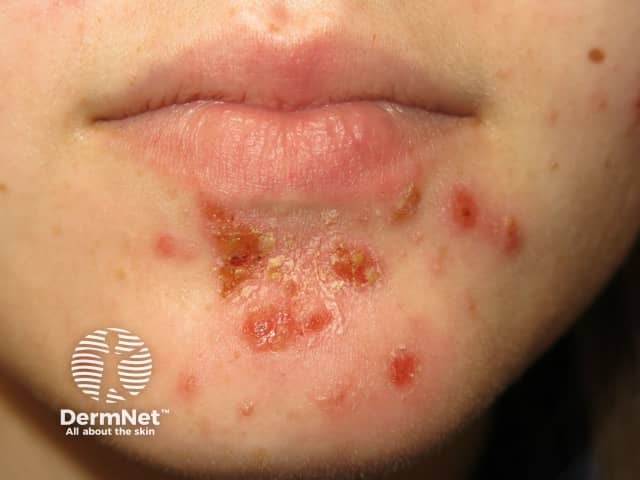
Impetigo
Dry or scaly rash
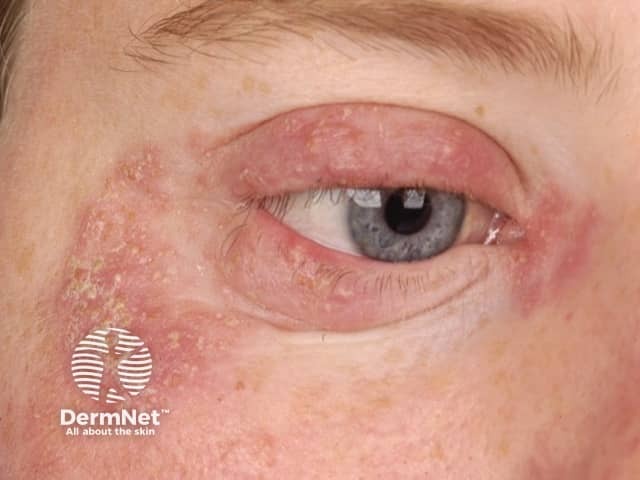
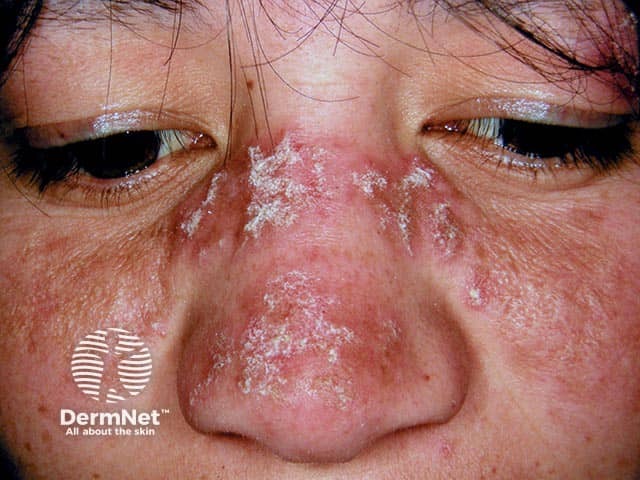
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis often also affects scalp, retroauricular sites, ears
- Hairline, eyebrows, medial cheeks, nasolabial folds, chin creases
- Scaly blepharitis
- Poorly defined, variable white or yellowish flaking
- May have erythematous patches or thin plaques
- Follicular prominence or follicular digitate keratoses
Psoriasis
- Psoriasis sites include eyelids, temples, retro- and pre-auricular skin and/or seborrhoeic dermatitis sites
- Also affects scalp, ears, elbows, knees, nails
- Well-demarcated erythematous plaques
- White scale
- More persistent than seborrhoeic dermatitis
Atopic eczema
- Atopic dermatitis often affects flexures: retroauricular, elbow and knee creases
- Symmetrical dermatitis of eyelids, perioral skin (up to lips)
- Intensely itchy
- Acute flare: oedema, erythema, crusting, fissuring
- Subacute: dryness, pinkness
- Chronic: dryness, lichenification, Dennie Morgan folds (2 creases in lower eyelids)
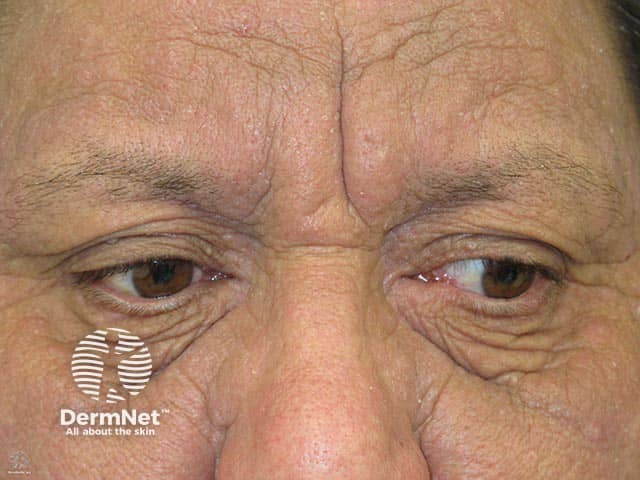
Atopic eczema
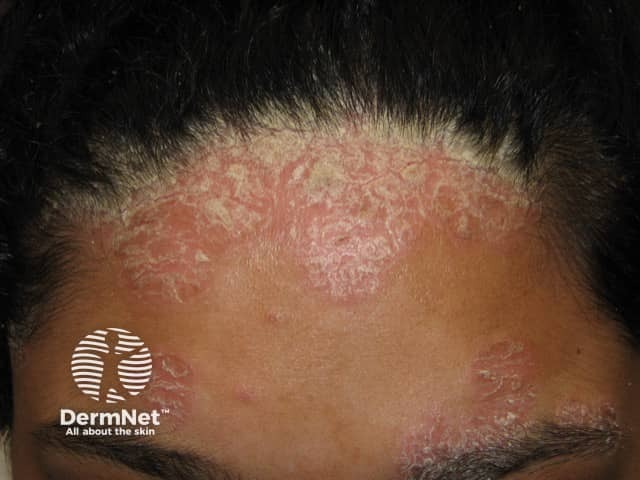
Psoriasis
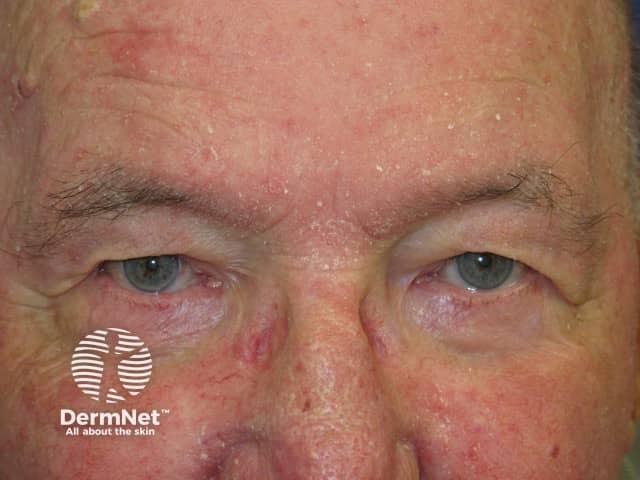
Seborrhoeic dermatitis
Contact eczema
- Acute, relapsing/intermittent or chronic presentation
- Irregular, variable, unilateral or asymmetrical dermatitis
- Sharp border if contact irritant dermatitis
- Patch tests positive if contact allergic dermatitis
Photosensitive dermatitis
- Exposed areas of face, arms, chest, legs
- Spares under hair, eyelids, creases
- Flares after exposure outdoors
- Can be drug-induced
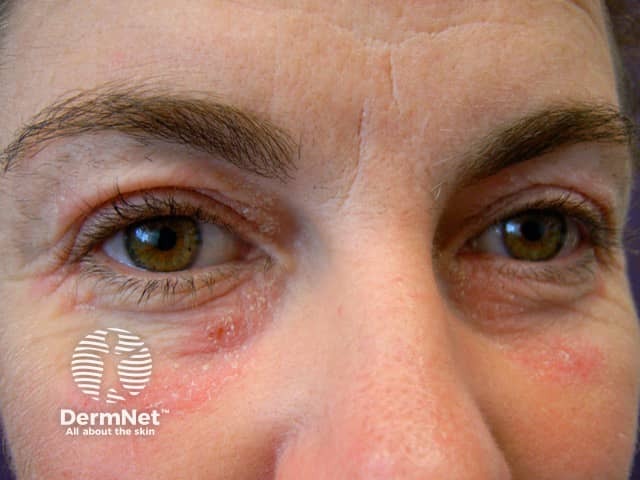
Contact eczema allergic
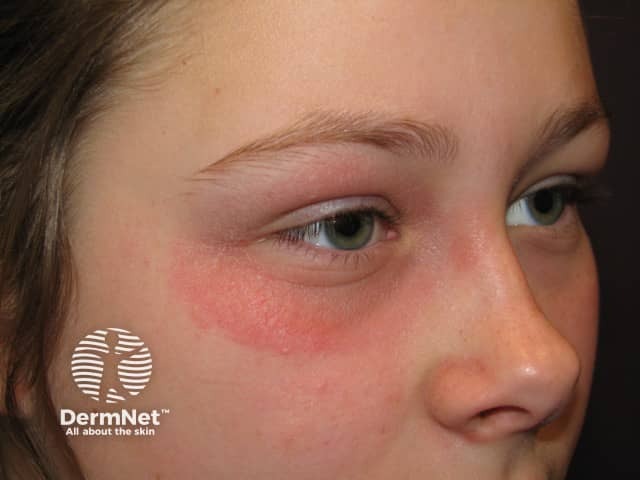
Contact eczema irritant
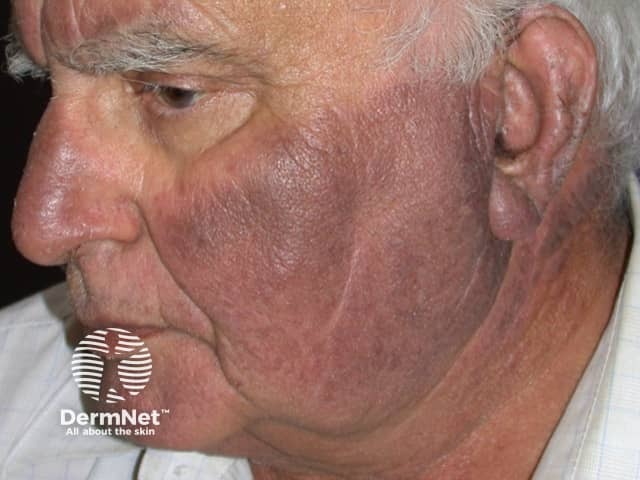
Photosensitive dermatitis
Tinea faciei
- Asymmetrical eruption
- Annular configuration is common
- Scaly edge
- Mycology positive
Actinic keratoses
- Located on sun-exposed sites of temples, forehead, nose, cheekbones, angle of jaw, upper lip, lower vermilion lip
- Actinic keratoses often involves persistent tender scaly papules, macules, plaques
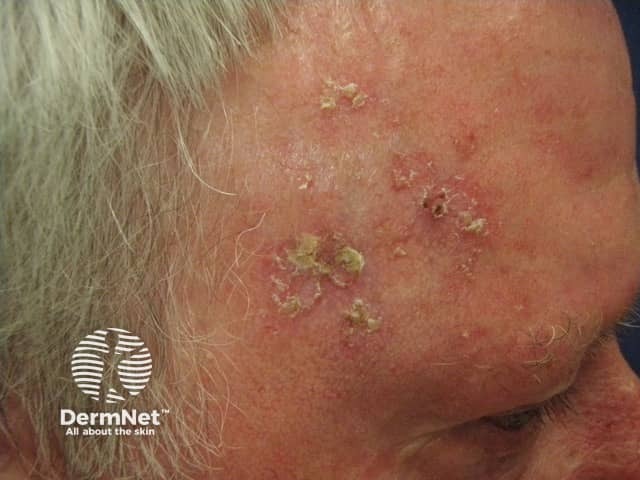
Actinic keratoses
Tinea faciei
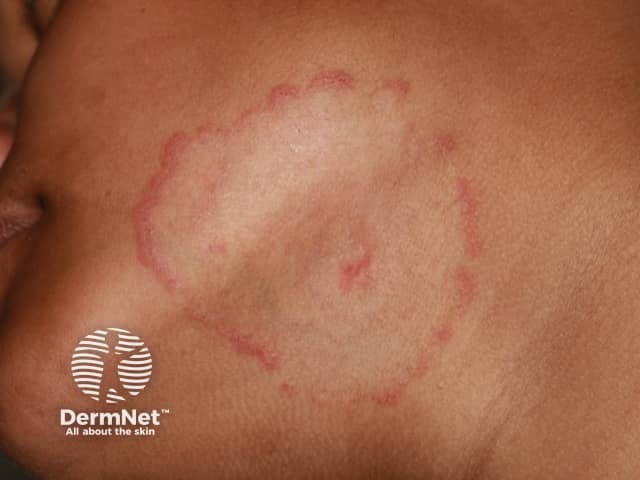
Tinea faciei
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
- Nose, cheeks, ears, lips, scalp
- Circumscribed plaques with follicular prominence, scale
- Post-inflammatory pigmentation, atrophic scarring
- CBC, ANA, ENA often normal
Lupus tumidus / Jessner lymphocytic infiltrate
- Cheeks, upper trunk
- Smooth surface to erythematous dermal plaques
Discoid lupus erythematosus
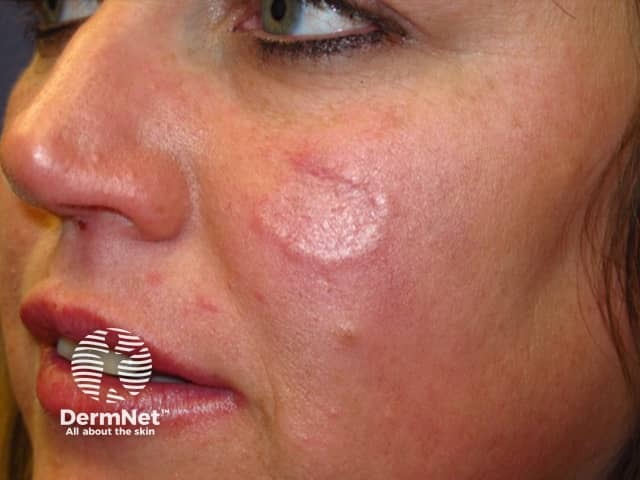
Lupus tumidus / Jessner lymphocytic infiltrate
Papulopustular rash
Acne
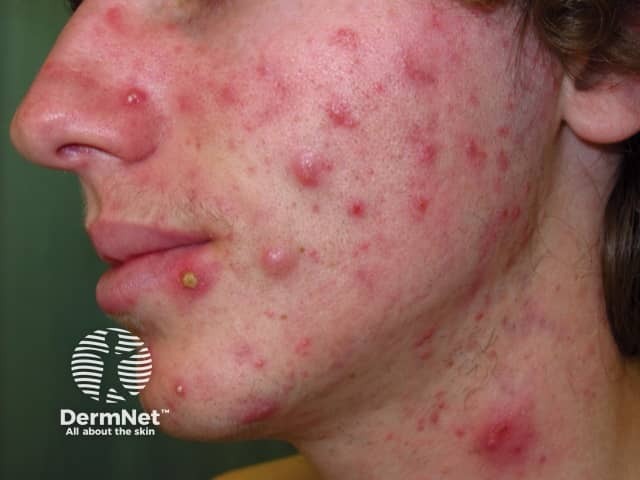
Acne
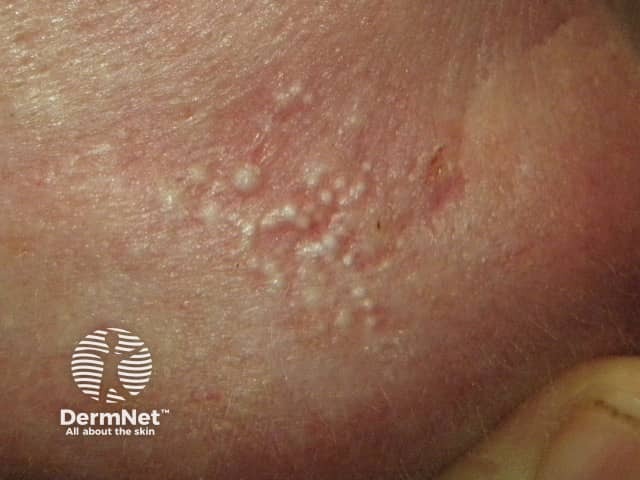
Closed comedones
- Onset of acne often at puberty
- Usually, symmetrical forehead, chin, lateral face, nose
- Mixed inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions
- Papules, pustules, nodules, comedones
Perioral/periorificial dermatitis
- Usually adult females using face cream, often topical corticosteroid
- Often, asymmetrical first in perioral sites, later in perinasal and periocular sites
- Spares a centimetre of skin around vermilion of lips
- Grouped erythematous papules and pustules on erythematous patches, flaky surface
- Can occur in children
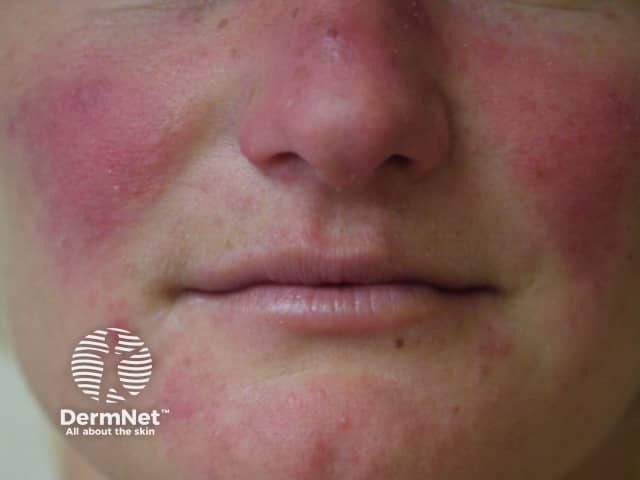
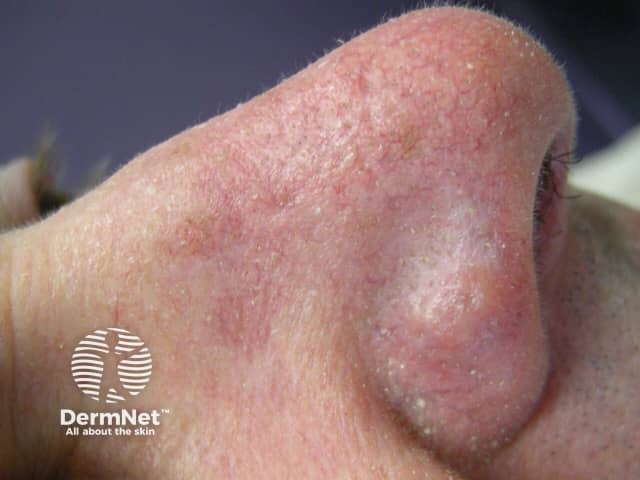
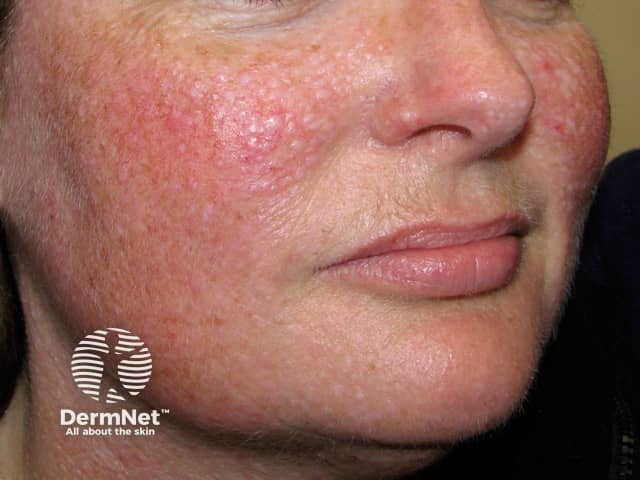
Rosacea
- Most prevalent in middle-aged adults
- Mid-facial: cheeks + nose, chin and forehead
- Erythema, flushing, papules, pustules, telangiectasia
- Rhinophyma causes enlargement of the nose in some patients
- Sensitive skin
- Lesions in rosacea can approach the lips
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae is most often associated with shaving
- Follicular papules, pustules, curled-in hair
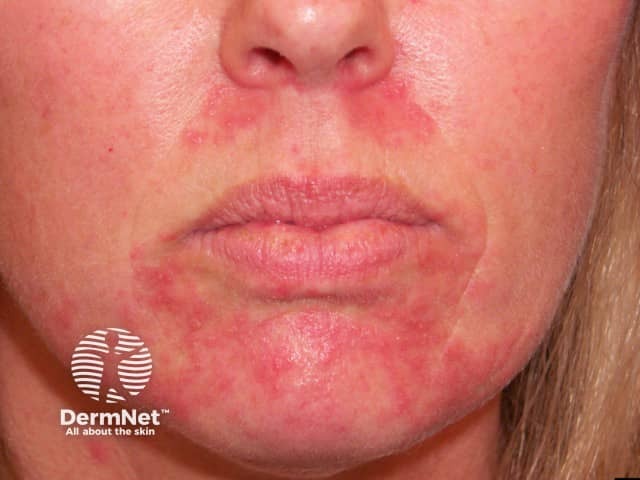
Perioral/periorificial dermatitis
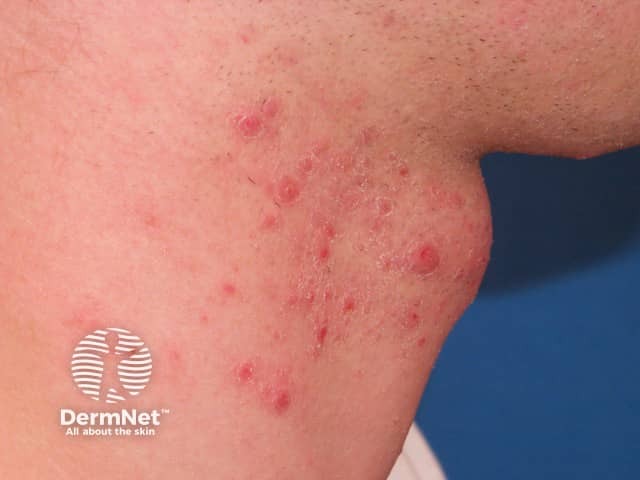
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
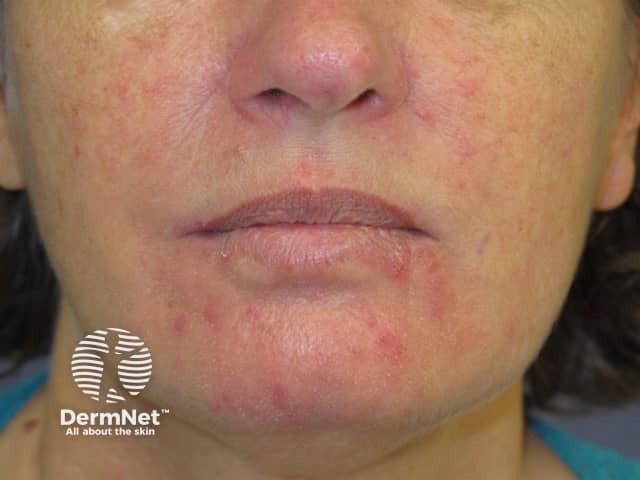
Rosacea
Face: erythema
Erythema is less pronounced in dark skin
Dermatomyositis
- Violaceous eyelids — may be swollen
- Poikiloderma on the trunk and limbs
- Gottron papules on fingers
- May have muscle weakness
Flushing
- Intermittent redness when hot, embarrassed or with certain foods
- Often lifelong tendency
- Systemically well
- Associated with rosacea
Sunburn
- Sun-exposed site
- Spares eyelids, furrows, under the chin
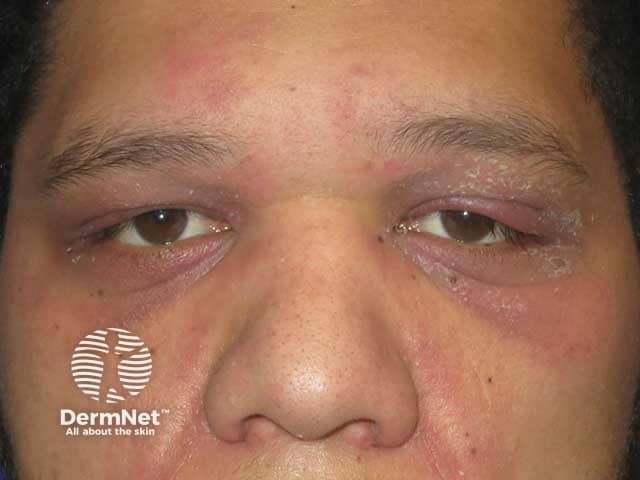
Dermatomyositis
Flushing
Sunburn
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Butterfly erythematous rash
- Systemic symptoms: tiredness, lethargy, arthralgia
- Check CBC, ANA, ENA
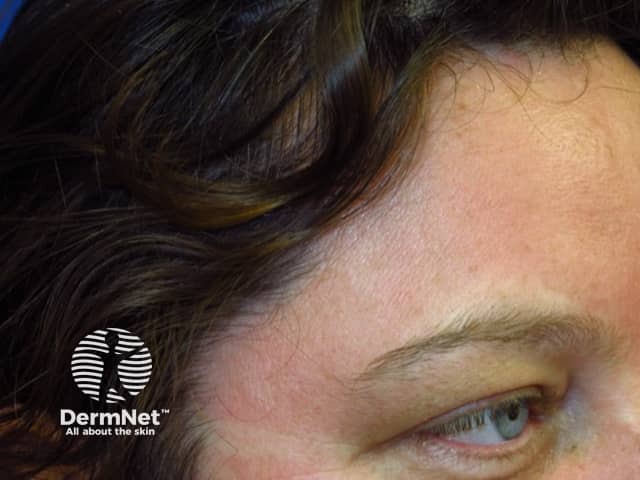
Telangiectasia
- May accompany flushing
- Vascular dilatation
- Various types
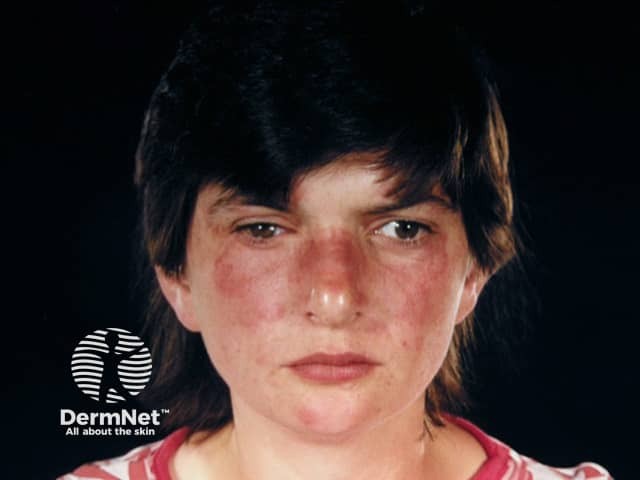
Systemic LE
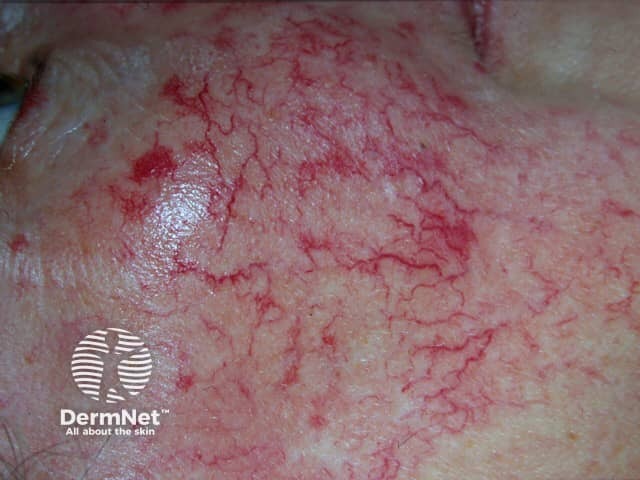
Telangiectasia
Face: brown macules/patches
Pigmentation is more pronounced in dark skin
Solar lentigines
- Sun-exposed sites
- Small to large freckles
- Well-demarcated flat or slightly scaly brown marks or thin plaques
Erythema dyschromicum perstans
- Grey-brown discolouration
- Any distribution
- Distinct border, sometimes red at first
Melasma
- Usually adult female
- Centrofacial, malar and mandibular patterns
- Spares eyelids, rare below jawline
- Symmetrical pigmentation with ragged border
Post-inflammatory pigmentation
- Preceding eczema, psoriasis, acne etc
- Distribution depends on cause
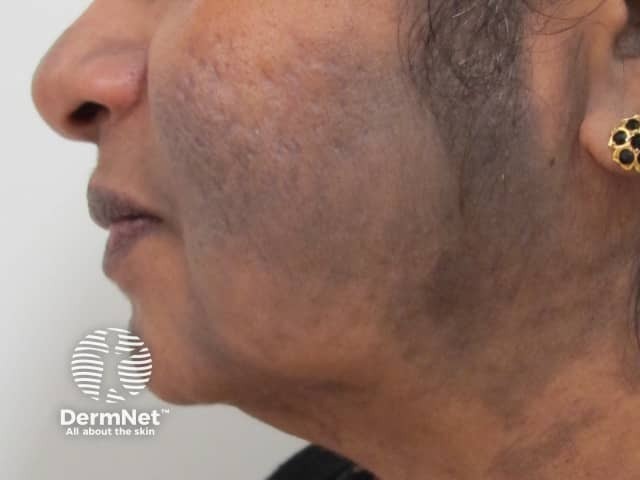
Erythema dyschromicum perstans
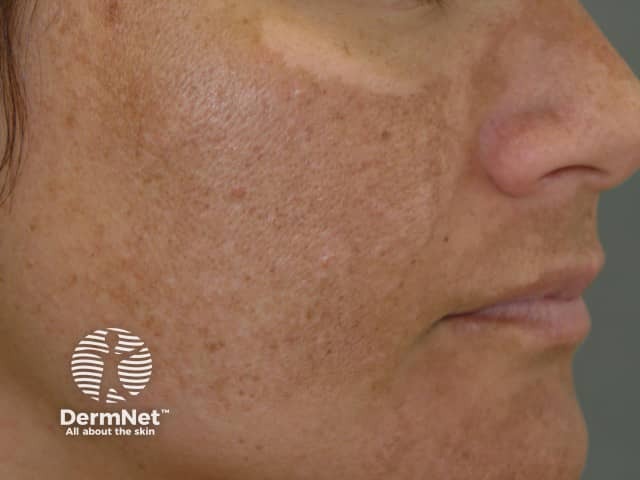
Melasma
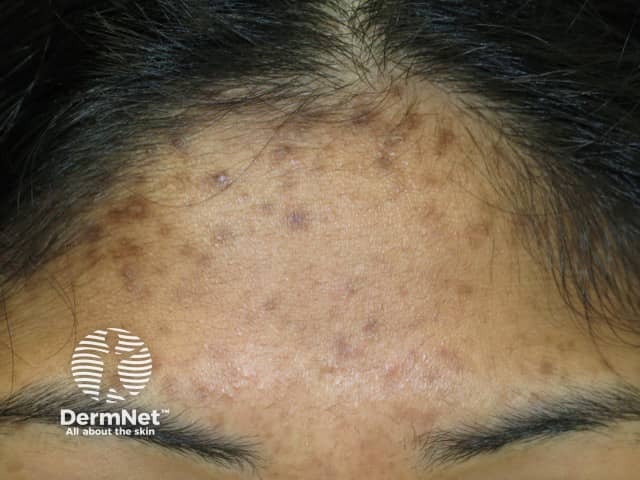
Post-inflammatory pigmentation
Face: pale or white macules/patches
Guttate hypomelanosis
- More commonly observed on limbs
Pityriasis alba
- Young child
- Cheeks
- Hypopigmentation, light scale
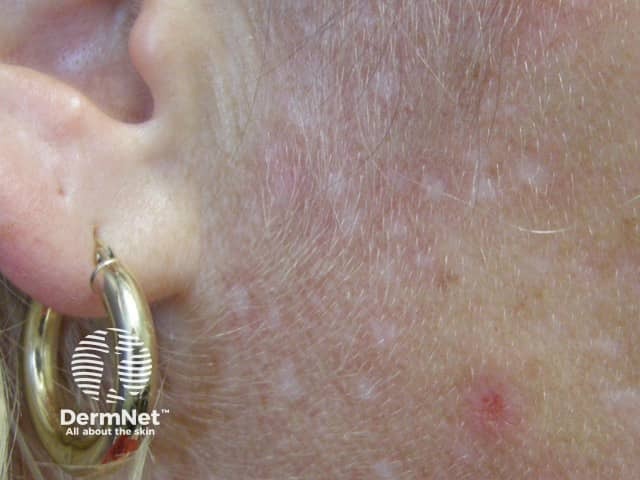
Guttate hypomelanosis
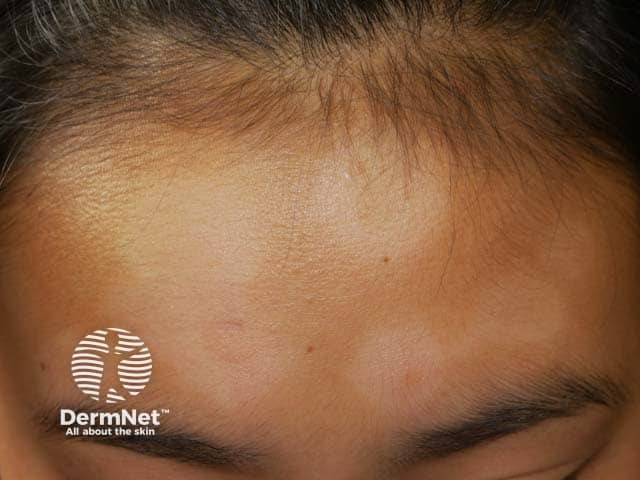
Forehead pityriasis alba
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation
- Preceding eczema, psoriasis, acne etc
- Distribution depends on cause
Vitiligo
- Most often periocular, perioral
- White, smooth surface
Post-inflammatory hypopigmentation
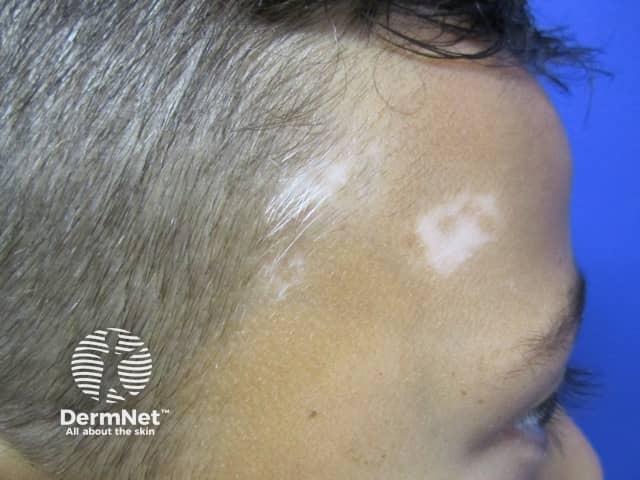
Vitiligo
Skin lesions
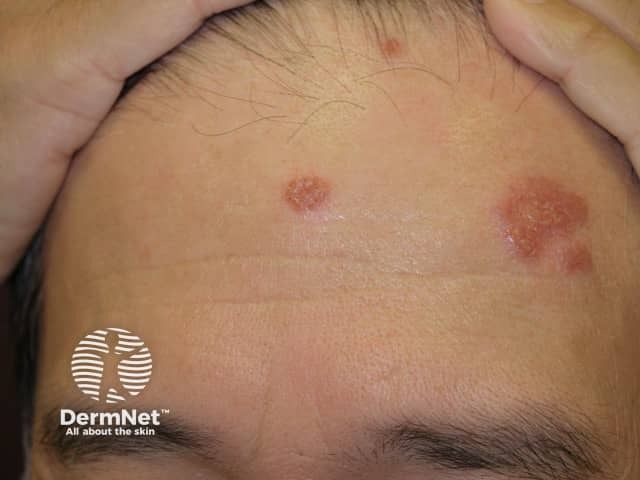
Granuloma faciale
- Middle-aged adult
- Solitary thickened smooth, purplish-brown plaque or plaques
Sarcoidosis
- Yellowish-brown to mauve infiltrated plaque
- May arise within existing scar
- Lupus pernio affects nose and ears
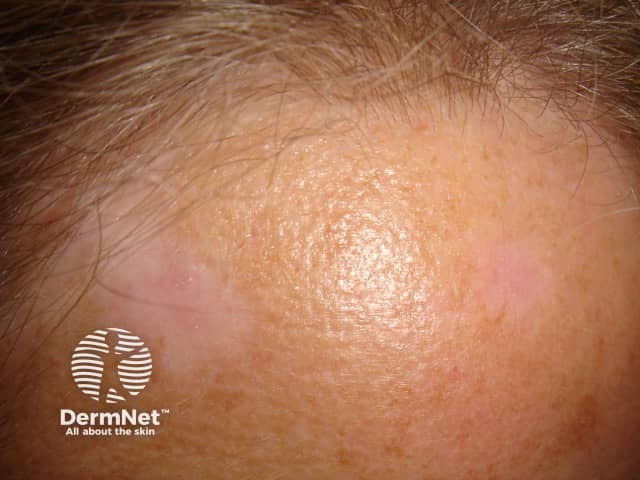
Sebaceous hyperplasia
- Mostly > 40 years
- Forehead, temples
- Yellowish papules with central follicular dimple
Sebaceous hyperplasia
Granuloma faciale
Sarcoidosis
Solar comedones
- Smoker, sun damaged older patient
- Periocular, cheekbones, nose, neck
- Usually symmetrical
Basal cell carcinoma
- Slowly enlarging, destructive papule, nodule or plaque
- Early erosion, ulceration and bleeding
Squamous cell carcinoma
- Enlarging tender scaly or crusted nodule
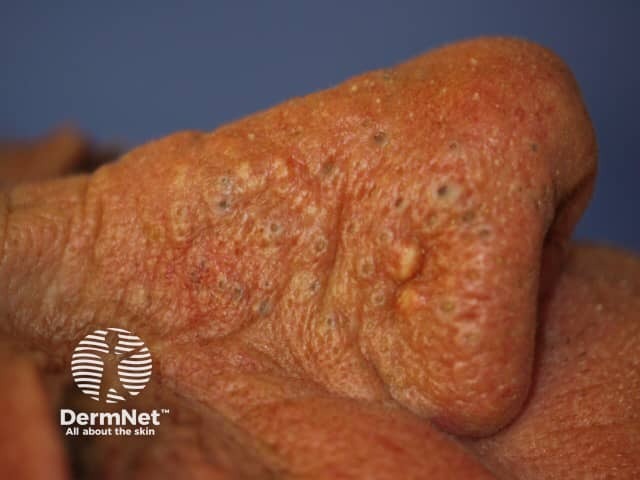
Solar comedones
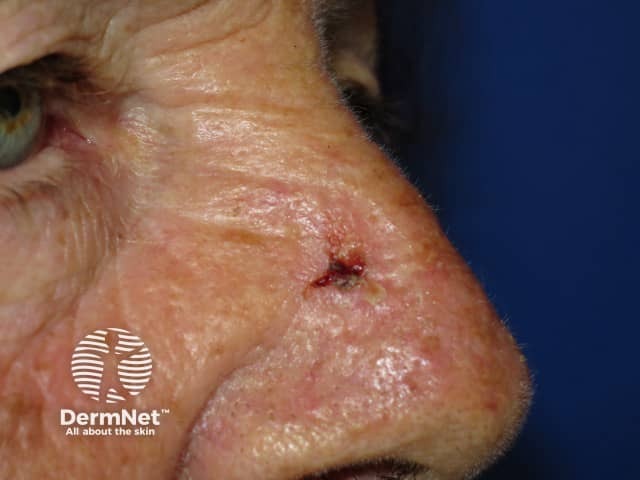
Basal cell carcinoma
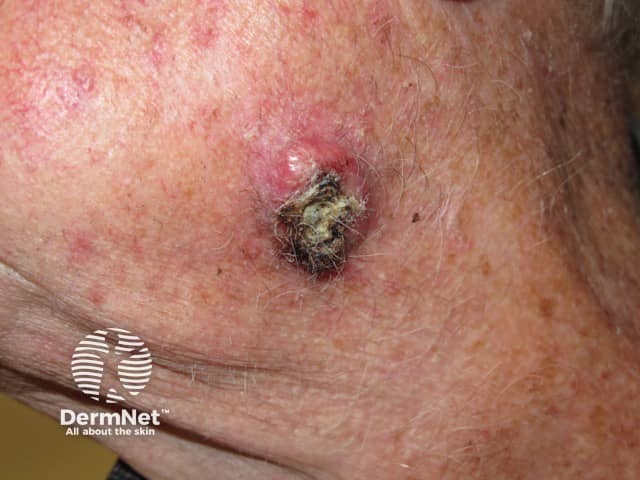
Squamous cell carcinoma
Adnexal tumours
- Various types and syndromes
- Follicular or eccrine origin
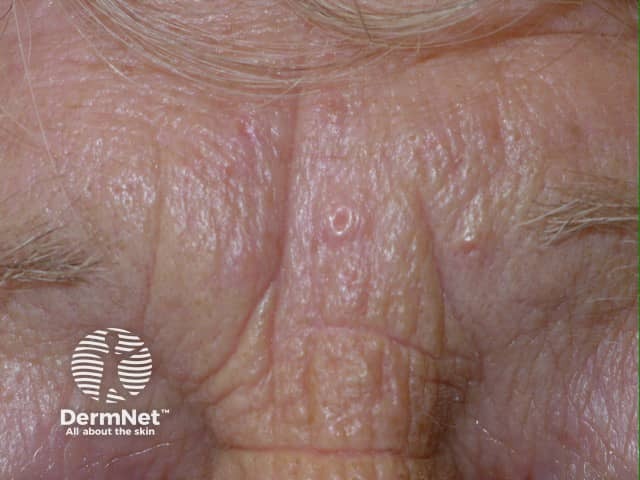
Milia
- Periorbital or cheeks
- Superficial firm small papules
- Scattered on forehead, cheeks
- Yellowish with central dell
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome
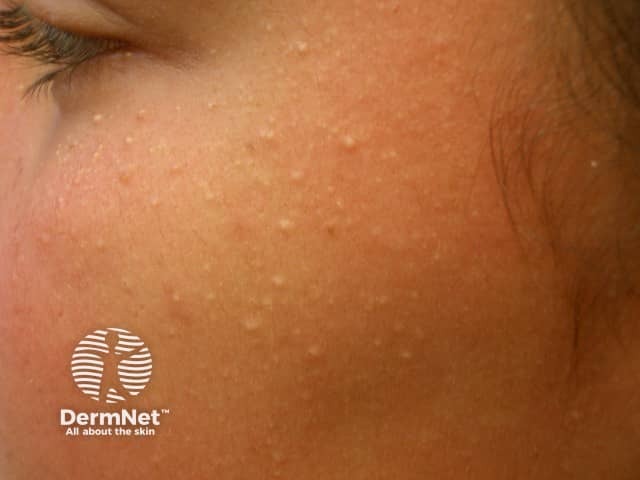
Milia
