Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Diagnosis and testing Terminology
Author: Brian Wu PhD. MD Candidate, Keck School of Medicine, Los Angeles, USA; Chief Editor: Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, July 2015.
Introduction Types Common stains Advantages and disadvantages
Histology and histopathology of biopsy samples are important in the diagnosis of skin conditions. They are frequently used in the detection and diagnosis of skin cancer.
Histology stains are used to colour different structures within the cells.
Before staining a slide, the tissue has to be prepared and mounted onto a glass slide.
The paraffin technique is the most common way to prepare a histological slide, and follows the following steps:
Other common histological techniques include:
Some of the most common types of stains.
This is the most frequently used combination for general staining of skin samples and is especially useful in the diagnosis and classification of cancer.
Mucin stains are best for the detection and dying of mucopolysaccharides. Examples of mucin stains include:
Melanin stains, as the name implies, are used for dyeing melanin and are commonly used in the diagnosis of melanoma. One typical example of a melanin stain is the Fontana-Masson.
Trichrome stains use a combination of three different dyes to achieve their effect. These are used explicitly to dye lipids. Common trichrome stains include:
The table below gives examples of different histological stains.
Name of Stain |
Colour(s) and other notes |
Example |
|---|---|---|
Alcian blue |
Blue; common mucin stain |
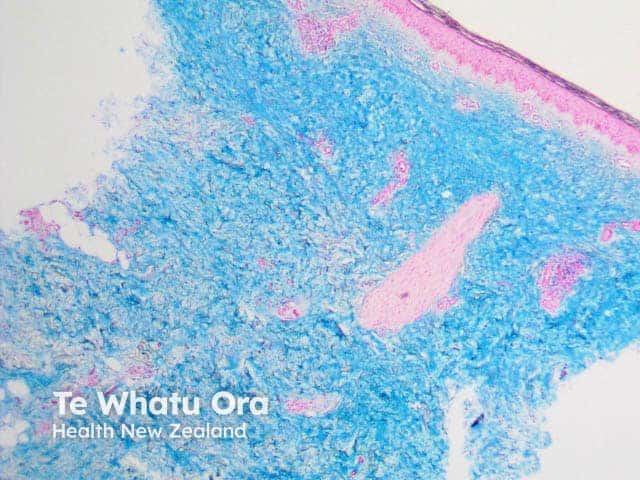
|
Aldehyde fuchsin |
Purple/black; used to stain beta cells in the pancreas |
|
Alkaline phosphatase |
Red/blue; used for endothelial tissue |
|
Bielshowsky stain |
Black; used for neural plaques and tangles |
|
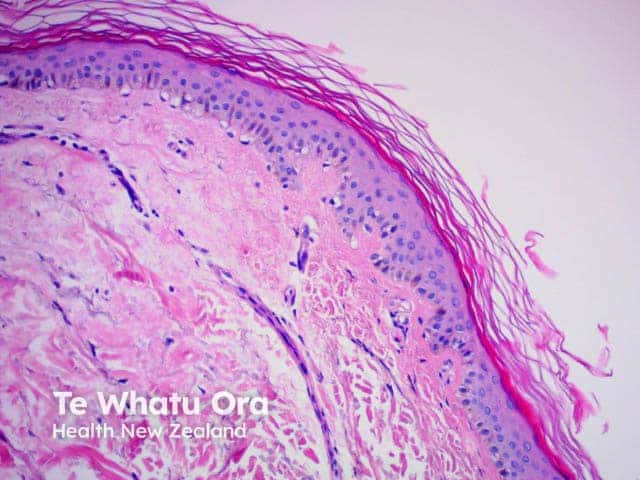
Congo red |
Red; typical for staining amyloid fibres |
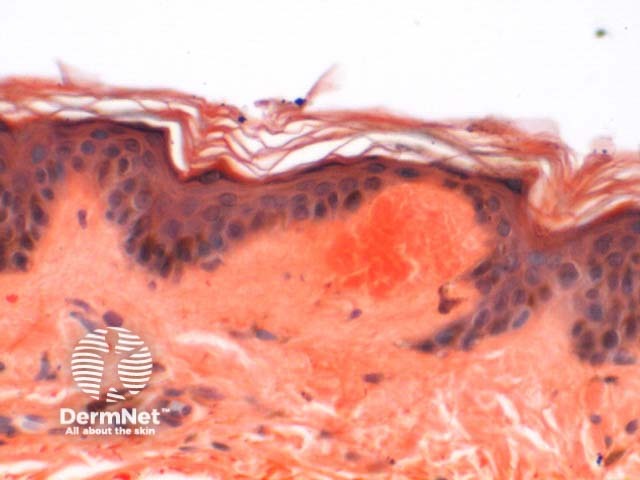 Figure 5 |
Crystal violet |
Violet; can stain glia and neurons |
|
Eosin |
Pink/orange/red; typical for general staining when combined with haematoxylin |
|
Fontana-Masson |
Black/pink or red; stains melanin |
|
Giemsa |
Blue/violet/pink; commonly used in blood or bone marrow smears |
|
Haematoxylin |
Blue/purple; standard for general staining when combined with eosin |

|
Luna stain |
Purple/black; can stain mast cells and elastin |
|
Nissl |
Blue; stains the rough endoplasmic reticulum in neurons |
|
Period Acid Schiff (PAS) |
Red/magenta; used to stain glycogen, basement membranes, reticular fibres, cartilage, glycoproteins, glycolipids and mucins in tissues. |
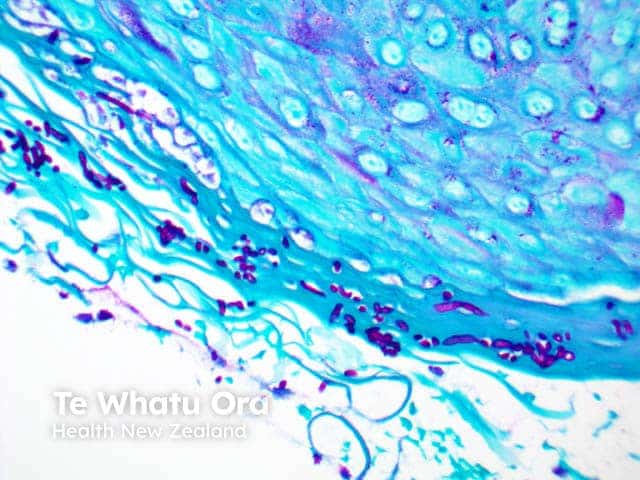
|
Red Oil 3 |
Red; used to stain fat emboli |
|
Reticulin stain |
Blue/black; stains reticular fibres |
|
Sudan black |
Brown-black; stains myelin tissue |
|
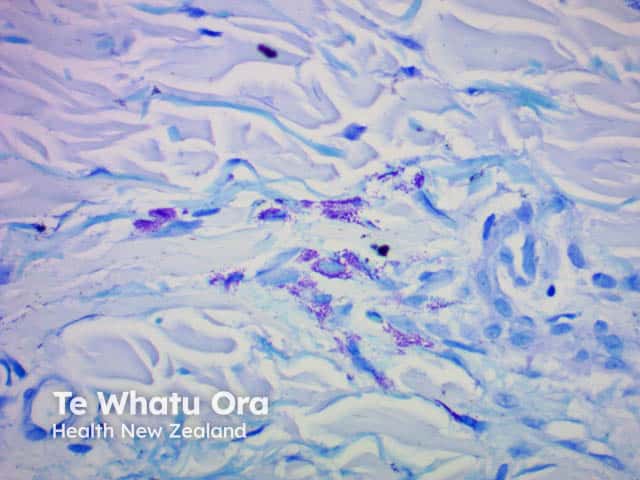
Toluidine blue |
Blue; stains mast cell granules |
|
van Gieson |
Red/blue/yellow; used to study blood vessels and skin, can stain collagen, nucleus, red blood cells, cytoplasm |
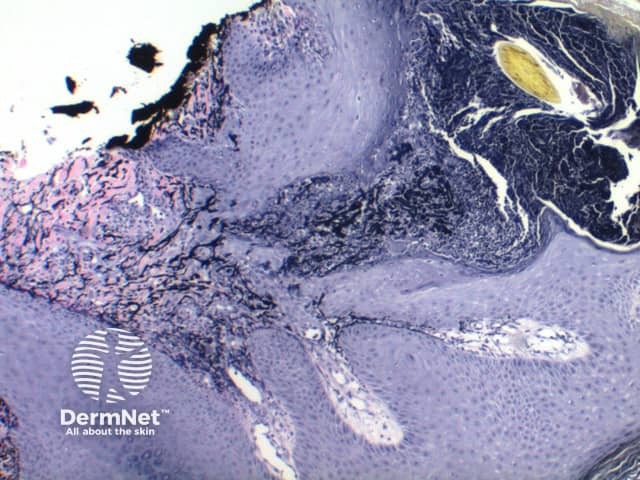 Figure 5 |
The advantages of histology and histological staining are:
The disadvantages of histology and histological staining include: