Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Lesions (benign) Diagnosis and testing
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, January 2017.
Introduction Histology Special stains Differential diagnoses
Keratosis lichenoides chronica (KLC) presents clinically with violaceous, papular and nodular lesions in a linear or reticulate pattern.
Histologically, keratosis lichenoides chronica is characterised by a lichenoid reaction pattern with marked basal cell death and vacuolar degeneration (figures 1-3). The dermal infiltrate shows a mixture of cells which may include plasma cells. The epidermal changes are highly variable — acanthosis, parakeratosis, and atrophy are all described features. Cornoid lamellae and eccrine infiltrates have been described.
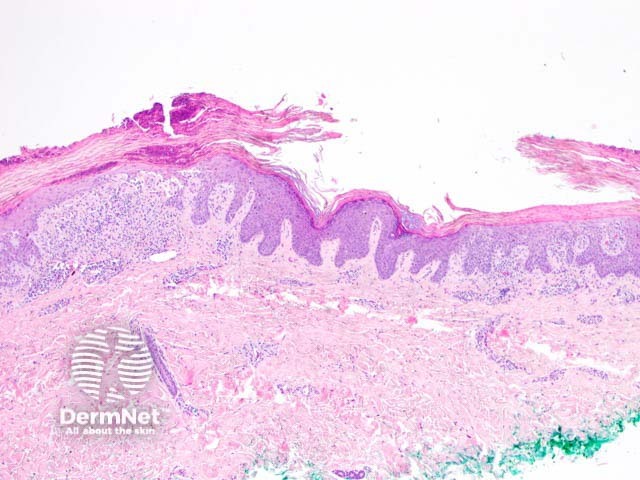
Keratosis lichenoides chronica figure 1
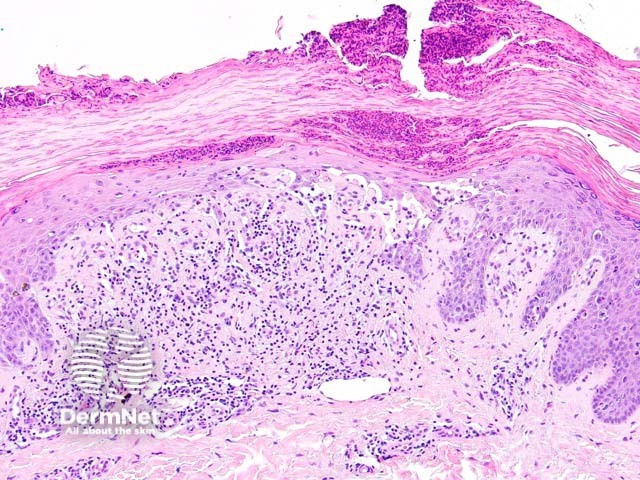
Keratosis lichenoides chronica figure 2
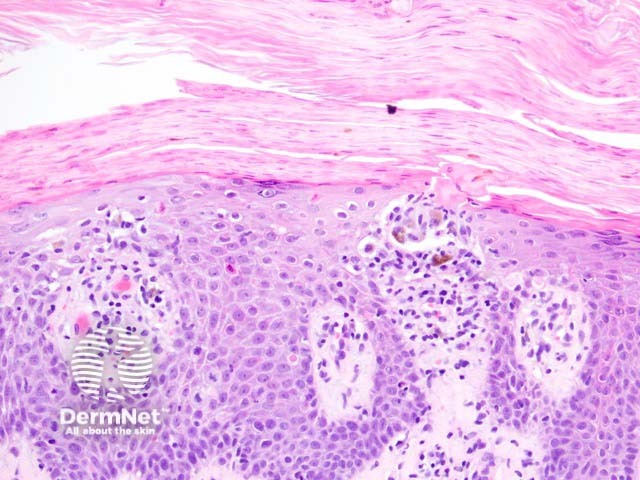
Keratosis lichenoides chronica figure 3
None are generally needed. PAS stain may be useful to exclude a superficial fungal infection.
Diagnosis is difficult without clinical correlation. Some authors feel this is likely an unusual chronic form of lichen planus.
Pityriasis lichenoides can show a similar pathology but has a distinct clinical presentation.