Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Reactions Diagnosis and testing
Author: Adjunct A/Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Clínica Ricardo Palma, Lima, Peru. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. September 2018.
Introduction Histology Special studies Differential diagnoses
Lichenoid drug reactions are induced by a medication or another exogenous source which can mimic other lichenoid dermatoses clinically and histologically.
In lichenoid drug reactions the pathology is nearly identical to lichen planus. There is a dense, band-like lymphocytic infiltrate in dermis that obscures dermoepidermal junction, cytoplasmic vacuolisation of basal keratinocytes and apoptotic keratinocytes that degenerate into colloid bodies (figures 1,2). In addition, there are usually eosinophils in the infiltrate (best seen in figure 3).
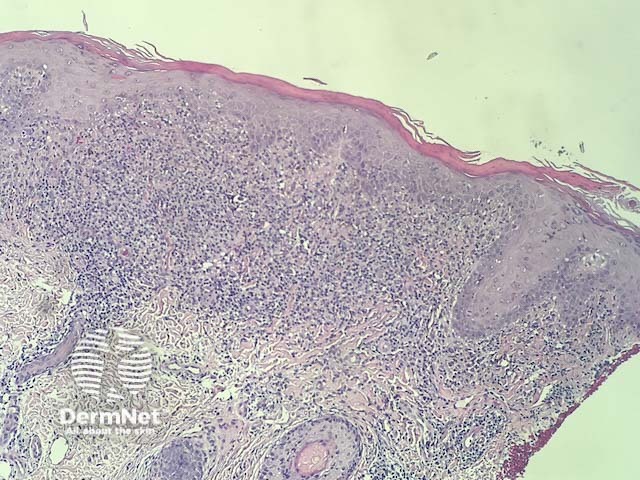
Figure 1
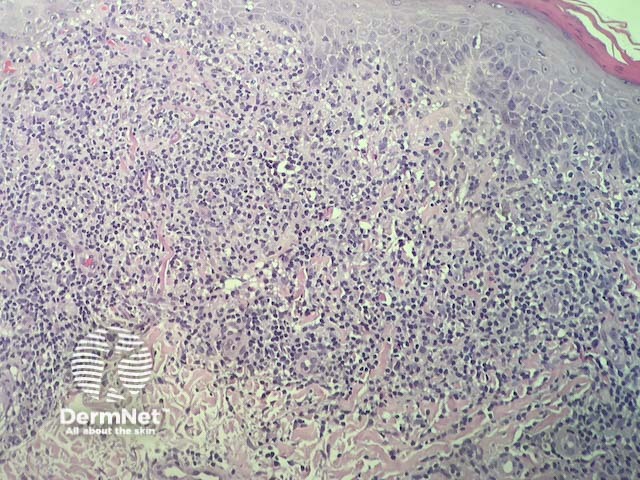
Figure 2
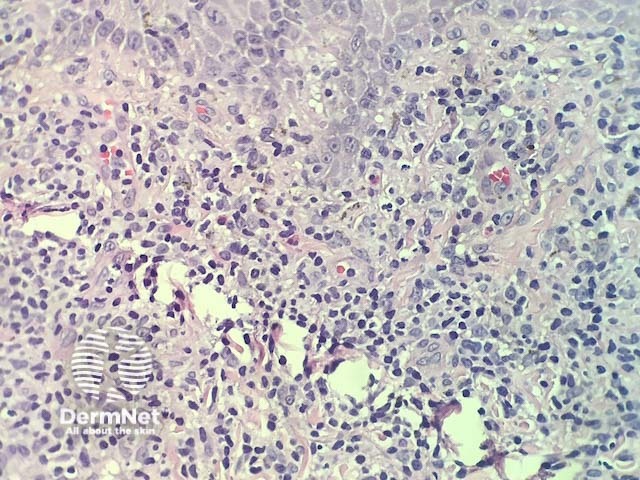
Figure 3
None are generally needed.
Other diagnoses to be considered include any lichenoid dermatosis. The key differential is lichen planus. Clinical correlation can be very useful. Key histologic features seen in lichenoid drug eruptions, that are not common in idiopathic lichen planus, include the presence of eosinophils and the presence of prominent parakeratosis.