Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Yuchen Zhang, Medical Student, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand. DermNet New Zealand Editor in Chief: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy Editor: Gus Mitchell/Maria McGovern. August 2017.
Introduction Demographics Clinical features Complications Diagnosis Differential diagnoses Treatment
Nipple papillomatosis is characterised by the benign growth of numerous papillomas arising from the lactiferous duct epithelium of the nipple. It is also known as florid papillomatosis of the nipple, nipple adenoma, and erosive adenomatosis.
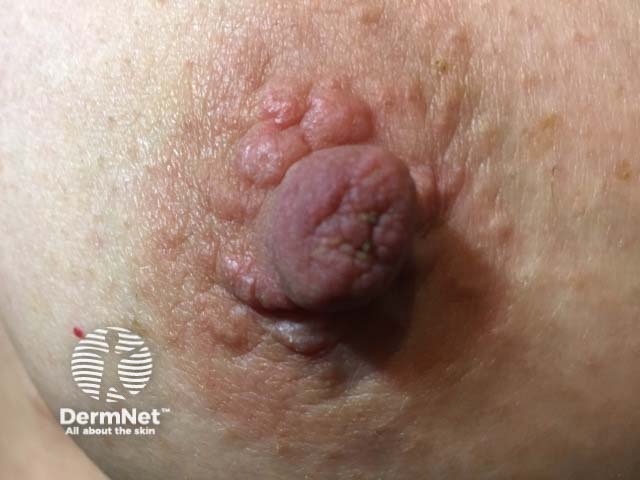
Nipple papillomatosis
Nipple papillomatosis is rare. It mainly occurs in women aged 35–55 years old, but it can occur at any age. It occasionally affects men.
Nipple papillomatosis presents as a palpable mass or swelling on the surface of the nipple. It may be discovered incidentally during a breast examination.
Other clinical features include:
Nipple papillomatosis is harmless. As for any fibrocystic change within the breast tissue, there are reported associations with a slightly increased risk of breast cancer when compared with the general population, although this risk is still very low.
Syringomatous adenoma is a variant of nipple papillomatosis, distinguished on histology by the absence of intraductal epithelial hyperplasia and oval, elongated ducts. Syringomatous adenoma tends to be infiltrative and locally invasive.
A skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of nipple papillomatosis.
Histologically, nipple papillomatosis shows proliferating ductal structures extending into the breast stroma, lined by a double layer of epithelium. Other histological features include the presence of keratin-filled cysts and tiny apical cell snouts.
Breast X-ray, mammography or ultrasound examination may be performed to exclude an underlying tumour.
The differential diagnosis for nipple papillomatosis includes:
Where practical, nipple papillomatosis is treated by complete excision of the lesion. This is a minor procedure usually performed under local anaesthetic. If the entire affected area is not removed, the affected area should be reviewed from time to time, especially if the appearance changes.
Nipple adenoma / florid papillomatosis of nipple — Pathology Outlines, July 2014 (accessed 17 June 2017).