Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Onychomycosis pathology — extra information
Onychomycosis pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Onychomycosis (tinea unguium) is a fungal infection of the nail bed, matrix or plate usually caused by a dermatophyte. Candida and non-dermatophytic moulds are more common in tropical environments.
Histology of onychomycosis
Sections of an infected nail plate must be examined with special stains with PAS or GMS to assess the presence of fungal forms. Often the nail will contain serum and collections of neutrophils as well as the fungal forms which penetrate the nail tissue (figure 1). PAS stain in figure 2 reveals dermatophytes penetrating the nail plate.
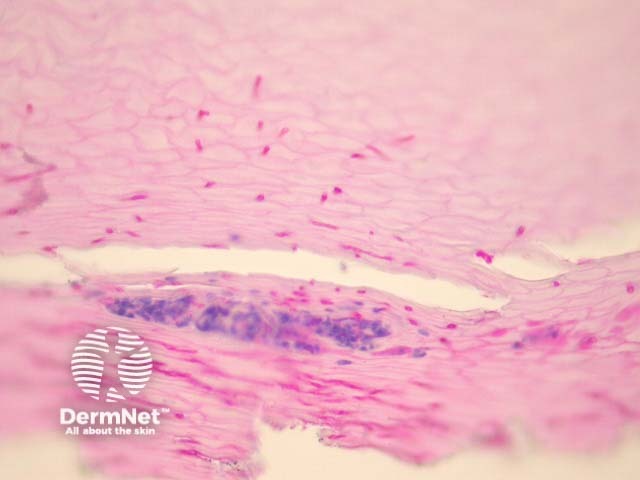
Figure 1
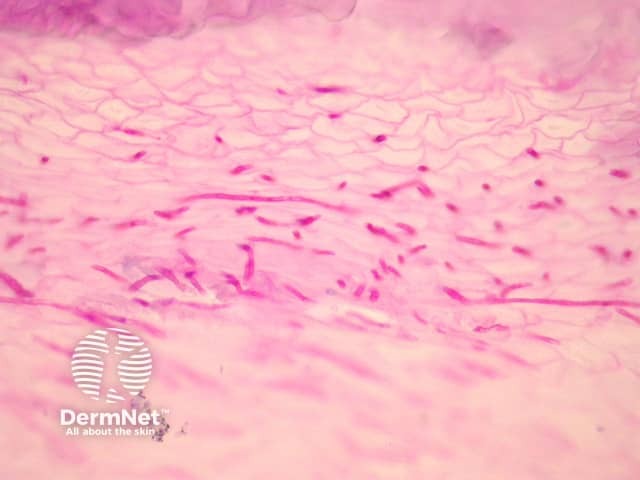
Figure 2
Special studies for onychomycosis
PAS or GMS stains are essential for the diagnosis and reveal organisms penetrating the nail tissue.
Differential diagnosis of onychomycosis pathology
Non-dermatophytes colonisation – Non-dermatophytes often colonize the subungual space. However, unless they can be demonstrated penetrating the nail plate they are not regarded as causative of onychomycosis.
Psoriasis – Neutrophilic aggregates may be seen but PAS/GMS will be negative for organisms.
Pitted keratolysis – The causative bacteria will be demonstrated with gram stain as thin filamentous bacterial forms.
On DermNet
