Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Naomi Ashman, Dermoscopist, Torbay Skin, Auckland, New Zealand; DermNet New Zealand Editor in Chief, Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Created February 2019.
What are rosettes? Appearance on dermoscopy Lesions with rosettes Histological explanation
Rosettes are a specific form of a white shiny structure seen with polarised dermoscopy. They are also known as four-dot clods.
Rosettes consist of four white dots arranged in a square resembling a four leaf clover and can only be seen with polarised light. They are always oriented at the same angle.
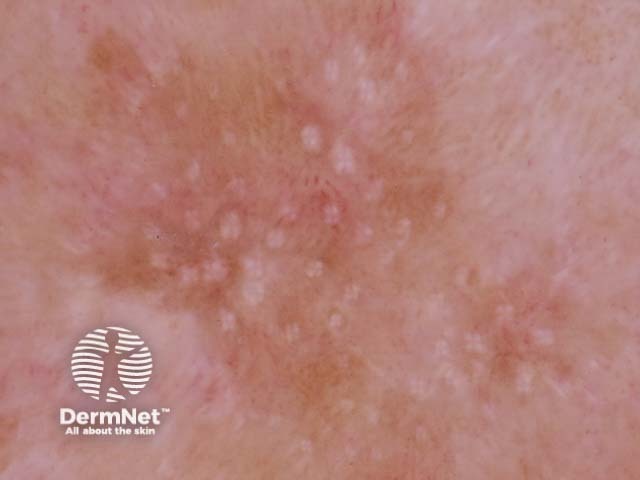
Rosettes in sun-damaged skin
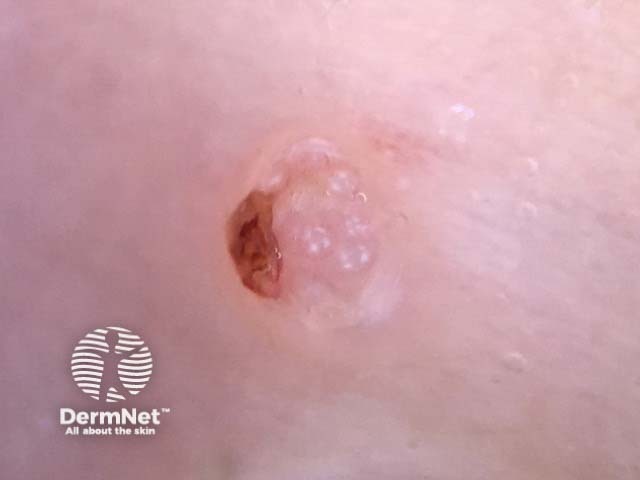
Rosettes seen in molluscum contagiosum
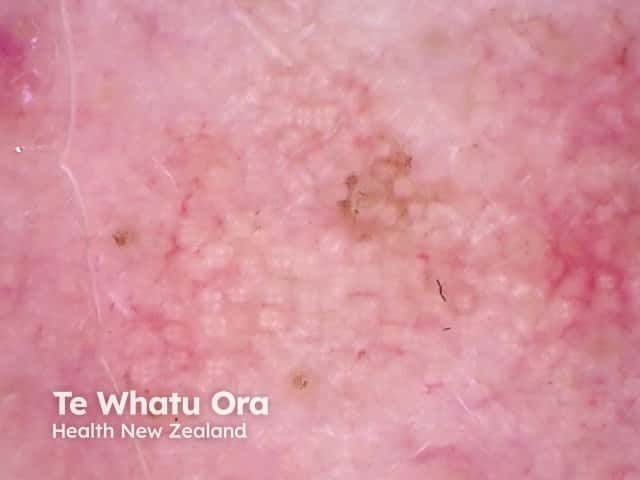
Rosettes in actinic keratosis
Although at first believed to be specific for actinic keratosis and squamous cell carcinoma, rosettes are sometimes seen in other lesions as well as in normal skin. Rosettes are most commonly found in:
The exact histological explanation of rosettes is unclear but they are thought to be due to an interaction between polarised light and narrowed keratin-filled, or fibrotic adnexal openings. Haspeslagh et al found that small rosettes (0.1–0.2 mm) corresponded to concentric horny material in follicular and eccrine ducts at the infundibular level and larger rosettes (0.3–0.5 mm) to perifollicular concentric fibrosis [1].