Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, April 2014. Copy Editor, Clare Morrison.
Aeromonas is an aquatic bacterium. Aeromonas is a very rare cause of bacterial skin and soft tissue infection. The most common species isolated is Aeromonas hydrophila.
Aeromonas can also cause gastroenteritis (traveller's diarrhoea), meningitis and peritonitis.
A. hydrophila can cause severe localised skin infection. It may present as:
Aeromonas skin infection is more likely to lead to severe complications in patients with weak immune systems, for example those on immunosuppressive medication or being treated for cancer.
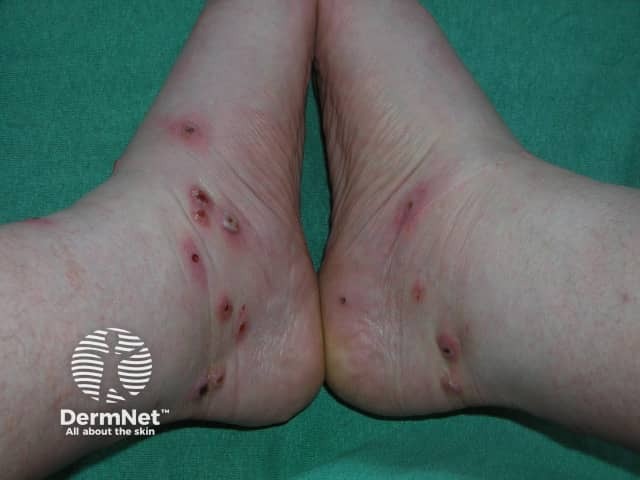
Infected leech bites
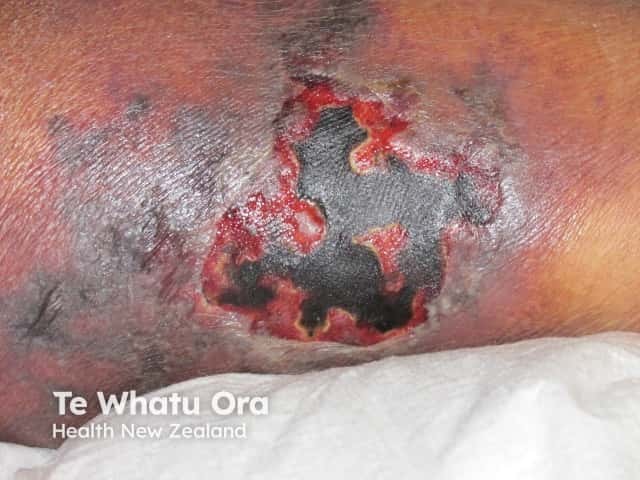
Necrotising cellulitis
A. hydrophila bacteria are found in fresh or salt water such as lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and estuaries, and are more prevalent in warm climates. They may also contaminate moist soil. The bacteria can resist heat, cold and chlorine. Some strains of A. hydrophila produce an aerolysin toxin that causes tissue damage.
Infection occurs when the bacteria that produce aerolysin toxin enter an area of broken skin, such as a shaving cut, abrasion, surgical wound, or insect bite.
Leech bites and medical leech therapy can also lead to A. hydrophila infection, because all leeches carry the bacteria in their gut.
The diagnosis of Aeromonas infection may be suspected in a person with a severe infection complicating a minor skin injury that has been exposed to water (or leeches).
In immunocompromised patients, Aeromonas infection is usually diagnosed by laboratory investigation, and infections are often polymicrobial (due to several different kinds of bacteria).
A. hydrophila is isolated by the laboratory from swabs taken from pustules or wound. It is a Gram-negative organism, which means the bacteria appear pink on microscopy using the Gram stain. The organism is identified by culture. Sensitivities should be performed, as some strains of Aeromonas are multidrug resistant.
A. hydrophila skin infection is treated with antibiotics such as tetracyclines, sulfonamides, trimethoprim + sulphamethoxazole or ciprofloxacin. It is usually resistant to penicillin.
An Aeromonas abscess is surgically drained. Recovery is followed by scarring with temporary or permanent hair loss.
Patients that are seriously ill should be urgently hospitalised.