Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Created 2008.
Nummular dermatitis (or eczema) is also known as discoid eczema (or dermatitis). It has two forms:
Exudative nummular dermatitis
The exudative variant starts acutely and may persist for weeks, months and rarely years. Although it may arise at any age, most subjects are over 50 years. In children, it is often thought to be a type of atopic dermatitis, but in adults it doesn't appear to relate to atopy. It is more common in males than females.
The initial plaque may appear at the site of trauma or infection. For example:
Nummular dermatitis is sometimes due to drug allergy (e.g. to interferon alpha, intravenous immunoglobulins, etanercept) or systematised contact allergy, especially to nickel, gold and mercury.
The initial lesions are papules or vesicles, which form confluent plaques. The plaques may be crusted, weeping or blistered and are intensely itchy. Secondary infection with pustules, pain and spreading erythema is not uncommon. Older lesions may be dry and excoriated.
Clusters of round or oval plaques may be localised to lower legs, the backs of the hands or other sites. Nummular dermatitis may also generalise to affect scalp, face, trunk and limbs. Generally the eruption is scattered, but sometimes the plaques are distributed symmetrically. In-between skin appears normal.
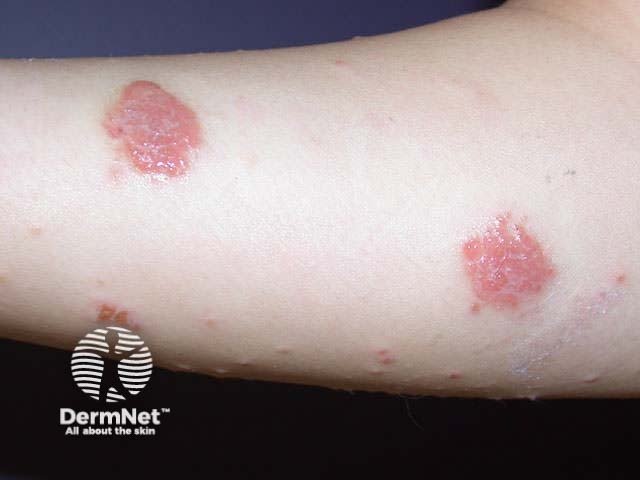
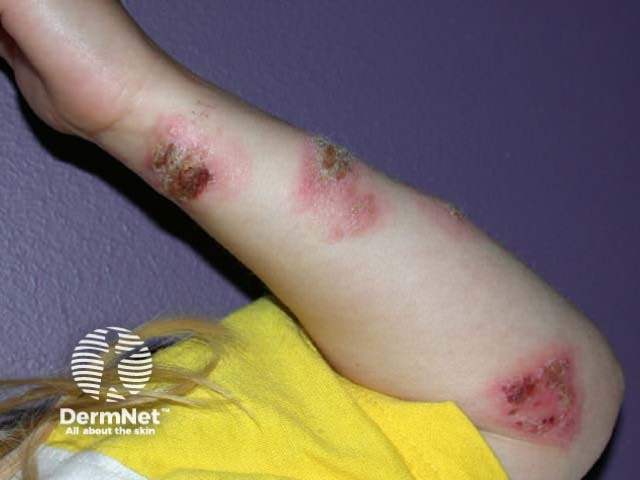
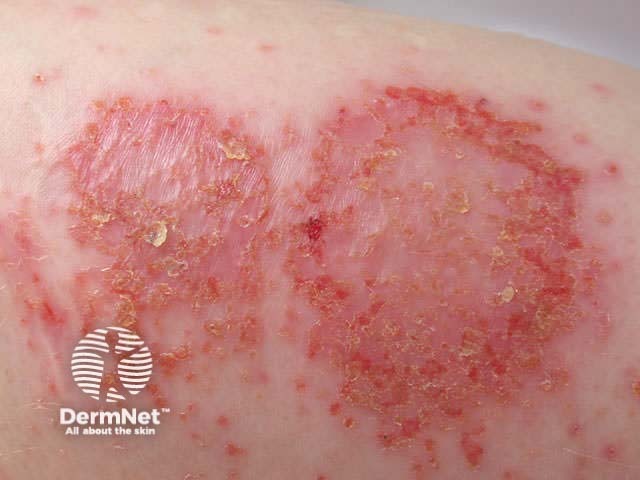
Dry discoid eczema
Dry discoid eczema can be localised or generalised. It often arises as the result of dry skin:
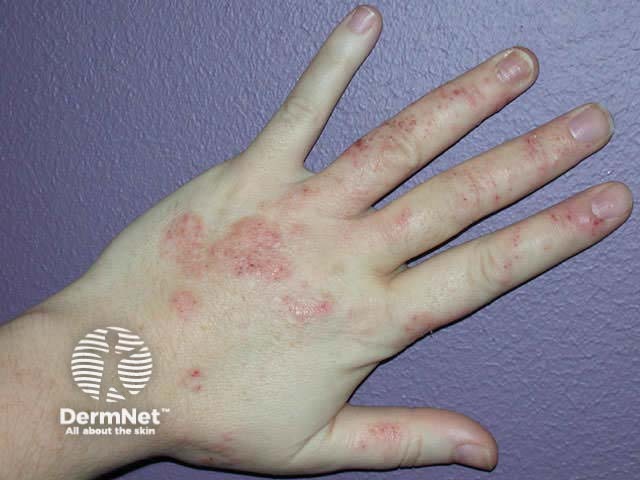
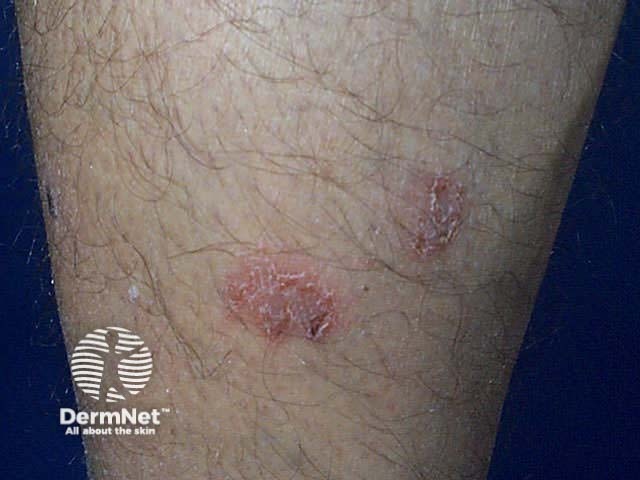
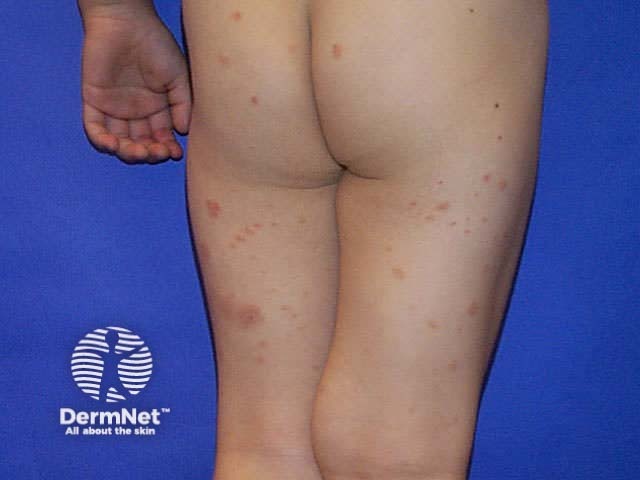
Sometimes dry discoid eczema is associated with elevated skin lesions such as seborrhoeic keratoses and melanocytic naevi (Meyerson's naevus).
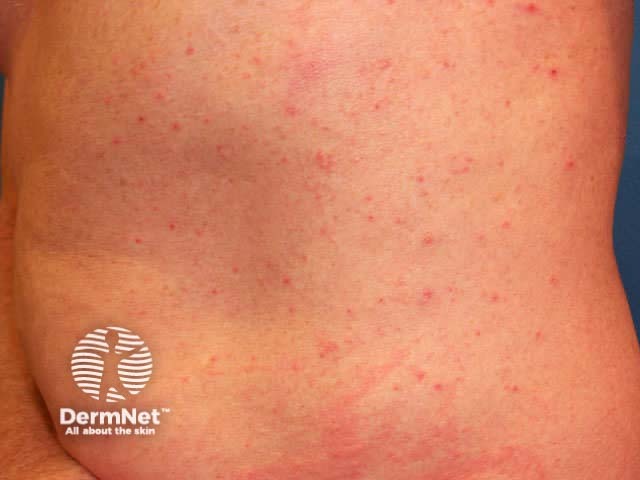
Autosensitisation dermatitis is a variant of discoid dermatitis affecting the trunk and limbs that follows a severe dermatitis in aother site (an ide reaction). The primary site is most often the lower legs due to stasis dermatitis. Autosensitisation dermatitis can be very extensive
Autosensitisation dermatitis Autosensitisation dermatitis 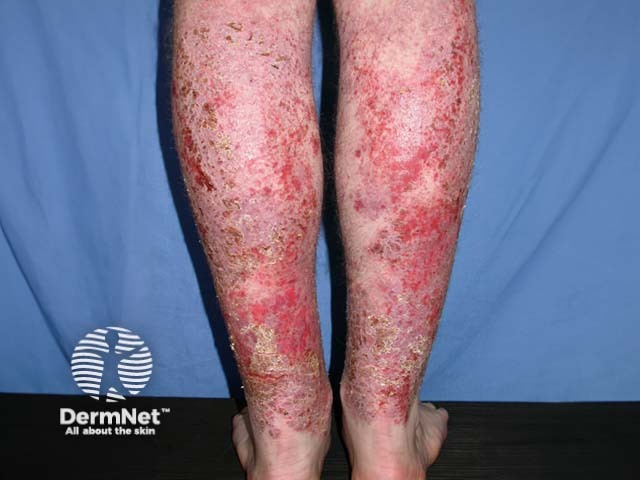
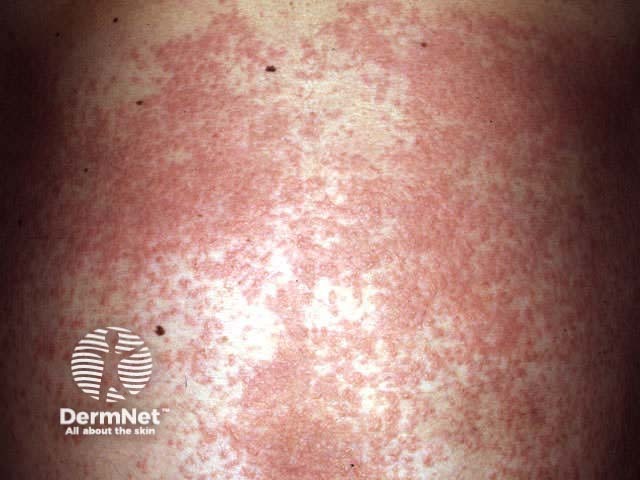
Skin swabs frequently culture abundant Staphylococcus aureus from exudative nummular dermatitis and sometimes from dry discoid dermatitis.
Skin scrapings for microscopy and fungal culture may be necessary to rule out tinea corporis.
Discoid eczema is frequently confused with the following skin disorders:
Management of nummular dermatitis involves:
Describe the use of oral corticosteroids in the management of nummular dermatitis. What are the contraindications, precautions, side effects and risks of this treatment and how should you manage these?
Information for patients
See the DermNet bookstore