Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Created 2008.
Dermoscopy is useful to distinguish pigmented basal cell carcinoma from other pigmented lesions. There are specific features that help to distinguish these. Pigment may be grey, brown, blue or black. They are rarely completely pigmented in white-skinned individuals.
The dermoscopic features of pigmented basal cell carcinoma include:
Blue ovoid nests Arborising blood vessels Focal ulceration Ulceration Spoke-wheel pigmentation Flecks of pigment Arborising telangiectasia Flecks of pigment Flecks of pigment Deeply pigmented border Multicoloured lesion Large nodule 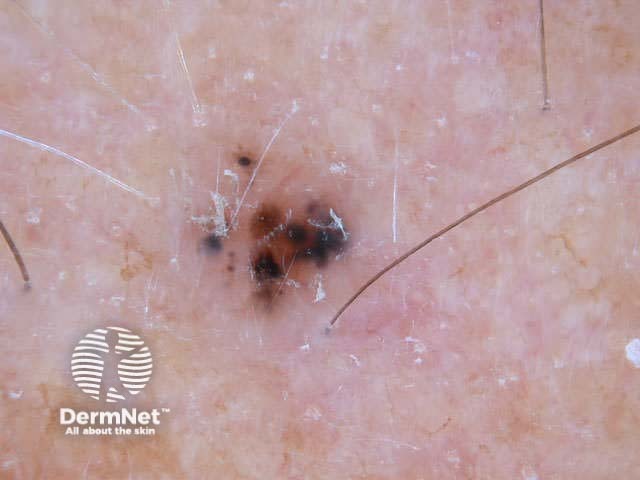
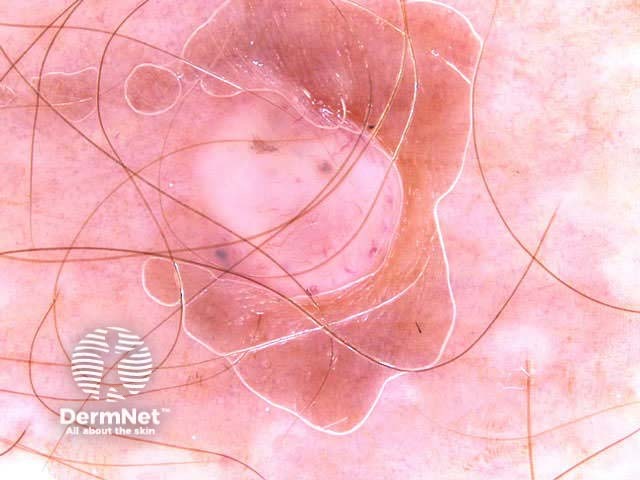
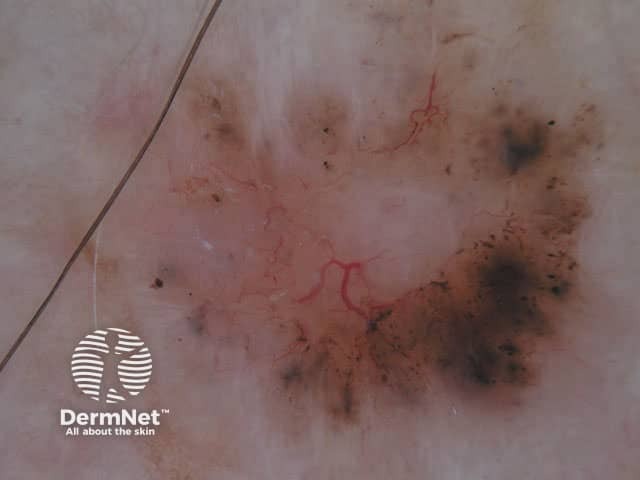
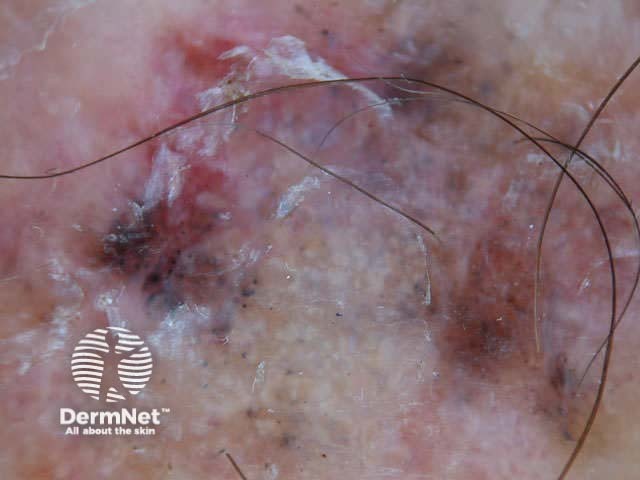
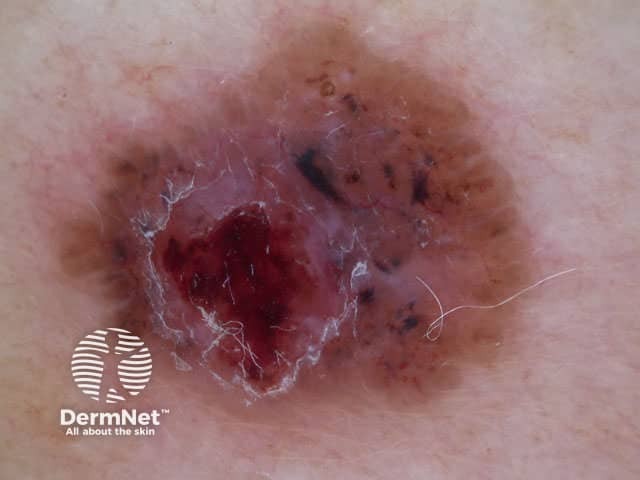
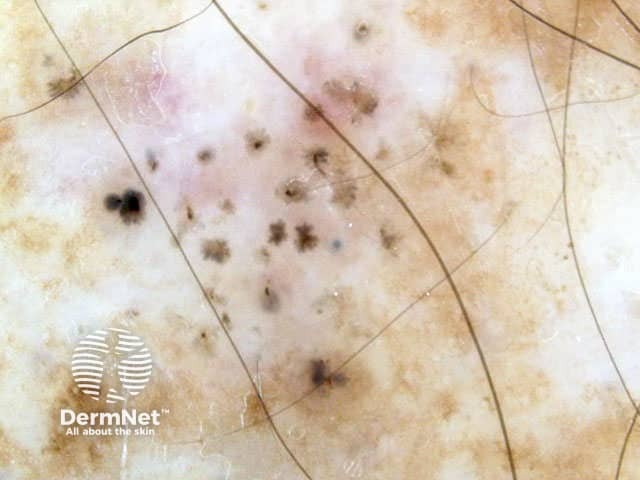
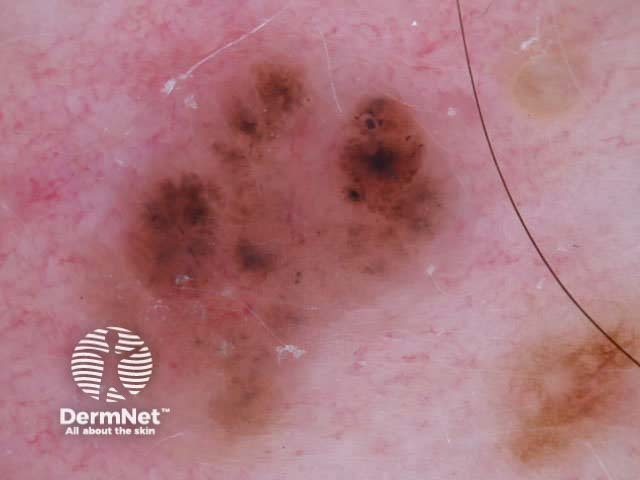
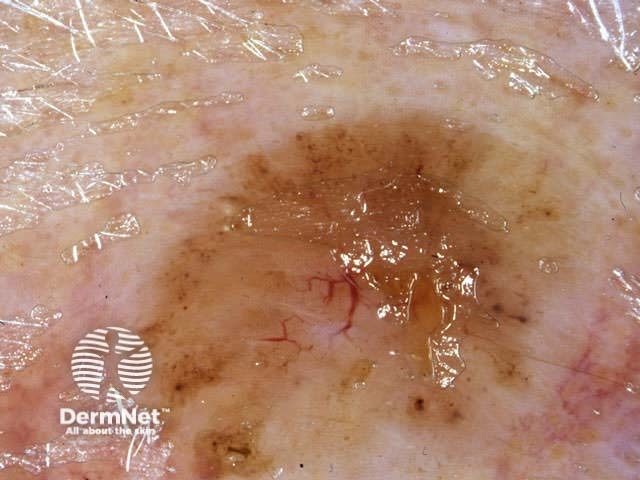
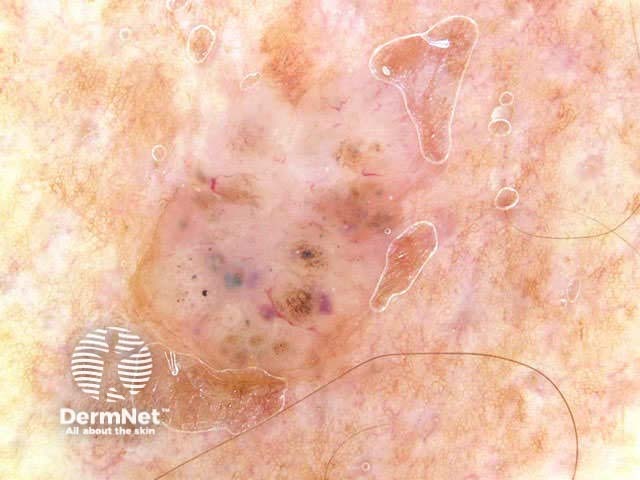

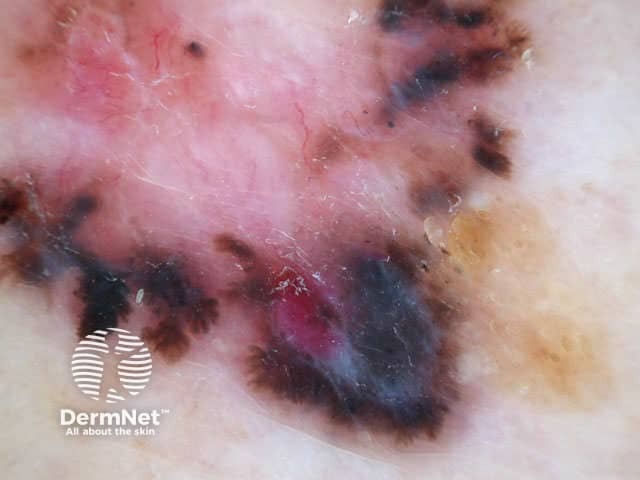
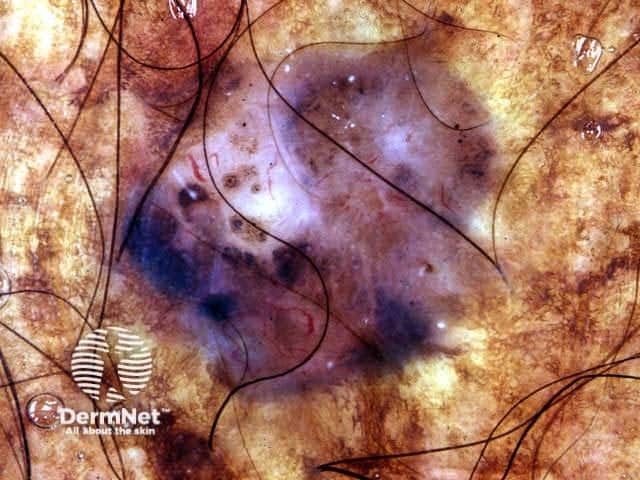
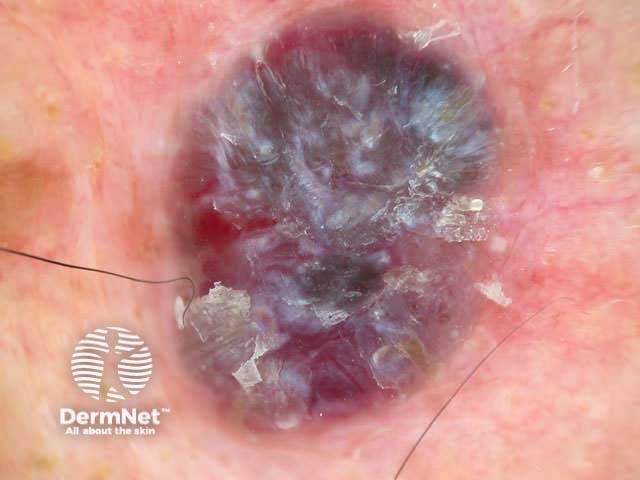
In some cases, it may be difficult to distinguish deeply pigmented or even non-pigmented basal cell carcinoma from melanoma.
Non-pigmented basal cell carcinomas are much more common than pigmented basal cell carcinoma. They contain flecks of grey colour.
Experienced dermoscopists can often diagnose superficial basal cell carcinomas by their typical bluish-pink colour, asymmetrical arborising vessels and focal ulceration. Slight scaling and white areas of regression may also be present. Chrystalline structures, i.e. white shiny lines, strands and larger irregular-shaped white areas, are common in all histological types of basal cell carcinoma. These short parallel or disordered lines and roundish white structures are often only visible on polarised dermoscopy.
Nodular basal cell carcinomas lose the blue hue and instead have a white rim around central ulceration. Milia may be present. Disordered and streaky crystalline structures may be seen.
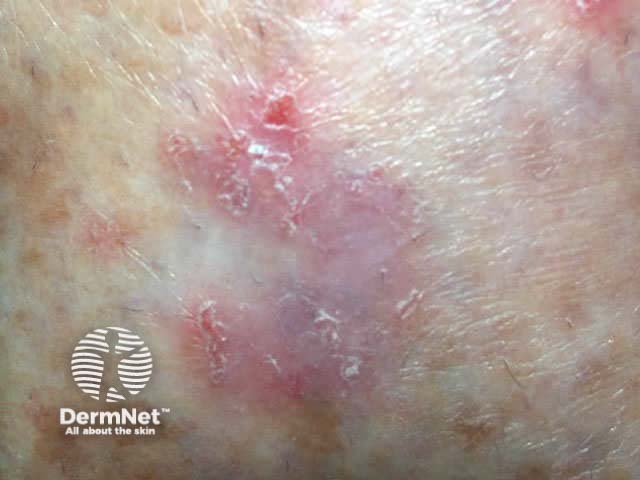
Bluish, scale, ulceration
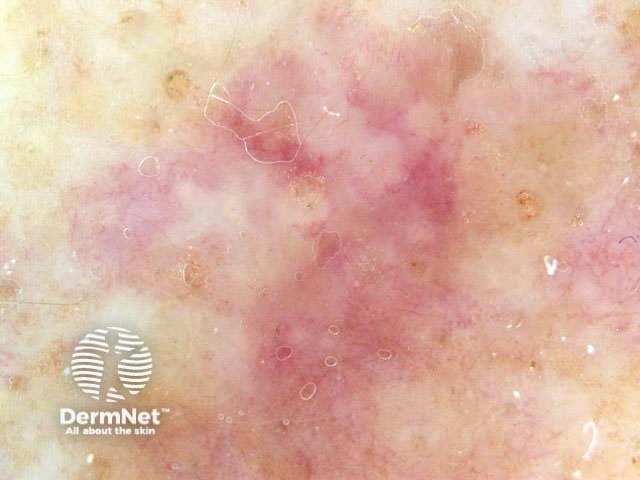
Subtle blue colour
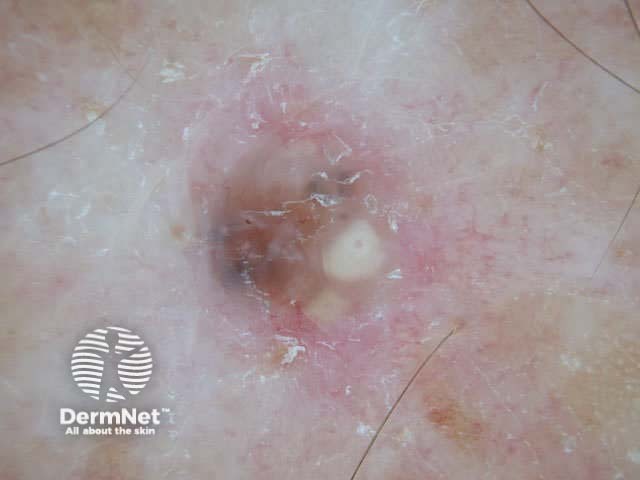
Milia formation
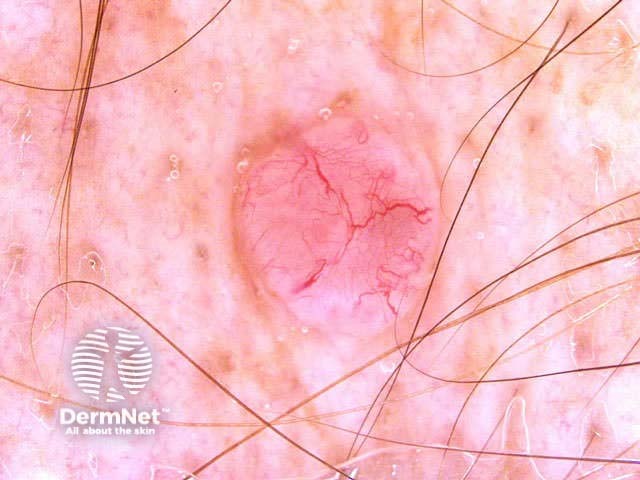
Prominent vasculature
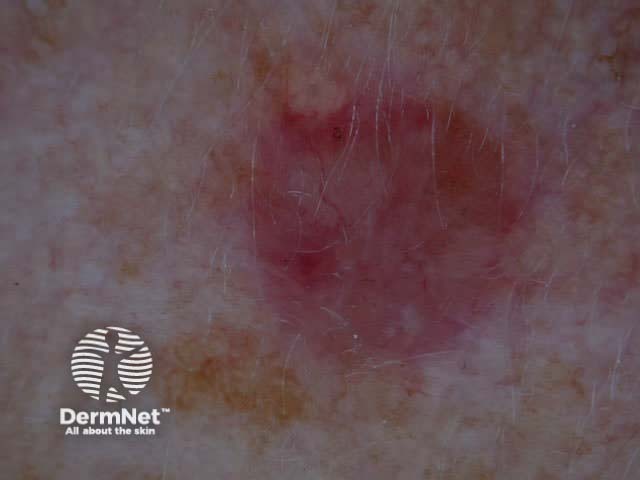
Vascular bcc
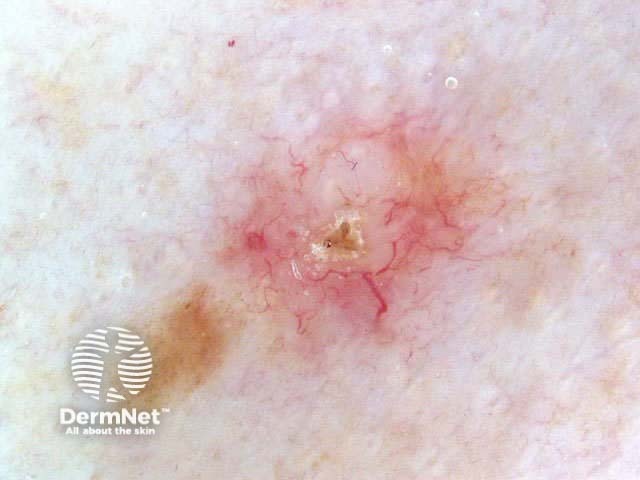
Crusting, telangiectasia
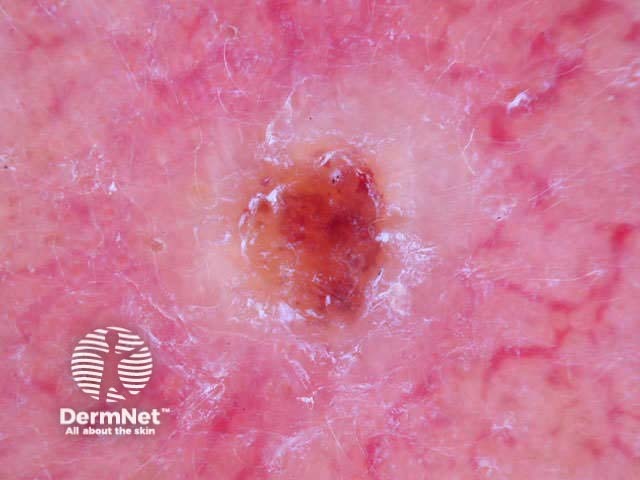
White nodule, telangiectasia
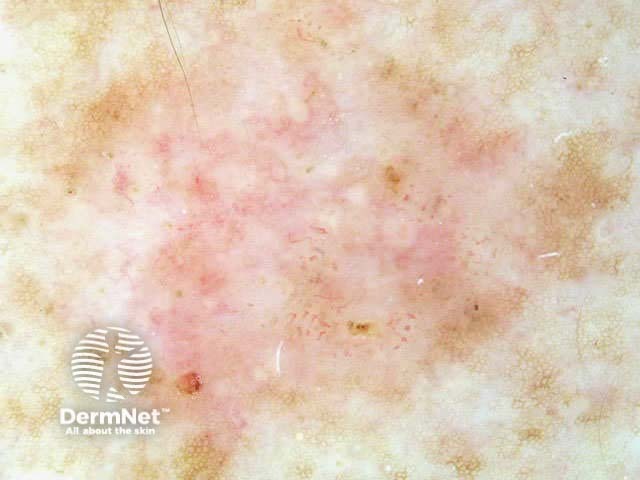
Tiny ulcers
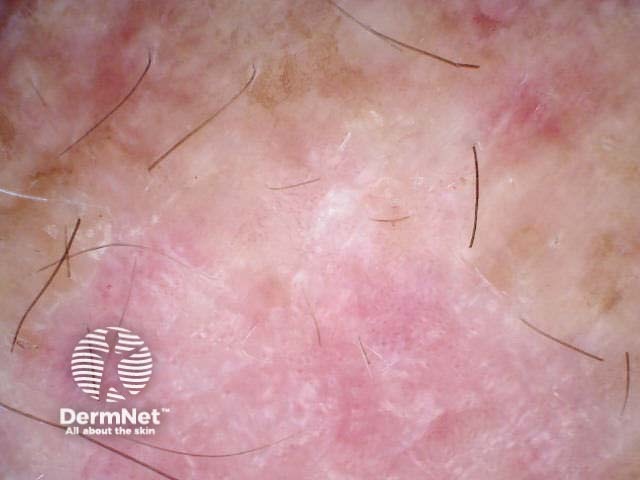
Superficial basal cell carcinoma
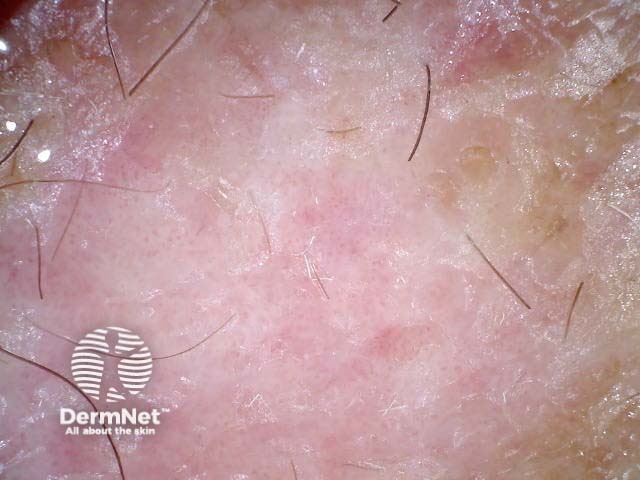
Superficial basal cell carcinoma
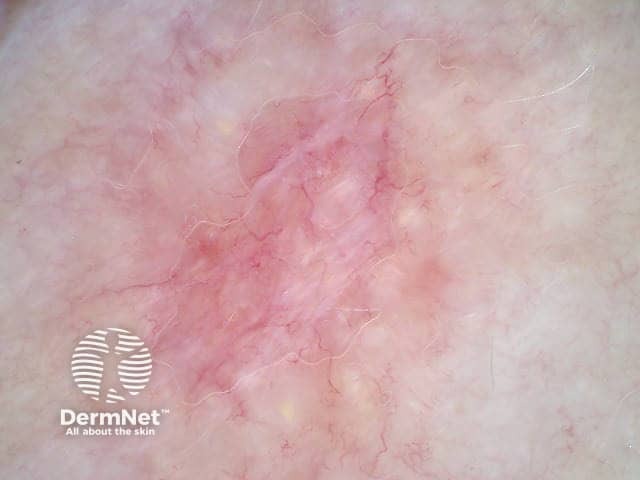
Cystic basal cell carcinoma (polarised view showing crystalline structures)
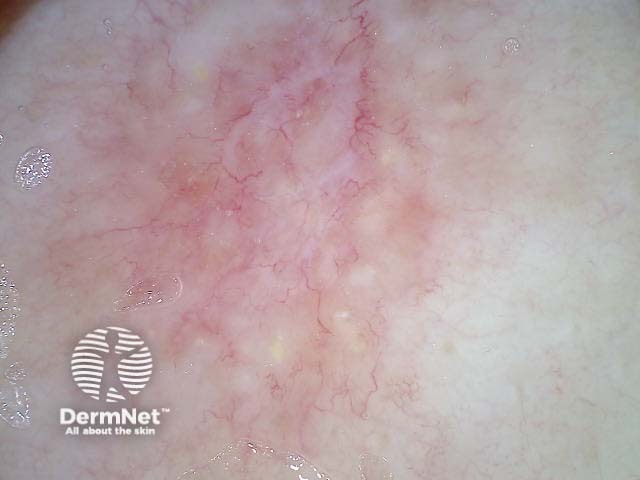
Cystic basal cell carcinoma (non-polarised view)
Imiquimod cream has restricted subsidy by PHARMAC for treating certain superficial basal cell carcinomas (New Zealand, September 2008). Observe the inflammatory response to treatment using dermoscopy.
See the DermNet bookstore.