Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Lesions (cancerous) Diagnosis and testing
Author: A/Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2014.
Introduction
Histology
Special studies
Differential diagnoses
Adenoid cystic carcinoma typically arises within salivary glands. Primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast are rare but well recognized.
In primary cutaneous adenoid cystic carcinoma, the tumour involves the dermis and may invade the subcutis (figure 1). The tumour is composed of basaloid cells arranged in a ductal or cribriform pattern. Characteristically there are eosinophilic hyaline membranes lining the pseudolumina within the tumour (figure 2, arrows).
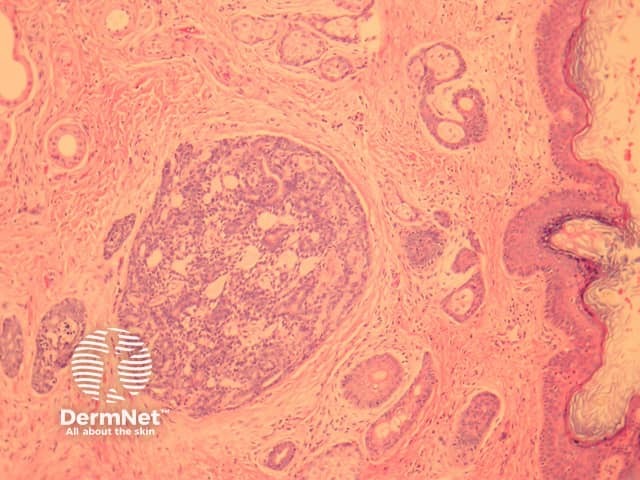
Figure 1
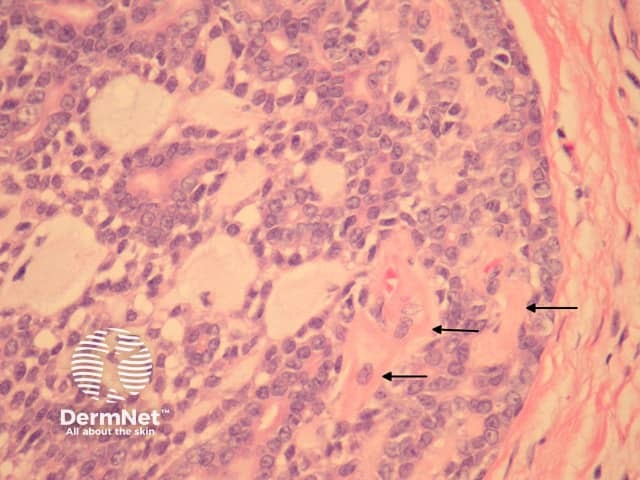
Figure 2
Adenoid cystic carcinoma is typically a morphologic diagnosis. The basement membrane material may be highlighted with PAS stain.
Cylindroma — These tumours exhibit a typical “jigsaw puzzle” architecture rather than the irregular cribriform and tubular architecture of adenoid cystic carcinoma.
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma – Can mimic adenoid cystic carcinoma. p63 immunohistochemistry can be helpful if this is a diagnostic consideration. Diffuse p63 positivity is more commonly seen with SCC.