Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Lesions (cancerous) Diagnosis and testing
Author: Naomi Ashman, Dermoscopist, Torbay Skin, Auckland, New Zealand. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. Created January 2019.
Introduction Dermoscopic features Characteristic lesions Histology
Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings are curved or crescent-shaped areas of pigment partially surrounding the adnexal openings of the face.
Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings are seen through the dermatoscope as pigmented crescents at the periphery of a follicle. They can be the same colour as the surrounding pigment as in a solar lentigo, or heavily pigmented, often with a greyish hue as seen in lentigo maligna melanoma [1].
Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings are characteristic of:

Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings in lentigo maligna dermoscopy
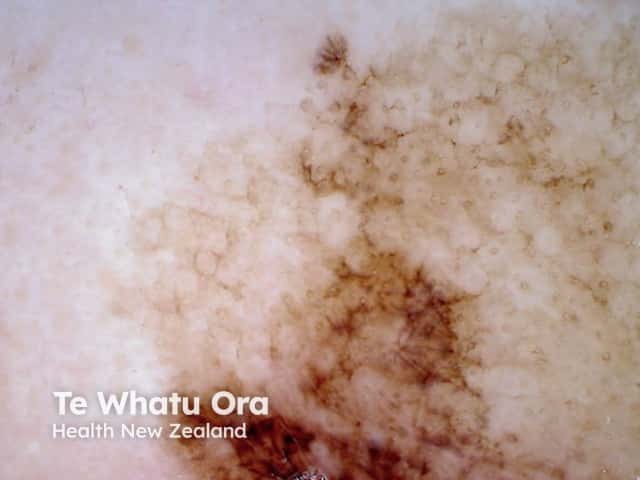

Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings in lentigo maligna dermoscopy
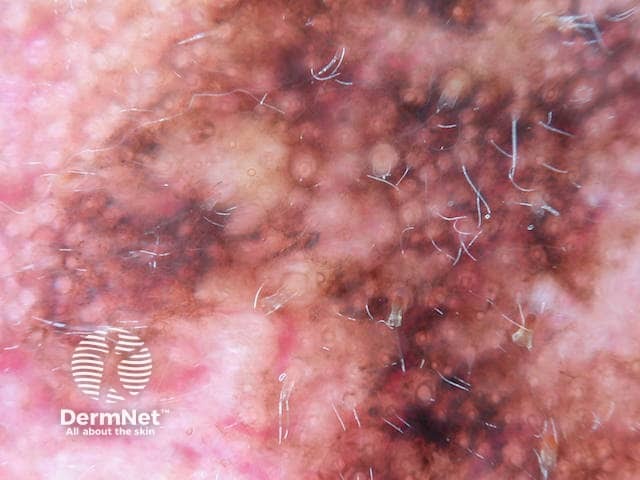
Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings in lentigo maligna melanoma
They can also occur in:
Although asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings are often said to be a clue to melanoma in situ, the clue actually has poor specificity [2].
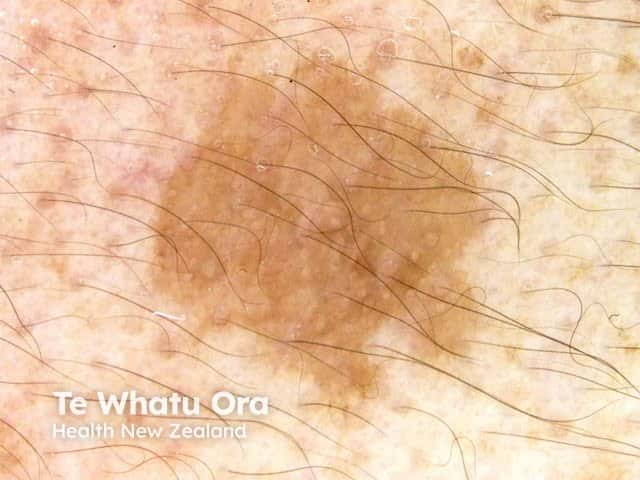
Mildly asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings in solar lentigo dermoscopy
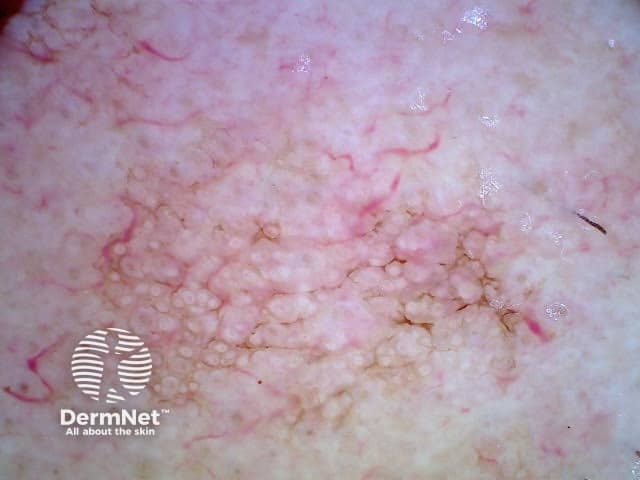
Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings in pigmented actinic keratosis dermoscopy
Asymmetrical pigmented follicular openings are due to abnormal melanophages spread asymmetrically up the hair follicle. In lentigo maligna, abnormal melanocytes may arise from stem cells in the follicular infundibulum.