Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Lesions (benign) Diagnosis and testing
Author: Dr Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Clinica Ricardo Palma, Lima, Peru. DermNet Editor-in-chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley. June 2018.
Introduction Histology Special studies Differential diagnoses
Clear cell fibrous papule is a rare variant of fibrous papule that has a clinical presentation identical to conventional fibrous papule of the nose. Its unusual morphology and rarity can cause diagnostic confusion.
In clear cell fibrous papule, the epidermis may be normal or show some degree of hyperkeratosis (figures 1,2). The dermis is expanded by a proliferation of clear cells arranged in sheets, clusters, or as single cells (figures 3,4). The clear cells show variation in size and shape. The nuclei are small and round without pleomorphism, hyperchromasia, or mitoses. The nuclei may be centrally located or may be eccentrically displaced by a large intracytoplasmic vacuole (Figures 3,4). Some clear cells may exhibit finely vacuolated cytoplasm with nuclear scalloping.
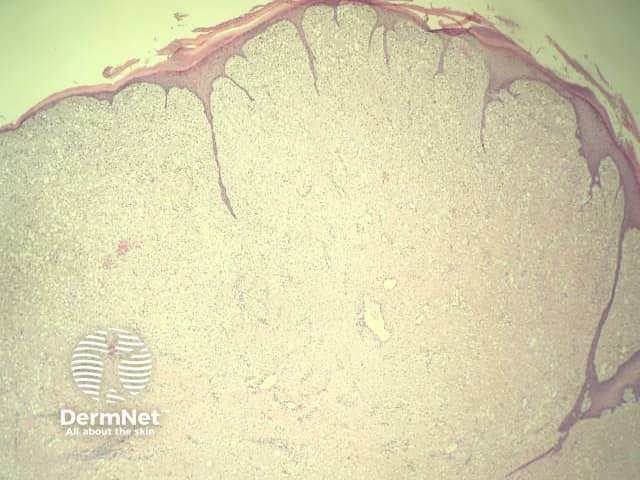
Figure 1
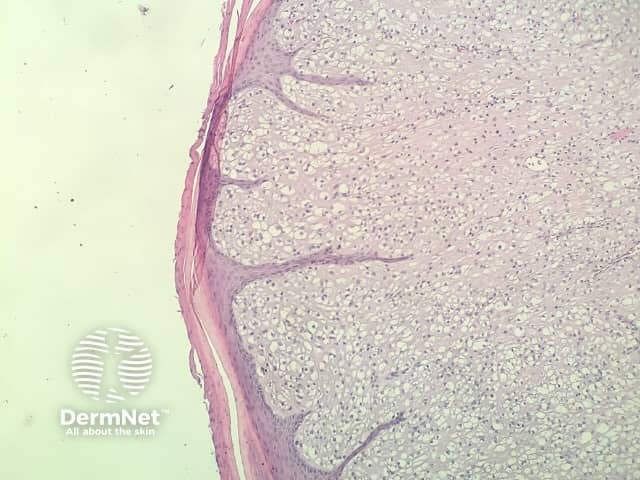
Figure 2
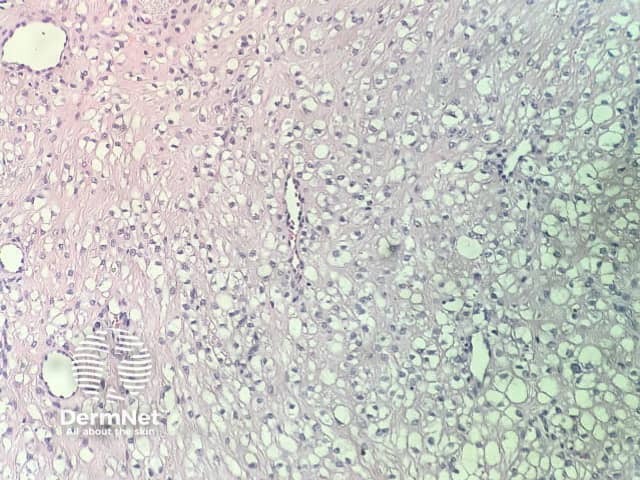
Figure 3
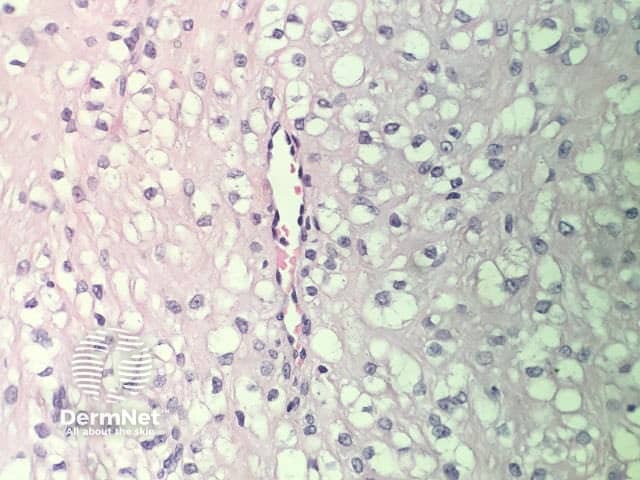
Figure 4
Immunohistochemistry of clear cell fibrous papule shows the clear cells are diffusely positive for vimentin and negative for cytokeratin AE1/AE3, epithelial membrane antigen, carcinoembryonic antigen, and HMB-45. S-100 protein often is negative but may be focally positive.
Other diagnoses to be considered include: