Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Systemic diseases Diagnosis and testing Metabolic
Author: Adjunct A/Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Clinica Ricardo Palma, Lima, Peru. DermNet Editor-in-chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. September 2018.
Introduction Histology Special studies Differential diagnoses
Eruptive xanthoma presents as crops of pink papules which are often pruritic. It occurs as a result of high concentrations of plasma triglycerides. Many patients have uncontrolled diabetes. The xanthomas usually disappear when the underlying condition is treated.
In eruptive xanthoma, the dermis contains a dense population of foamy histiocytes (histiocytes filled with lipid material as well as extracellular lipid (figures 1–3). There is often an associated acute and chronic inflammatory response (figure 4).
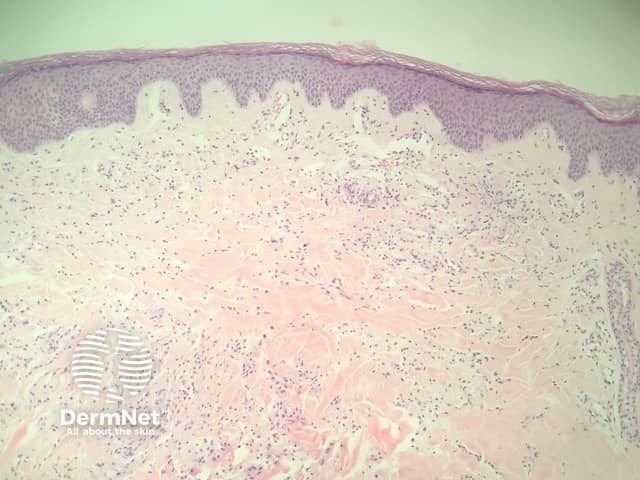
Figure 1
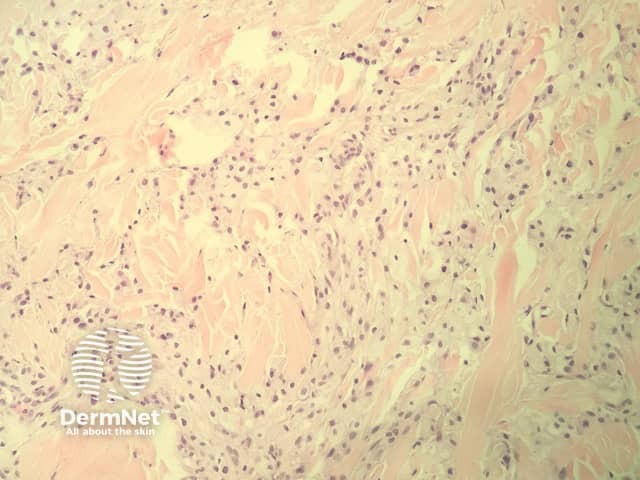
Figure 2
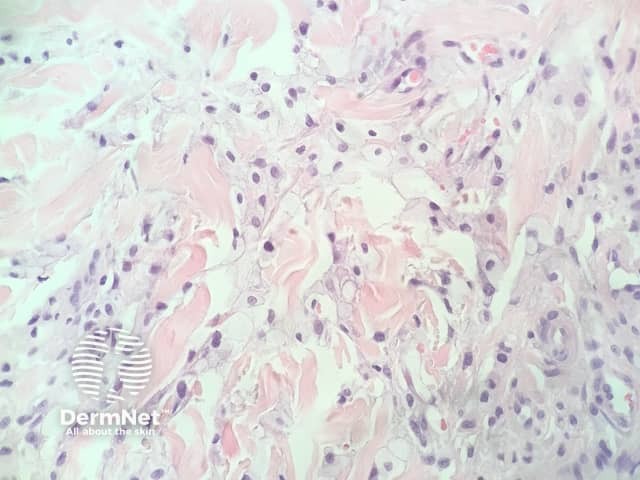
Figure 3
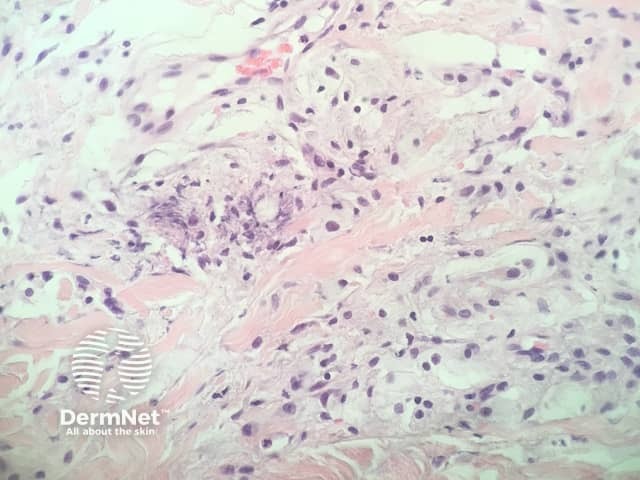
Figure 4
None are generally needed. Special stains to highlight lipid deposition have been described but are rarely needed.
There are a wide range of conditions which result in the accumulation of foamy histiocytes in the dermis and may mimic eruptive xanthoma. The correct diagnosis is generally confirmed by correlating the features of the biopsy with the clinical presentation and serologic findings.
Other xanthomatous conditions include: