Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Lesions (benign) Diagnosis and testing
Authors: Dr Charlotte Foster, Anatomical Pathology Registrar, Tauranga, New Zealand; Dr Ben Tallon, Consultant Dermatopathologist, Tauranga, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. September 2021
Seborrhoeic keratosis is a benign acanthoma comprised of epidermal keratinocytes. Clinically it presents as a sharply demarcated warty plaque with a ‘stuck-on’ appearance and greasy texture.
Seborrhoeic keratosis is a well-demarcated exophytic, flat or, less commonly, endophytic lesion composed of a proliferation of epidermal keratinocytes. Seborrhoeic keratosis can be recognised by a papillomatous architecture, acanthosis, hyperkeratosis, and horn cysts. The hyperkeratosis produces a characteristic loose lamellar stratum corneum. Squamous eddies may be present if particularly acanthotic.
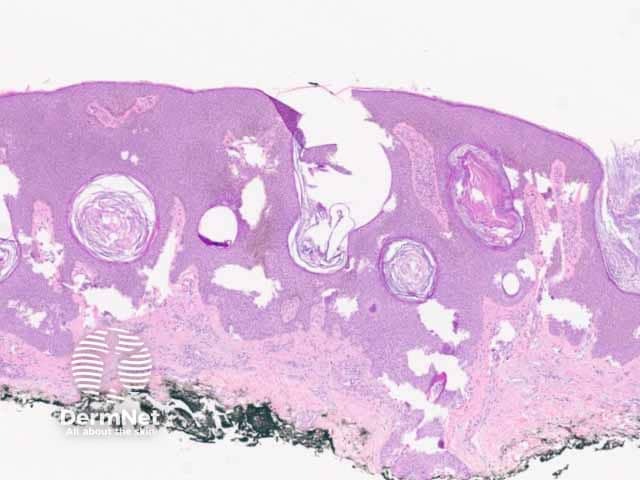
Figure 1: regular acanthotic seborrhoeic keratosis
There are multiple distinct histological patterns:
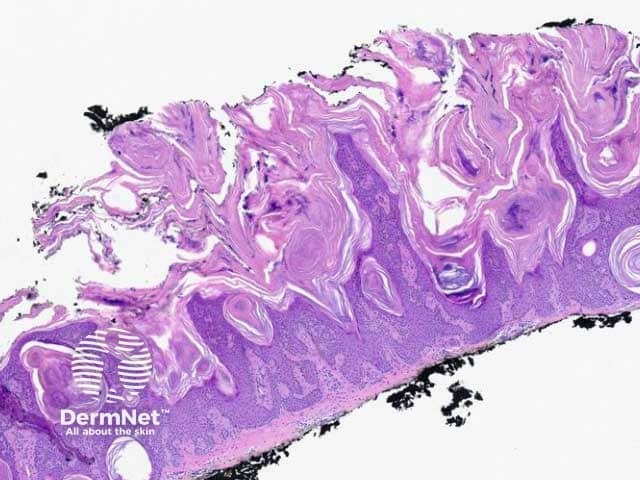
Figure 2: keratotic papillomatous pattern
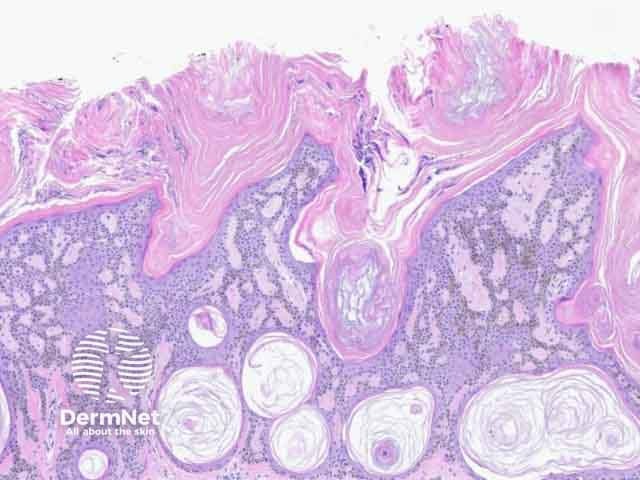
Figure 3: reticulated adenoid pattern
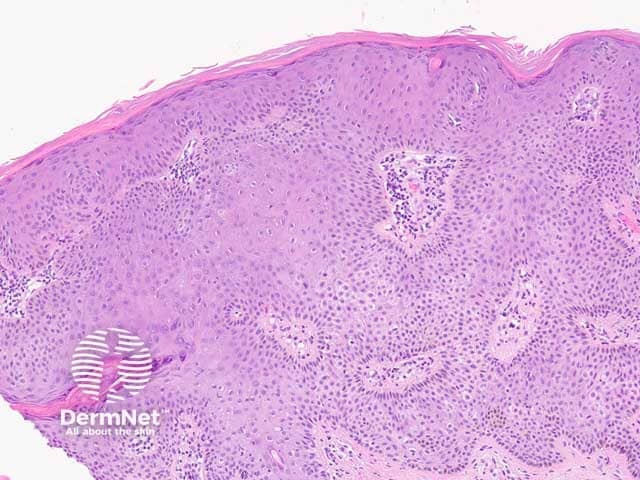
Figure 4: clonal pattern
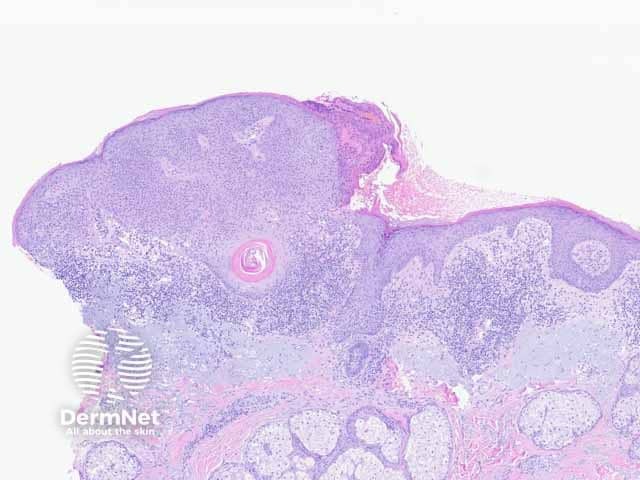
Figure 5: irritated pattern
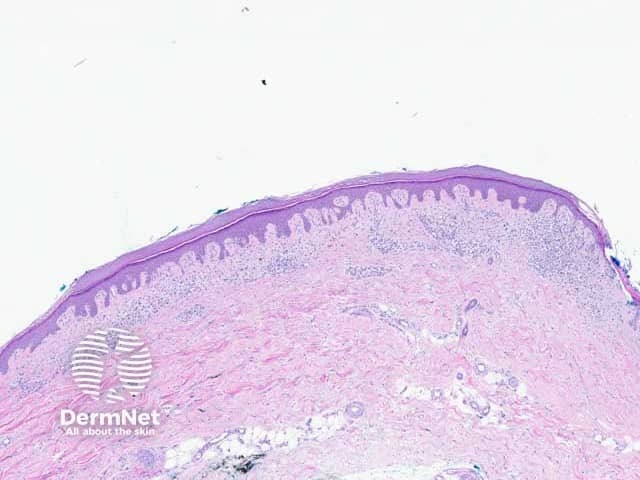
Figure 6: macular pattern
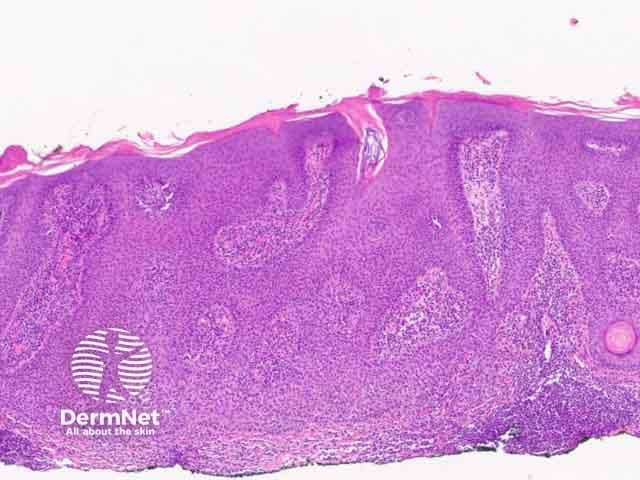
Figure 7: inflamed pattern