Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Reviewed and updated by Dr Amanda Oakley Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand; Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer; and Clare Morrison, Copy Editor, June 2014.
Steroid acne is the name given to an acne-like skin condition that occurs in people with high levels of circulating corticosteroids. They may have Cushing disease or they may be undergoing treatment with systemic steroid medications.
Severe acne is also a side effect of the use of anabolic steroids.
There are two forms of steroid acne:
Steroid acne is distinct from steroid rosacea, which is due to the long-term application of topical corticosteroids.
Steroid acne most often affects adolescent or adult patients who have been taking moderate or high doses of oral steroids such as prednisone or dexamethasone for several weeks. They can have a variety of underlying medical conditions.
Steroid acne most often occurs on the chest but may also develop on the face, neck, back and arms.
The steroids may aggravate a prior tendency to acne. It may affect any site prone to acne (eg face). The lesions tend to be more uniform in appearance than is usual with acne.
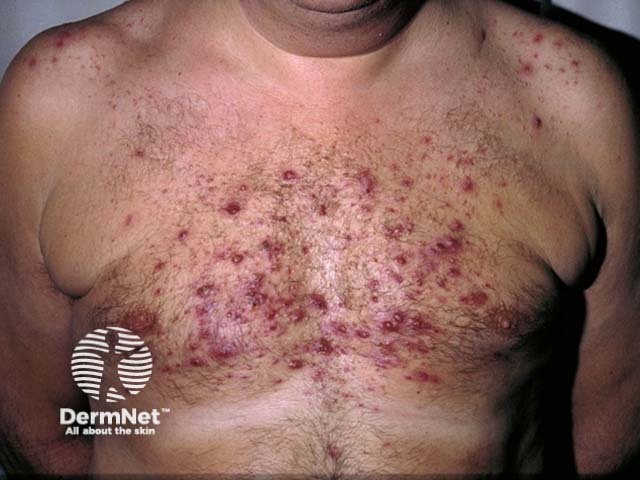
Steroid-induced acne vulgaris
In many patients, steroid acne is the same condition as Malassezia folliculitis. It is due to a proliferation of malassezia yeasts (also known as pityrosporum). It presents with itchy superficial papules and pustules on the chest and back.
In malassezia folliculitis, unlike acne vulgaris, most of the lesions are the same size. Comedones are not usually seen.
See more images of steroid acne...
Steroid acne may clear despite continuing the steroid medication. It usually, however, persists until the steroid medication is discontinued.
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition and its cause.
Severe steroid acne may be treated with oral isotretinoin. This is effective for both types of steroid acne.