Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Waxing is an effective method of removing unwanted hair in both large and small areas. Waxing is one method of epilation, which means that the entire hair shaft is removed from below the skin's surface. It is one of the most effective methods for temporary hair removal.
There are two types of waxing techniques, warm waxing and cold waxing. Both methods can be done at home using waxing kits available from the pharmacy. Warm waxing is more effective than cold waxing and is usually performed in a salon. The basic steps to warm waxing are:
Pain experienced is dependent on the pain threshold of each individual. Once the strip is removed hand pressure can be applied to the area to minimize discomfort. The area will be red and sensitive for a few hours.
Waxing is one of the most effective methods of epilation because hair is removed completely from the hair shaft in large quantities. After waxing it may take 2-3 weeks for hair to regrow.
It is unknown what the long-term effects of repeated waxing have on hair growth but the repeated damage to the hair follicles may result in permanent reduction of unwanted hair.
Almost anyone wanting to remove unwanted hair is a candidate for waxing. It can be used to remove hair from large or small areas including the moustache, chin, eyebrows, legs and bikini line.
Caution needs to be exercised in people using oral retinoids (isotretinoin and acitretin). Waxing should not be performed until treatment with these medications has been stopped for at least 6 months to 1 year. Waxing whilst taking these medications may cause tearing of the skin and possible scarring. Individuals using topical retinoids (e.g. Retin A®) should stop the medication 3-4 weeks prior to waxing to avoid skin injury and soreness.
Waxing should not be performed on skin that is irritated, sunburned or broken.
It is very important not to have the wax too hot to avoid burning the skin.
Side effects from waxing include:
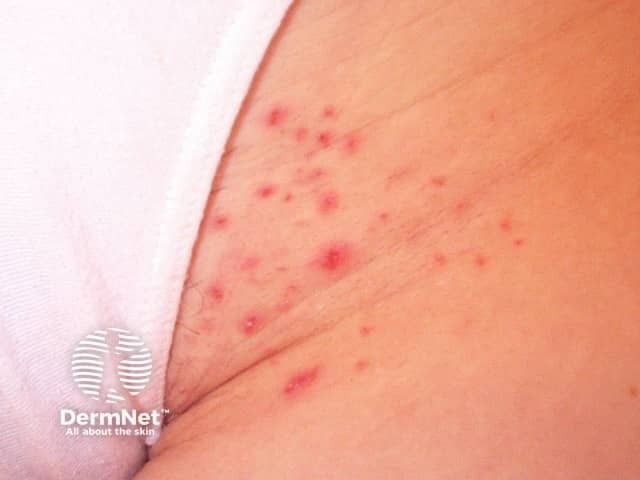
Folliculitis after waxing