Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Last Reviewed: March, 2024
Author: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer (2002); updated by Dr Ian Coulson, Dermatologist, United Kingdom (2024).
Edited by the DermNet content department
What is neomycin?
Where is it found?
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Alternative names
Further information
Neomycin is an antibacterial agent. Neomycin is prone to causing allergic contact dermatitis and was declared the Contact Allergen of the Year for 2010 by the American Contact Dermatitis Society (ACDS).
Neomycin is used widely in topical creams, ointments, lotions, eye preparations and eardrops. It is also commonly found in combination preparations with other antibacterials and topical corticosteroids. These prescription and non-prescription preparations are used to treat a variety of skin, eye and external ear disorders that have become infected and inflamed. Neomycin tablets taken orally may be used to suppress gastrointestinal bacteria before surgery to avoid infection. It has also used in the past as a preservative in some vaccines and may still be present in trace amounts. Listed below are some of the sources of neomycin in New Zealand in 2018.
Sensitisation in some countries is relatively high (such as Brazil), where it is a component of products available without prescription.
Systemic contact dermatitis can occur in sensitised individuals who take oral neomycin.
In neomycin allergic individuals, contact with neomycin from topical preparations produces classic allergic contact dermatitis reactions. It can sometimes produce a follicular pattern of contact dermatitis. Prolonged or repeated use may cause an inflamed, weepy rash in the affected area. It is thought that individuals that suffer from atopic dermatitis may be more sensitive to neomycin. Atopic dermatitis is often treated with topical combination preparations of neomycin and corticosteroids and it is only when the original condition doesn't improve or the condition becomes worse that neomycin sensitivity is suspected. Sometimes the appearance of the superimposed neomycin allergy may be modified by the corticosteroid component of the combination preparation used to treat the atopic dermatitis, thus making the diagnosis difficult. In most cases, allergy to neomycin needs to be confirmed by patch testing.
Neomycin taken orally or by injection may sometimes cause severe allergic reactions that can be life-threatening in neomycin-sensitive individuals.
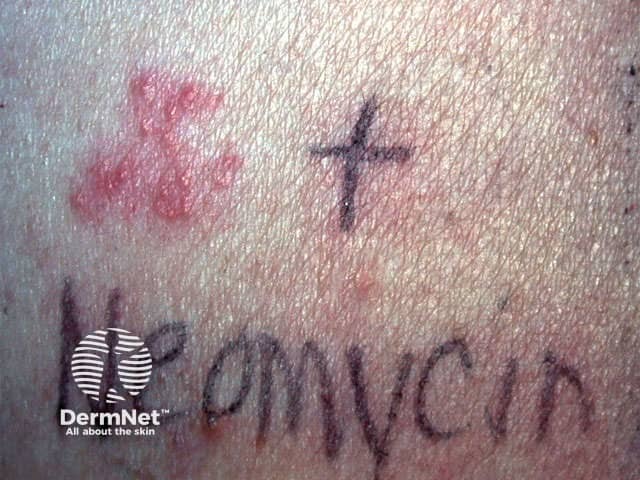
Patch tests
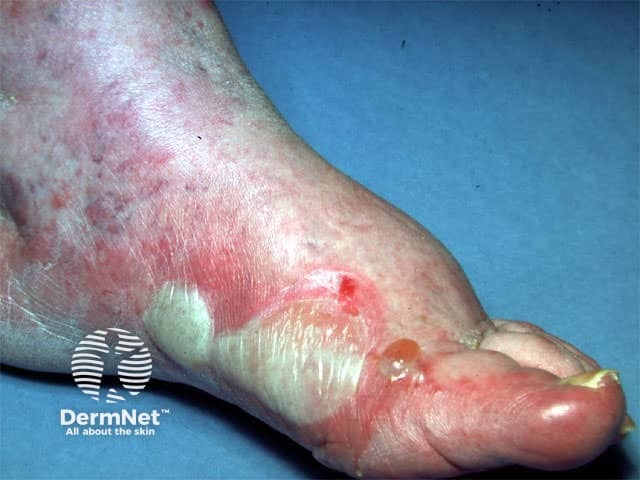
Foot dermatitis
Neomycin allergy is diagnosed by performing patch tests and in some cases intradermal tests. A 20% neomycin in petrolatum is the recommended concentration used for patch testing. A positive reaction shows a delayed indurated papule appearing after 48–72 hours. The patch test may not always be positive. If the test is negative, an intradermal test may be considered. This involves injecting a small amount of neomycin (1:1000) into the dermis of the skin. A positive reaction is similar to that of a positive patch test, a papule appearing in 24–48 hours and persisting for one or more weeks.
Treatment of neomycin allergy requires the prompt removal of the causative agent and then management as for any acute dermatitis/eczema; this may include application of topical corticosteroids and/or emollients. In severe cases, oral steroids may be necessary.
Contact dermatitis superimposed on atopic dermatitis can usually be treated the same as for contact dermatitis on non-atopic skin. In the acute phase, wet dressings may be required. Topical corticosteroids can then be introduced. In some situations where contact allergic dermatitis is severe, short courses of oral corticosteroids may be used.
Alert your doctor or dentist to the fact that you have an allergy to neomycin.
Carefully read the labels of all products for possible sensitisers. Over-the-counter products containing neomycin or other related substances that you may react to include first-aid or antibiotic creams and ointments, eye and ear preparations. If you are unsure, ask your pharmacist for suitable alternative products.
Allergy to neomycin may make you sensitive to other related compounds. As a precaution you should avoid using products containing any of these substances.
Medical, dental and veterinary workers that are neomycin sensitive need to take special precautions when their work requires contact with neomycin or related compounds. Protective clothing including gloves, masks and eyewear should be worn.
Your dermatologist may have further specific advice, particularly if you are highly sensitive to neomycin.
CAS number: 1405-10-3
Sensitiser: neomycin
Patch test: 20% neomycin in petrolatum