Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Autoimmune/autoinflammatory Diagnosis and testing
Author: Professor Balachandra Ankad, Department of Dermatology, S Nijalingappa Medical College, Bagalkot-587103, Karnataka, India. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. December 2020.
Introduction Clinical features Dermoscopic features Differential diagnoses Histological explanation
Lichen sclerosus is a chronic inflammatory skin condition with sclerotic and atrophic lesions of the anogenital area and extragenital skin.
Lichen sclerosus presents as distinctive porcelain white crinkled or thickened patches that tend to scar.
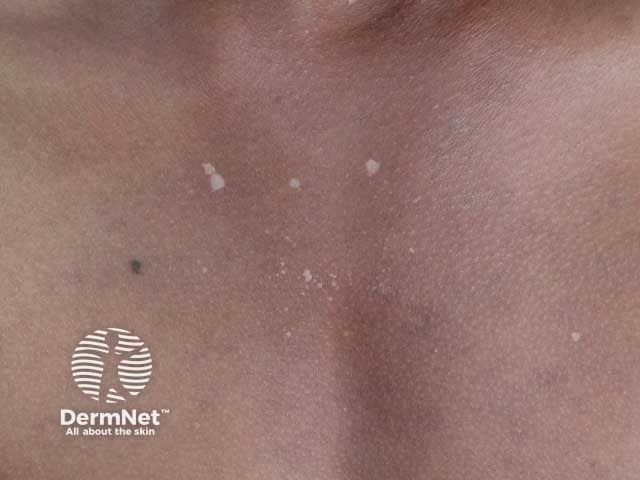
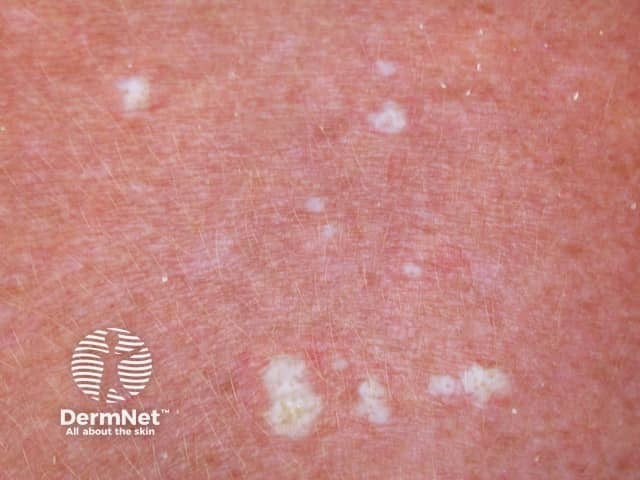
Extragenital lichen sclerosus
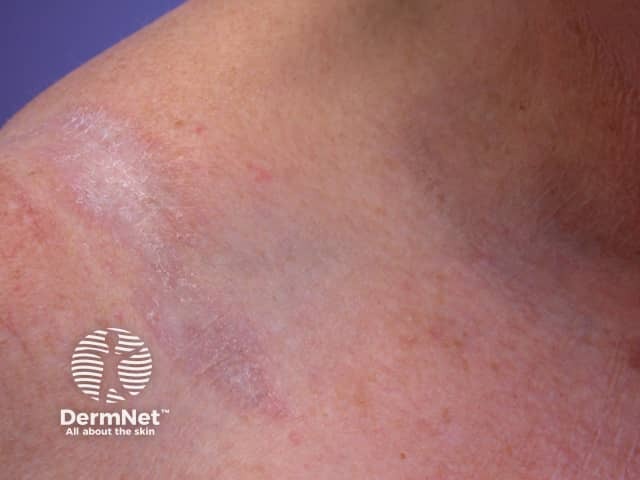
Extragenital lichen sclerosus
See also Extragenital lichen sclerosus images, Images of penile lichen sclerosus, Perianal lichen sclerosus images, and Vulval lichen sclerosus images.
Dermoscopy of cutaneous lichen sclerosus varies with the age of the lesion.
Early lesion (less than 2 years):
Late lesion (more than 2 years):
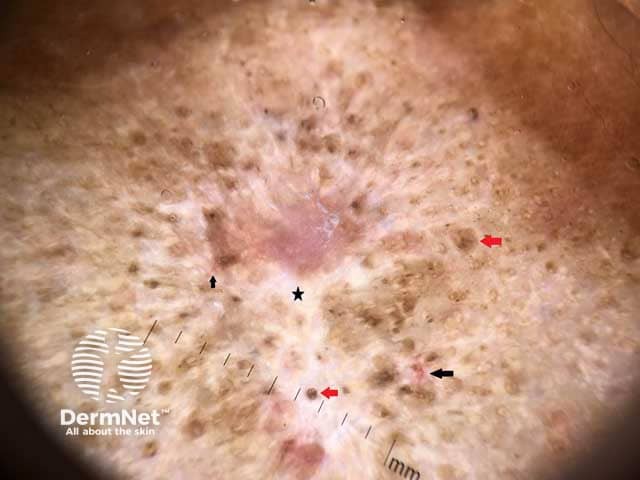
White area (black star), follicular plugs (red arrows), telangiectasia (black arrows)
Dermoscopy of genital lichen sclerosus shows:
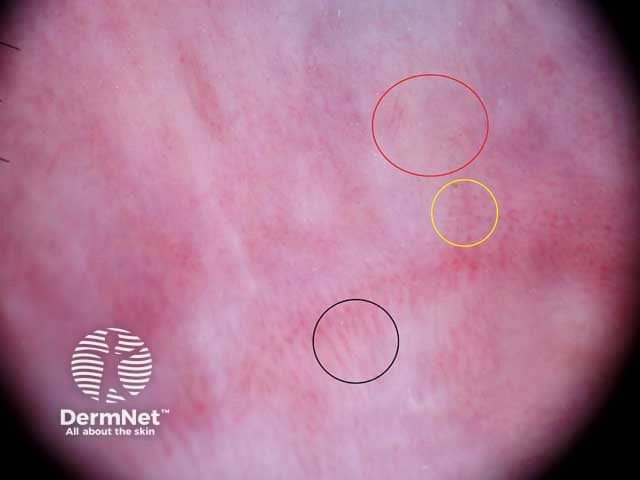
Vessels circled: hairpin (black), short linear and branching (red), dotted (yellow)
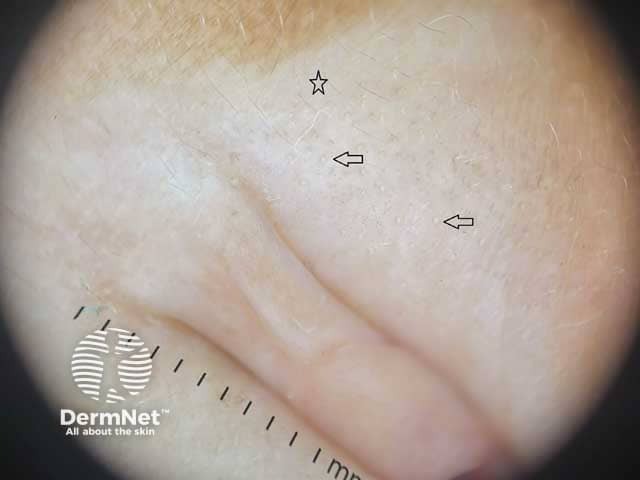
White areas (star) and comedo-like openings (arrows)
Vitiligo dermoscopy: white structureless areas described as having a ‘white glow’ due to the lack of pigment network.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis dermoscopy: white structureless ‘cloudy sky’ areas in various patterns such as amoeboid, petaloid, feathery, and nebuloid.
Morphoea dermoscopy: fibrotic beams (’white clouds’), pigment network, and spreading telangiectasia.