Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Dr. Abdurrahman Almurayshid, faculty member at Prince Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University, College of Medicine, Dermatology, Saudi Arabia. June 2015.
Introduction Histology Special studies Differential diagnoses
Familial benign pemphigus, also called Hailey–Hailey disease, is an acantholytic skin disorder caused by mutations in the ATP2C1 gene, with autosomal-dominant inheritance. The ATP2C1 gene is vital for keratinocyte adhesion and differentiation.
In benign familial pemphigus, acantholysis affects the whole epidermis, giving the classic description of the dilapidated brick wall (figures 1–4). The hair follicles are usually spared, typically, with acanthosis and dyskeratosis.
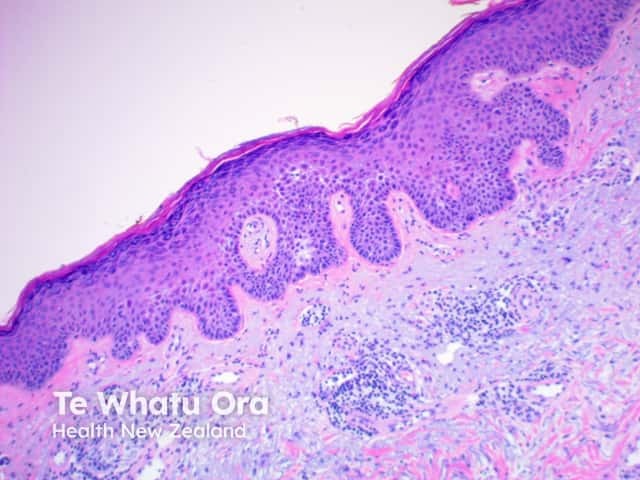
Figure 1
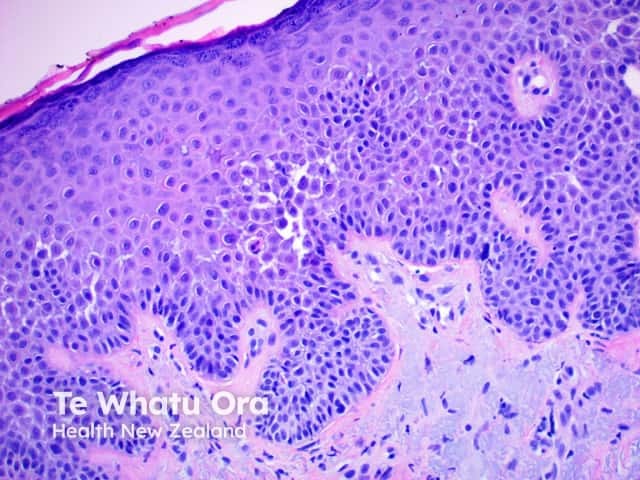
Figure 2
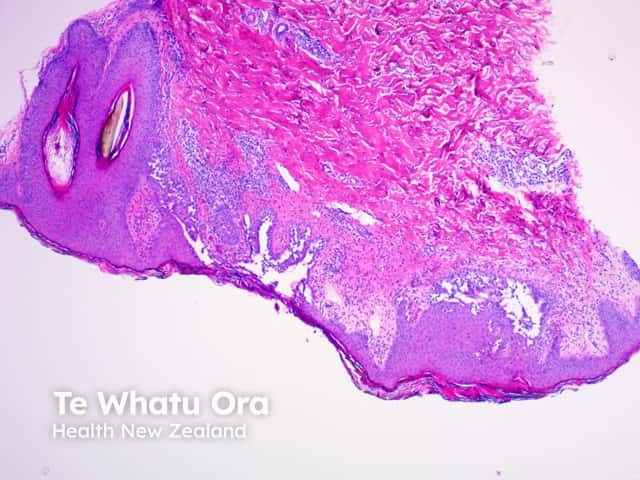
Figure 3
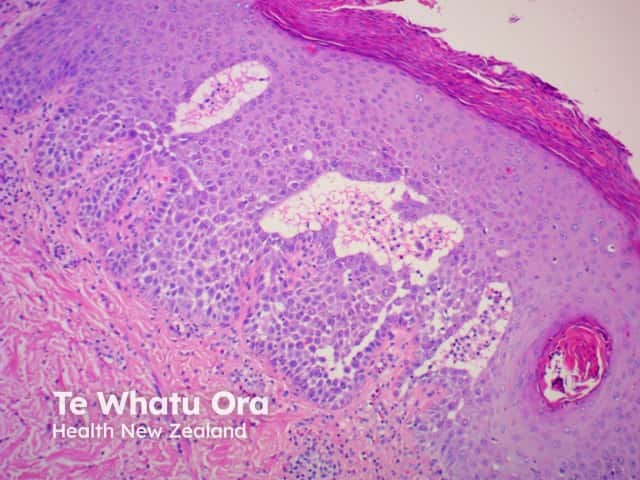
Figure 4
Direct immunofluorescence is applied to fresh tissue to exclude an immunobullous disease, particularly pemphigus vulgaris.
Grover disease: usually more focal histologically.
Pemphigus vulgaris: positive direct immunofluorescence and more likely to involve hair follicles.