Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author(s): Charlotte Krones, Western Health, Melbourne, Australia (2022)
Reviewing dermatologist: Dr Ian Coulson
Edited by the DermNet content department
Introduction Uses How it works Benefits Side-effects and risks Contraindications
Lebrikizumab is a novel, high-affinity, monoclonal antibody or biological agent that selectively inhibits interleukin 13 (IL-13) for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted lebrikizumab Fast Track designation for atopic dermatitis (AD) in Dec 2019. In July 2022, there were one phase II and eight phase III clinical trials assessing the use of lebrikizumab given by subcutaneous injection in moderate to severe AD, with expected submission for FDA approval in 2023 in the United States, and European medicines agency (EMA) approval in the European Union.
Lebrikizumab has shown promising efficacy and a favourable safety profile in moderate to severe AD, including pruritus improvement as early as two days after commencing treatment.
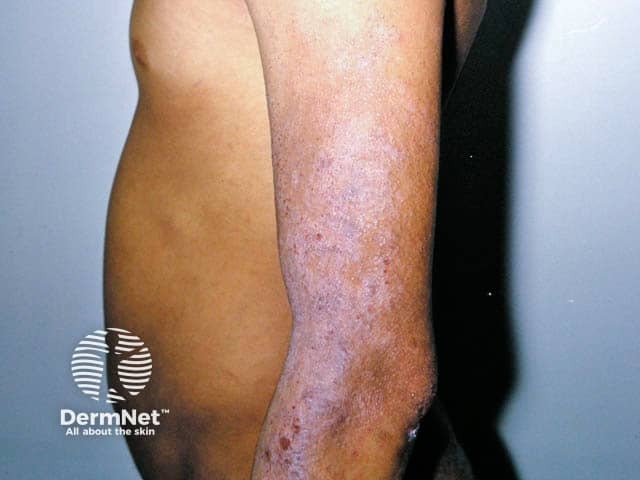
Chronic changes of atopic eczema with inflammation, scale and lichenification on the arm in skin of colour (AD-patient3)
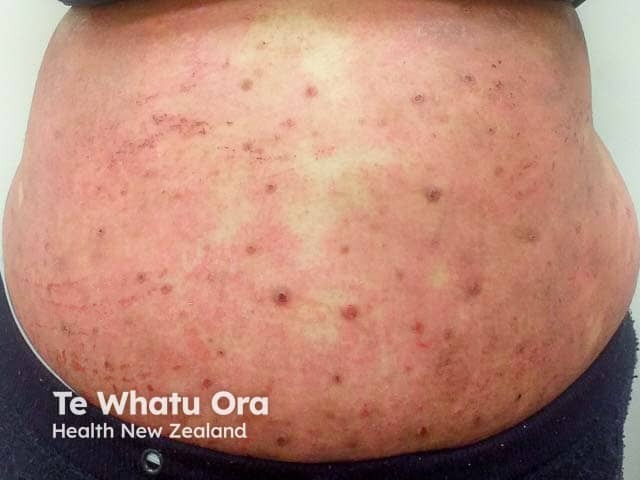
Extensive excoriated atopic dermatitis in an adult with skin of colour
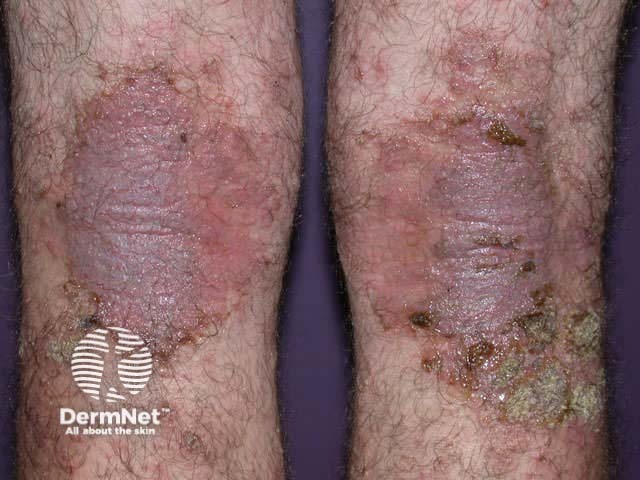
Atopic dermatitis
Clinical trials for the use of lebrikizumab in the following conditions are currently underway:
Preliminary clinical trial results suggest that lebrikizumab may significantly improve AD disease severity when used in conjunction with topical steroids. It should also be used in combination with standard aspects of AD management such as moisturisers and emollients.
Lebrikizumab is thought to work by downregulating inflammatory processes that contribute to atopic dermatitis.
Lebrikizumab is an IL-13 antagonist. It is understood to inhibit IL-13 by neutralizing the cytokine and preventing binding and heterodimerization of receptor subunits IL-13Rα1 and IL-4Rα. Lebrikizumab binds to IL-13 with high affinity and blocks downstream signalling, reducing inflammation and thereby helping to relieve symptoms of AD and improve the barrier function of the skin.
Clinical trials have demonstrated promising results for lebrikizumab, including rapid improvement in atopic dermatitis symptoms and severity, and high rates of sustained itch relief and skin clearance at one year of treatment.
Other benefits include:
Lebrikizumab seems to be generally well tolerated.
Reported adverse events include:
Data on drug-to-drug interactions are limited.
See also immunisation in immunosuppressed dermatology patients for information on vaccination.
Approved datasheets are the official source of information for medicines, including approved uses, doses, and safety information. Check the individual datasheet in your country for information about medicines.
We suggest you refer to your national drug approval agency such as the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory agency (MHRA) / emc, and NZ Medsafe, or a national or state-approved formulary eg, the New Zealand Formulary (NZF) and New Zealand Formulary for Children (NZFC) and the British National Formulary (BNF) and British National Formulary for Children (BNFC).