Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Harriet Cheng BHB, MBChB, Dermatology Unit, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, New Zealand, 2013.
Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma is a rare multisystem histiocytic disease usually affecting older adults. The typical clinical lesion is an asymptomatic yellowish indurated plaque in a periorbital location. Approximately 80% of cases are associated with paraproteinaemia. Additional extracutaneous features include ophthalmic involvement, cryoglobulinaemia and lymphoproliferative disorders.
Palisading xanthogranulomas with foci of necrobiosis are found in the mid dermis and panniculus (Figures 1, 2). Involvement of the panniculus is septal (figure 2) and may mimic panniculitis. Focal areas of necrobiotic collagen appear as amorphous eosinophilic debris (Figure 3) and often contain cholesterol clefts. Granulomas consist of foamy histiocytes (Figure 4, arrow), and giant cells (Figure 5). Both touton and foreign body giant cells are found. Quite striking angulated giant cells with darkly staining nuclei adjacent to areas of necrobiosis are a characteristic feature. Plasma cells are typically prominent. Sometimes there are dense lymphoid infiltrates with germinal centres.
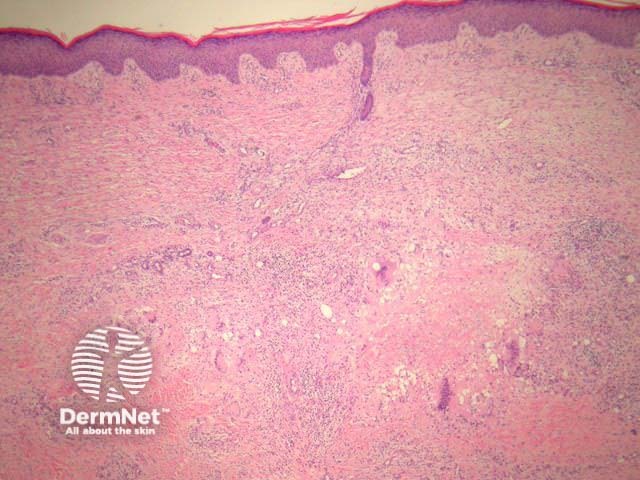
Figure 1
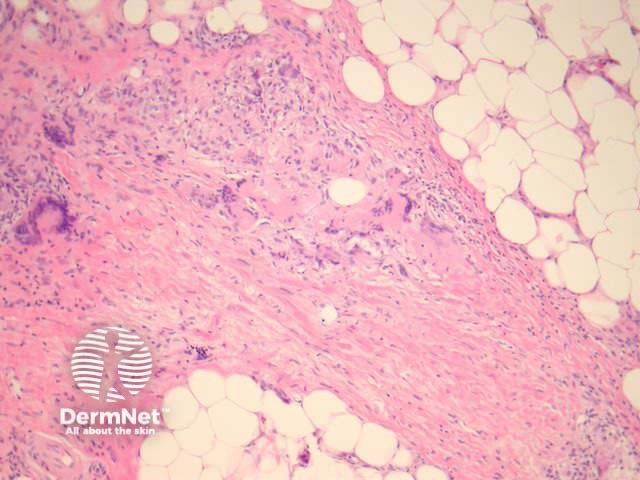
Figure 2
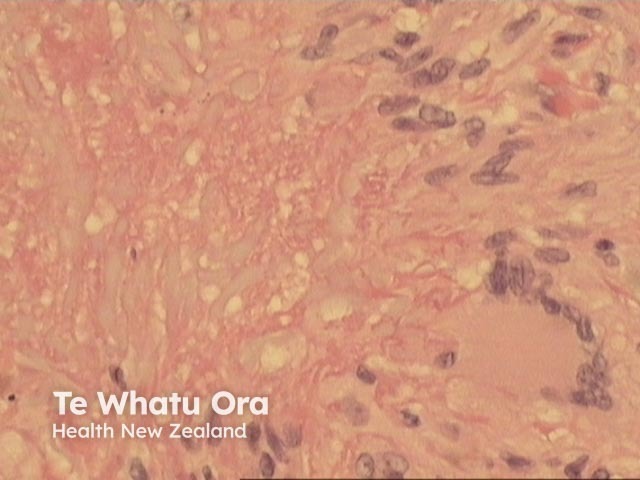
Figure 3
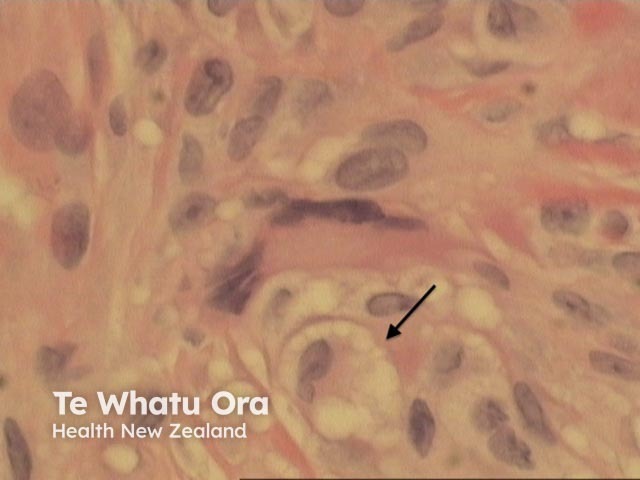
Figure 4
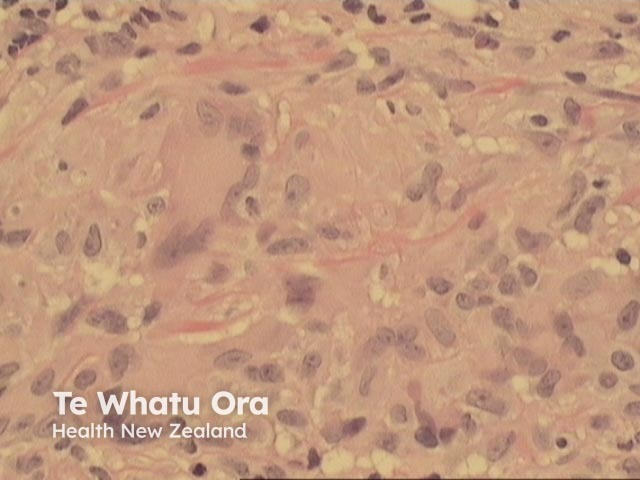
Figure 5
Oil red O staining for fat may reveal focal lipid droplets. Small amounts of interstitial mucin may be found on Alcian blue staining.
Necrobiosis lipoidica: presence of numerous cholesterol clefts, bizzare and touton type multinucleated giant cells differentiate necrobiotic xanthogranuloma from necrobiosis lipoidica. Necrobiosis lipoidica characteristically has a horizonatally layered pattern of necrobiosis (“layer cake” pattern). However, differentiation may be difficult on small punch biopsies. Clinical correlation is helpful.
Granuloma annulare: zones of necrobiosis surrounded by palisading macrophages and lymphocytes. Giant cells and plasma cells are much less prominent than in necrobiotic xanthogranuloma. Absence of cholesterol clefts.