Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Lesions (benign) Follicular disorder
Authors: Dr James Landero and Dr Ben Tallon, Dermatologists, Skin Dermatology Institute, Tauranga, New Zealand. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. September 2018.
Introduction Clinical features Diagnosis and histological features Differential diagnoses Treatment
Panfolliculoma is a benign neoplasm of follicular differentiation that was initially described by Ackerman et al. in 1993. The morphological characteristics of panfolliculoma are similar to those of trichoblastoma, but it shows greater follicular differentiation.
Panfolliculoma is a very rare tumour; therefore, incidence data are lacking. There are fewer than 40 cases in the literature.
A panfolliculoma usually presents as a neoformation or a slow increase in growth, resembling other lesions, such as basal cell carcinoma, infundibular cyst, and trichoepithelioma. Clinically, it presents as a solitary cystic tumour in the head or trunk up to 3–4 cm in diameter.
Panfolliculoma is diagnosed histologically by the presence of differentiation in all parts of the hair follicle — the infundibulum, stem, and bulb/papilla (figures 1–4). The lesions are well circumscribed, and lack cellular atypia. Within the cellular components are granules of trichohyalin (figure 3), pale/clear cells of outer root sheath epithelium, and abortive hair shaft formation (figure 4).
They have been subclassified into three main variants: nodular, superficial, and cystic (figure 1), with an additional case that presented with sebaceous differentiation.
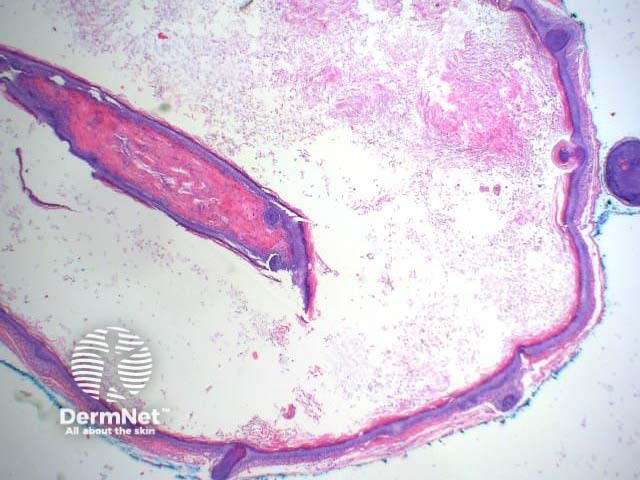
Figure 1
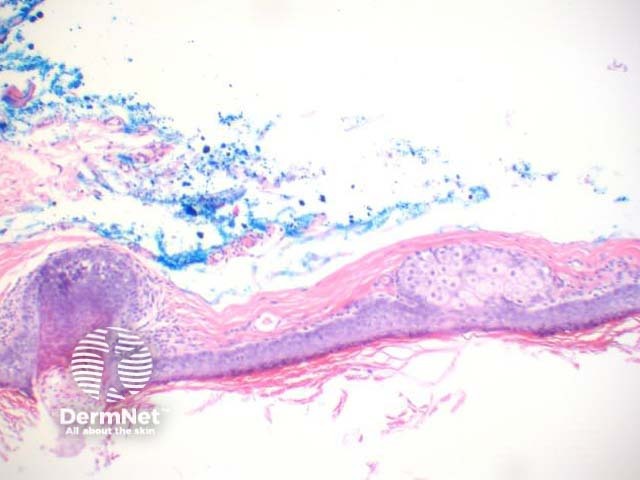
Figure 2
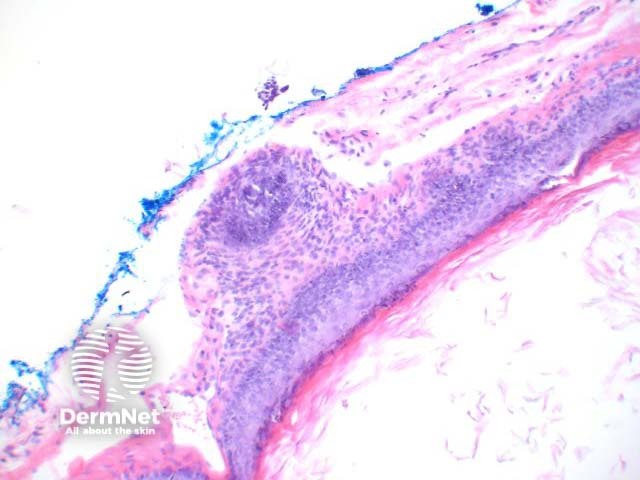
Figure 3
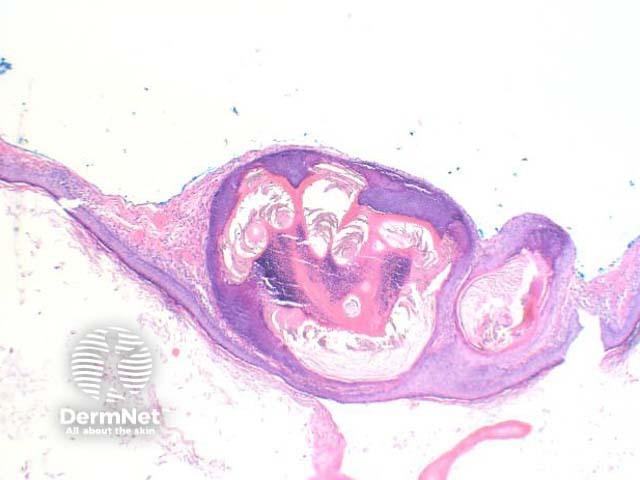
Figure 4
While not typically needed for the diagnosis, cytokeratin (CK)903 and CK 5/6 stain the tumour cells, whereas Ber-EP4 labels the germinative cells but not the follicular papillae.
Panfolliculoma differs from trichoblastoma by the presence of differentiation toward all elements of the follicle, including cystic structures containing corneocytes. Matrical differentiation is less conspicuous than it presents in matricoma.
Panfolliculomas are considered benign tumours and are treated by simple excision.