Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Authors: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer (2002); Dr Ian Coulson, Dermatologist (2023)
Introduction
Reactions
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Alternative names
Further information
Thiomersal is an organic compound containing mercury and thiosalicylate. It is an antiseptic with both bactericidal and fungicidal action.
Historically, it was commonly used as a preservative in topical pharmaceutical preparations, cosmetics, and biological products such as vaccines. Its use is diminishing, especially in cosmetics.
Cosmetics |
Pharmaceutical/self-hygiene products |
Biological products |
|
|
|
Localised allergic contact dermatitis (itchy red patches) may occur in sensitive individuals. This may include redness and swelling at the injection site when injectable thiomersal-containing products are used. Most reactions are usually mild and resolve spontaneously after a few days. Hypersensitivity reactions may be due to either the mercury or thiosalicylate component of thiomersal.
Although thiomersal as a preservative in vaccines (particularly multi-dose vials) has a long record of being safe and effective, there are concerns regarding exposure to mercury-containing compounds. In the USA, all vaccines administered to children 6 and below are thiomersal free as they are dispensed in single dose units.
Due to mercury exposure concerns, thiomersal use has declined in recent years and many products, including vaccines, have been reformulated without thiomersal.
Thiomersal allergy can be diagnosed by performing patch tests using 0.1% thiomersal in aqueous solution.
Because thiomersal is used as a preservative in antigen preparations for scratch or intradermal testing, false positive reactions may occur in mercury-sensitive individuals.
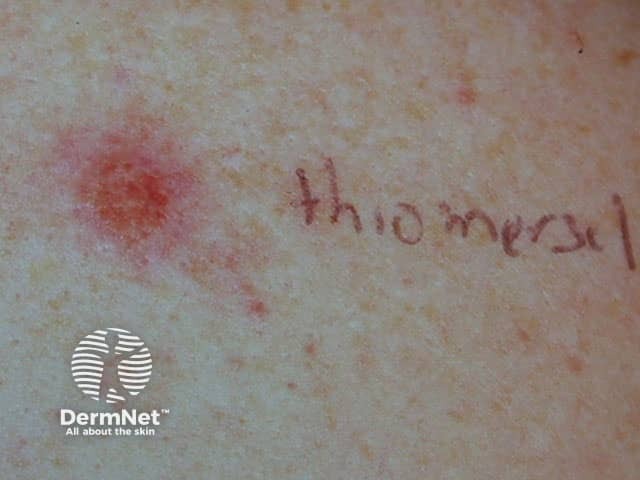
Positive patch test to thiomersal
If you are diagnosed with thiomersal allergy then avoid exposure to thiomersal-containing products.
Once the dermatitis appears on the skin, treatment is as for any acute dermatitis/eczema, eg, topical corticosteroids, emollients, treatment of any secondary bacterial infection (Staphylococcus aureus).
Once thiomersal sensitivity is confirmed you should try to avoid exposure to any products containing thiomersal preservative. Read product labels and avoid products that contain thiomersal or any of its alternative names. If unsure, ask your pharmacist for advice or a suitable alternative.
Alert your doctor to the fact that you have an allergy to thiomersal. Wherever possible your doctor should use vaccines free of thiomersal. However, if you require vaccination with thiomersal-containing vaccines for which there are no alternatives, discuss with your doctor the risks versus benefits. In general, an allergic reaction to thiomersal is much less a risk to bear than the potential illnesses from not being vaccinated.
Your dermatologist may have further specific advice, particularly if you are highly sensitive.
Patch Test: thiomersal 0.1% in aqueous solution