Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author(s): Nikhil Dwivedi, Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine, Bond University, Australia. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. July 2022.
Introduction Demographics Causes Clinical features Variation in skin types Complications Diagnosis Differential diagnoses Treatment Prevention Outcome
A Becker naevus (nevus in American English) is a late-onset epidermal naevus or birthmark characterised by a large brown patch and occurs mostly in males.
Also referred to as Becker melanosis and Becker pigmentary hamartoma, it is an overgrowth of the epidermis (upper layers of the skin), pigment cells (melanocytes), and hair follicles. It develops during childhood or adolescence, usually on the shoulders or upper trunk but occasionally found elsewhere.
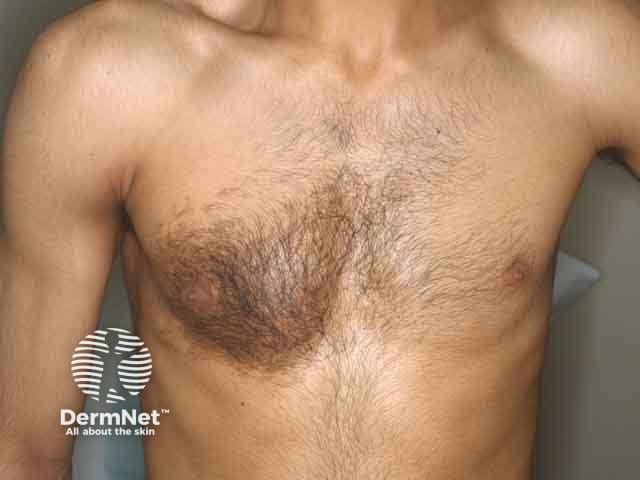
Hyperpigmentation and hypertrichosis over the chest in Becker naevus
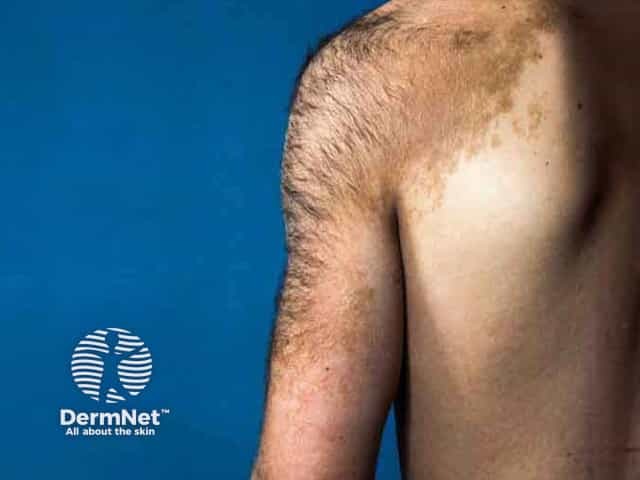
Pigmentation and hypertrichosis in Becker naevus (BN-patient3)
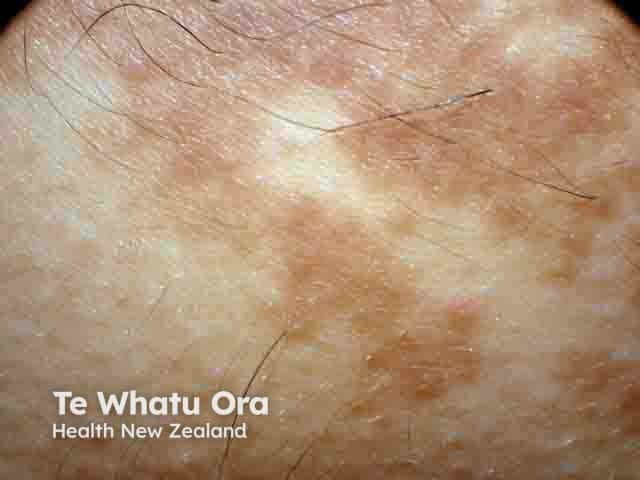
Close-up of Becker naevus showing pigmentation and hypertrichosis (BN-patient4)
While the exact aetiology is unknown, it is thought that a currently unidentified gene defect may be the cause. Its development may be triggered by circulating androgens (such as testosterone), which may explain why it appears in males at puberty.
Becker melanosis is not known to be hereditary and does not typically run in families, however, there are some reports of multiple family members being affected.
Features include:
Rarely, like other birthmarks, there may be some abnormality of underlying tissues derived from the same embryonic cell type, the ectoderm. This is known as the Becker naevus syndrome, a type of epidermal naevus syndrome. These abnormalities may include:
In darker skin phenotypes, the naevus can appear darker and leathery.
It is predominantly a clinical diagnosis based on clinical history and examining the lesion. It may be necessary to undertake a biopsy so that a Becker naevus can be differentiated from a café-au-lait macule.
There is no effective treatment for the majority of Becker naevi. However, there are some strategies to minimise the appearance and treat complications.
No prevention strategies currently exist.
The Becker naevus cannot be removed, however, the cosmetic appearance and complications, such as acne, may be improved. There are no current reports of Becker naevi undergoing malignant changes.