Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Wafaa Binti Mowlabaccus, Medical Student, Department of Medicine, University of Mauritius, Reduit, Moka, Mauritius. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. July 2020.
Introduction
Demographics
Features
Common melanocytic lesions
Common keratinocytic lesions
Common lesions of vascular origin
Common fibrous lesions
Common subcutaneous lesions
Skin tags
A benign skin lesion is a non-cancerous skin growth.
Any individual from any age group can present with a benign skin lesion.
The features in common for benign skin lesions include:
Benign lesions can be classified by their cellular origin: melanocytic, keratinocytic, vascular, fibrous, fat, and so on,
Common benign skin lesions of melanocytic origin include the ephilis, lentigo simplex, and melanocytic naevus (mole).
Ephilides are genetically determined well-defined small brown macules with the following characteristics:
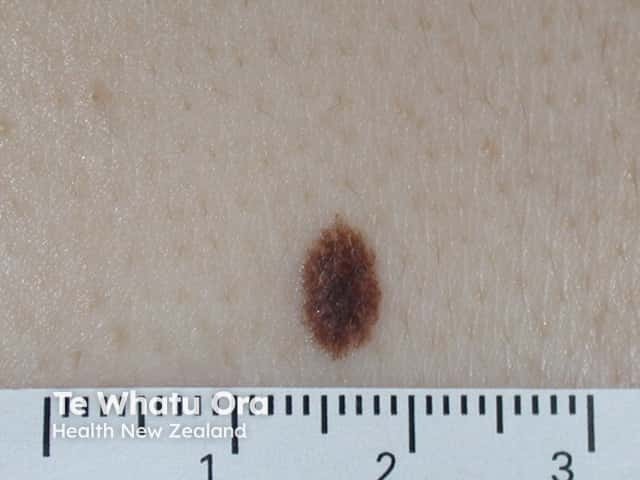
Lentigo simplex is not sun-induced. It has the following characteristics:
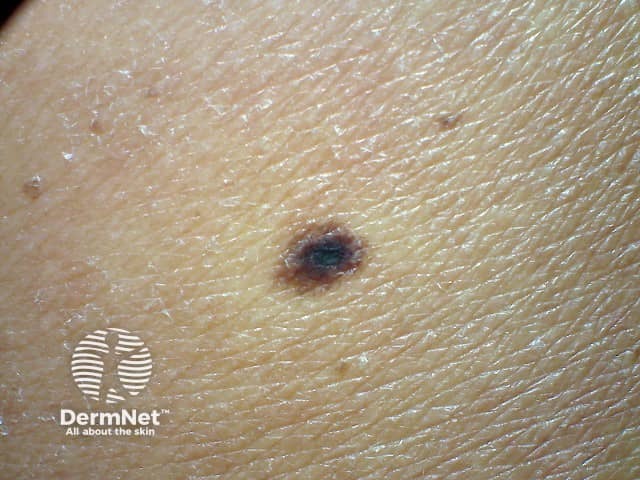
A melanocytic naevus can be histologically classified as a junctional, compound, or dermal naevus depending on the location of nests of naevus cells.
A junctional naevus has naevus cells at the base of the epidermis.
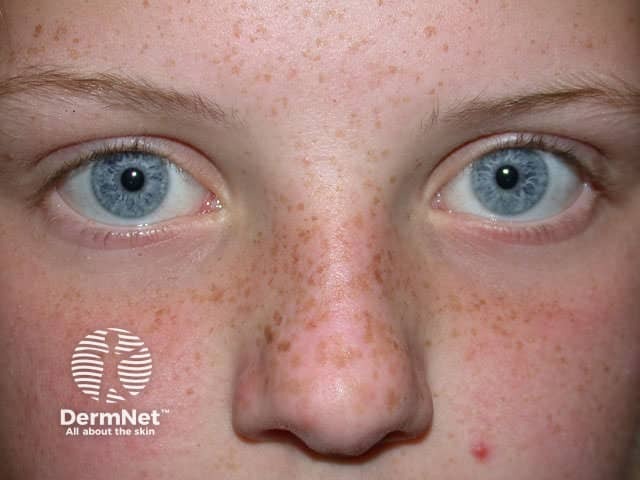
Ephilides
Lentigo simplex

Junctional naevus
A compound naevus has papular and flat components due to junctional and dermal naevus cells.
A dermal naevus is characterised by naevus cells in the dermis.
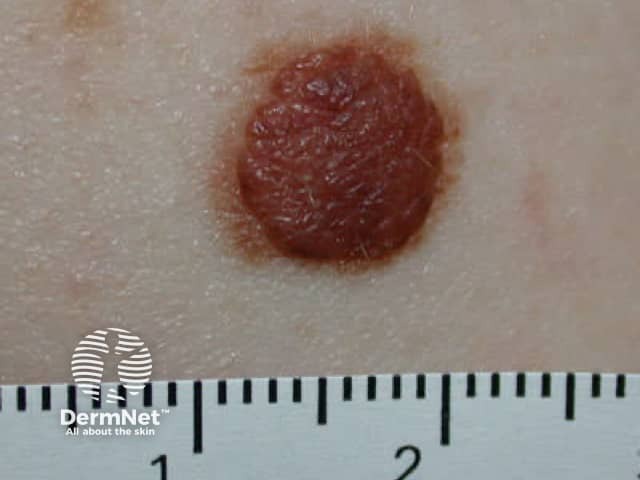
Compound naevus
Dermal naevus
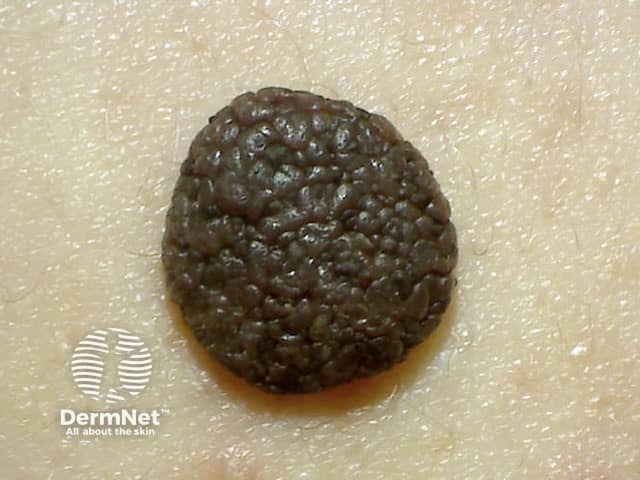

Papillomatous dermal naevus
Benign keratoses include solar lentigo and seborrhoeic keratosis.
A solar lentigo is a sun-induced pigmented macule.
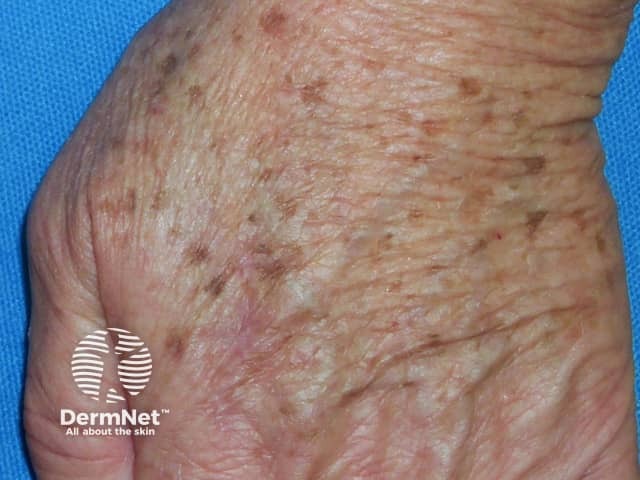
Solar lentigo
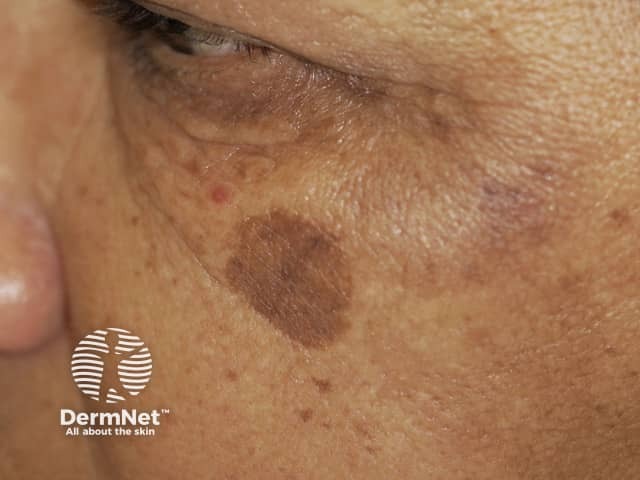
Solar lentigo
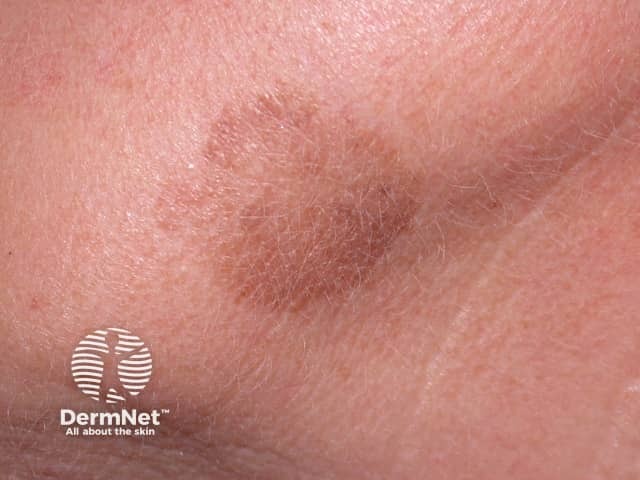
Solar lentigo
Seborrhoeic keratosis presents as a variable warty plaque.
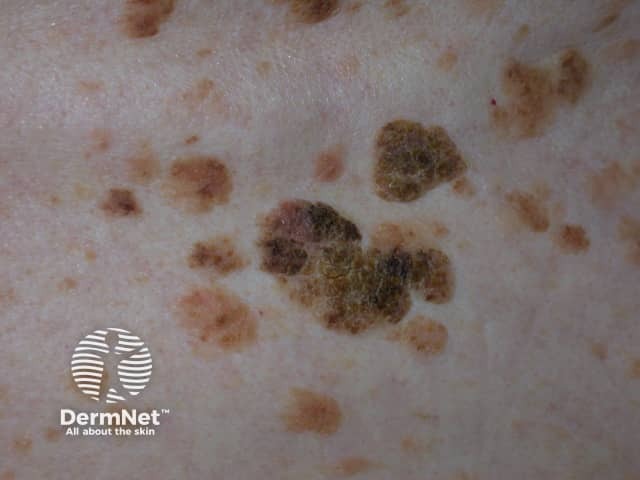
Seborrhoeic keratosis
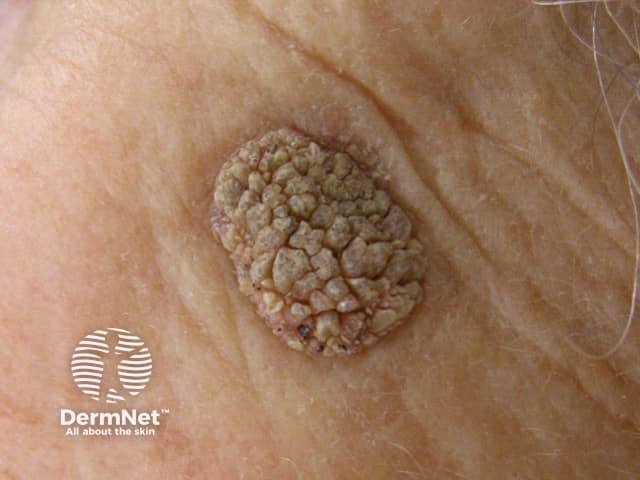
Seborrhoeic keratosis
Seborrhoeic keratosis
Stucco keratoses are flat-topped keratotic papules.
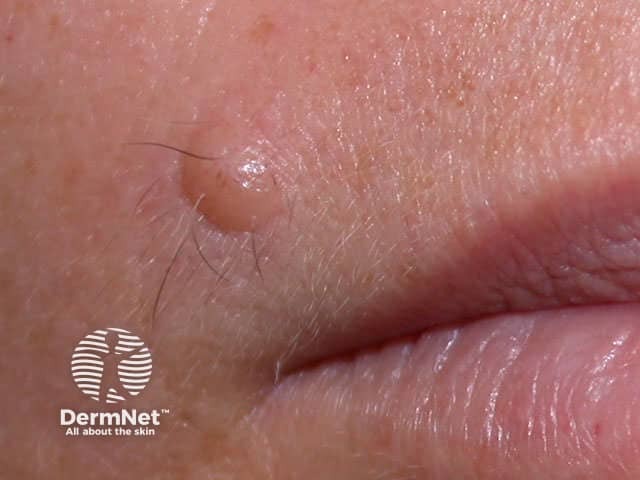
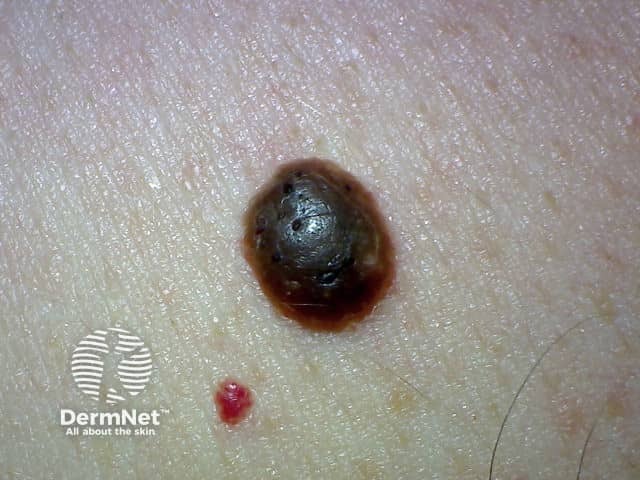
Epidermoid cyst is a follicular nodule with a central punctum.
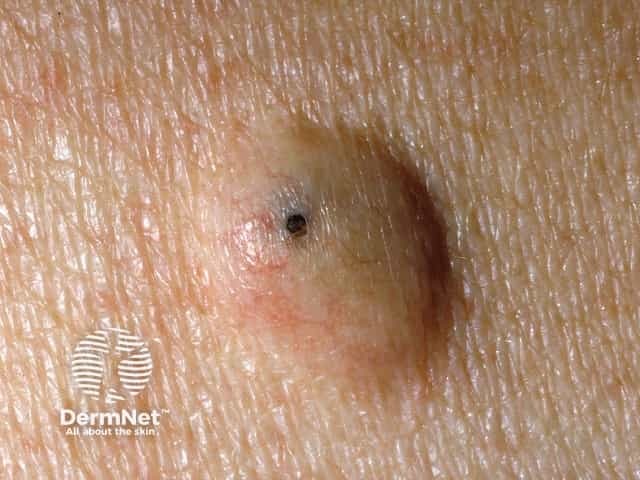
Epidermoid cyst
Epidermoid cyst
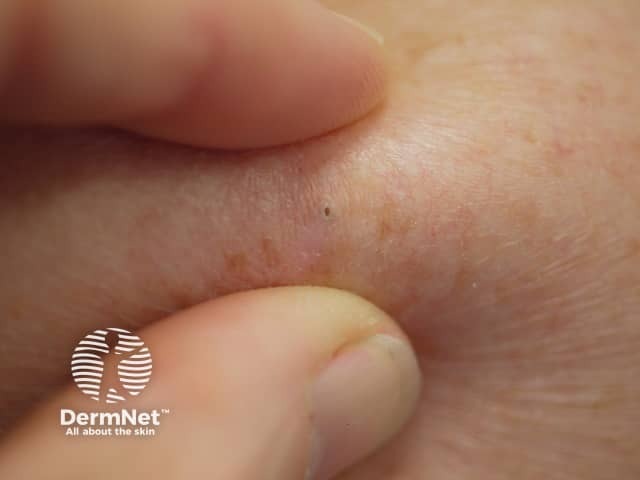
Palpating an epidermoid cyst
Corns and calluses are localised areas of thickened skin induced by pressure
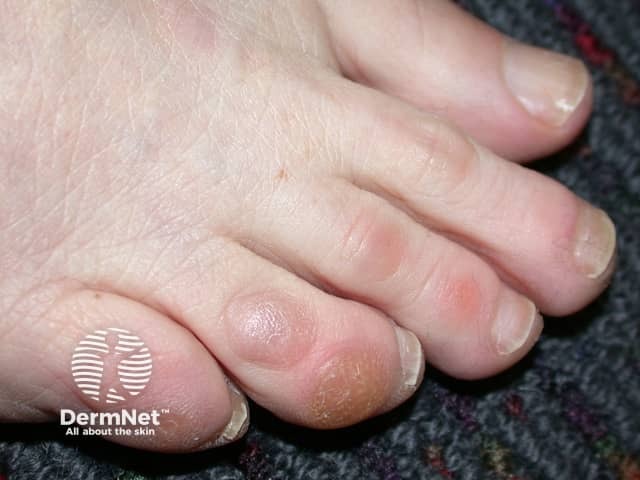
Corn (clavus)
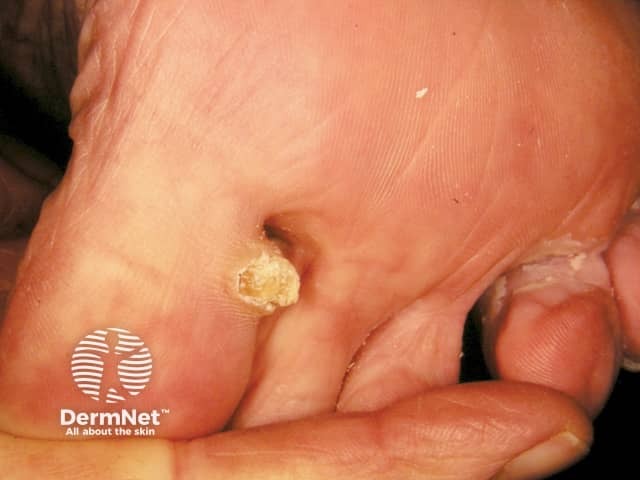
Corn (clavus)
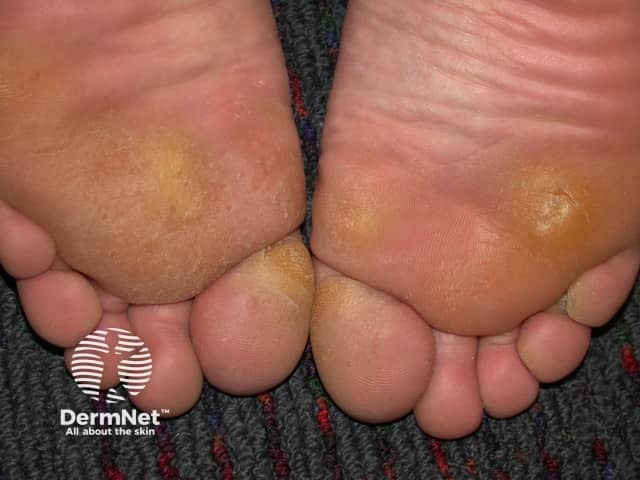
Calluses
Sebaceous hyperplasia occurs on the forehead and cheeks of adults.
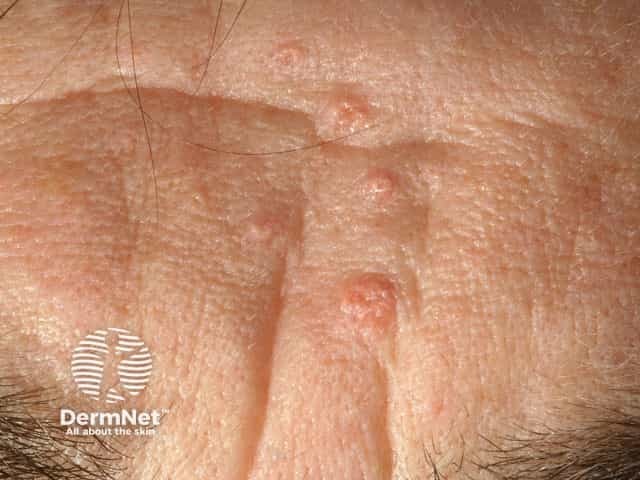
Sebaceous hyperplasia
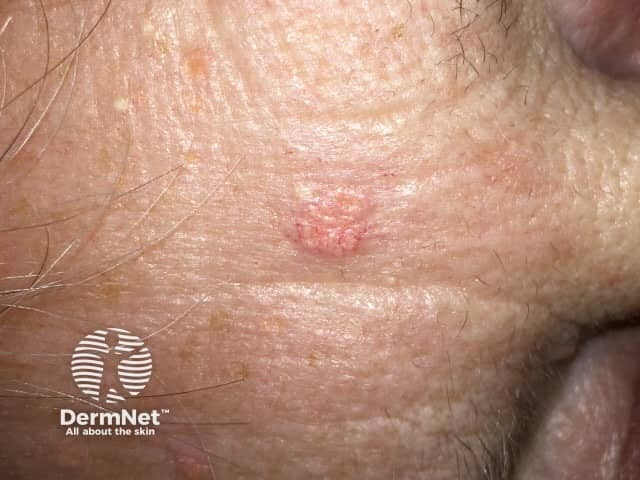
Sebaceous hyperplasia
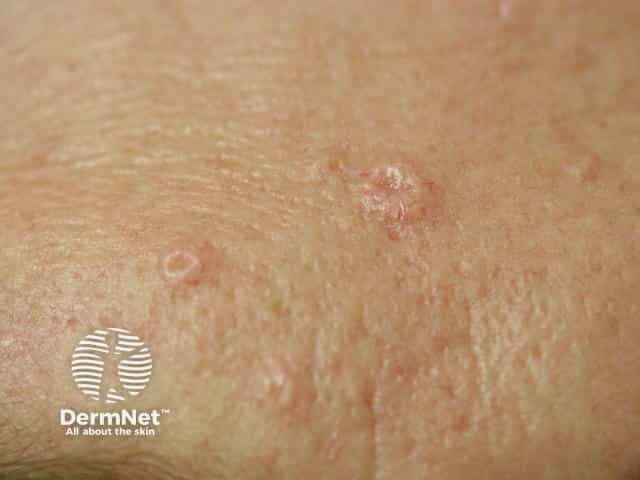
Sebaceous hyperplasia
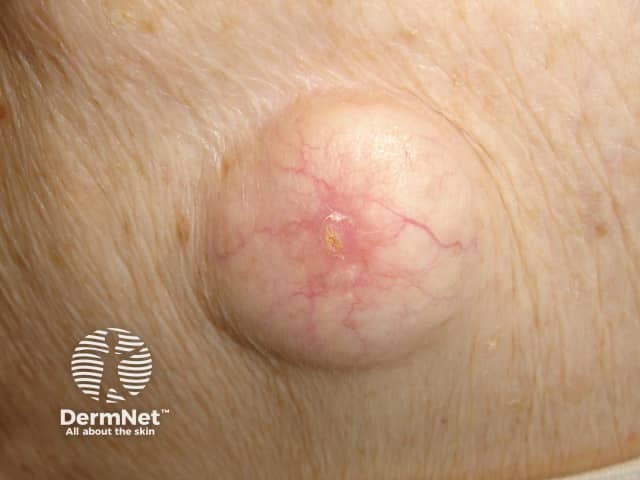
An angioma is due to the proliferation of the endothelial cells.
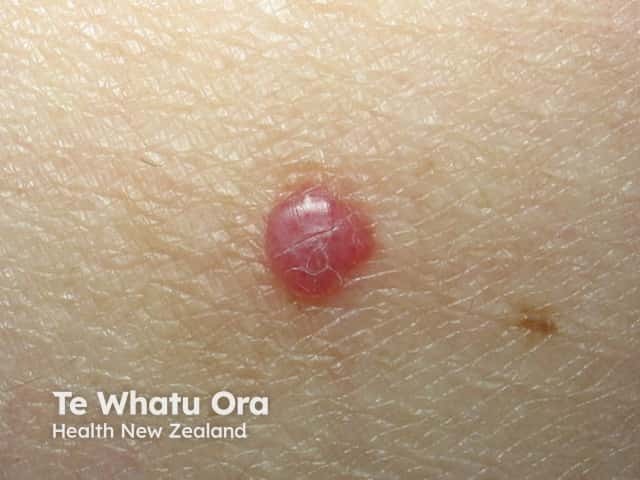
Cherry angioma
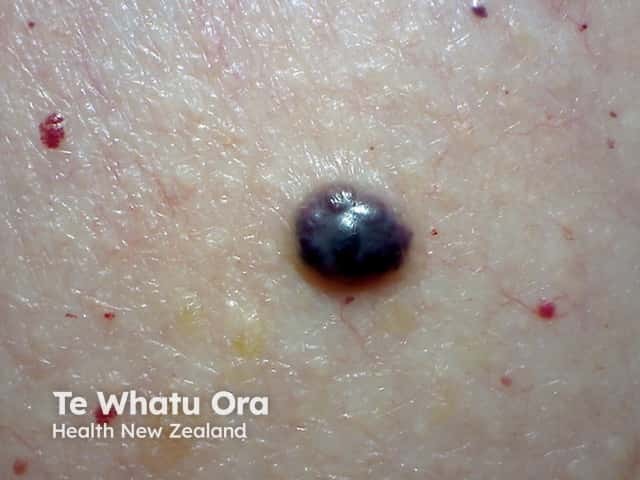
Cherry angioma
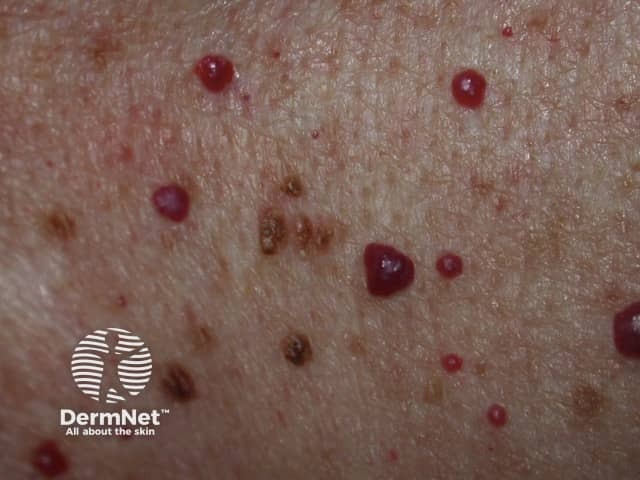
Cherry angioma
A pyogenic granuloma is a vascular response to trauma and bacterial infection.
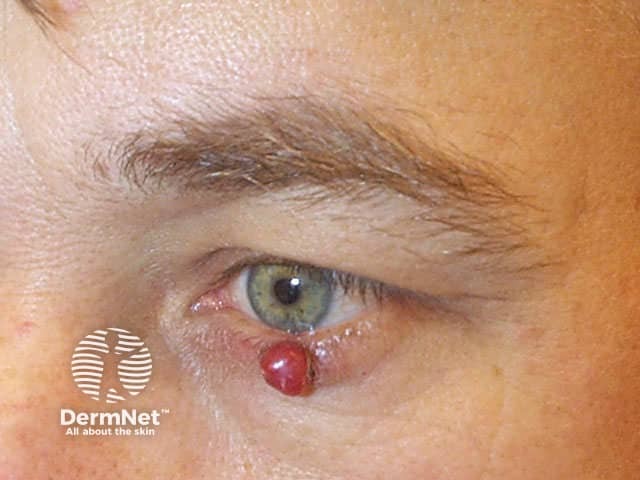
Pyogenic granuloma
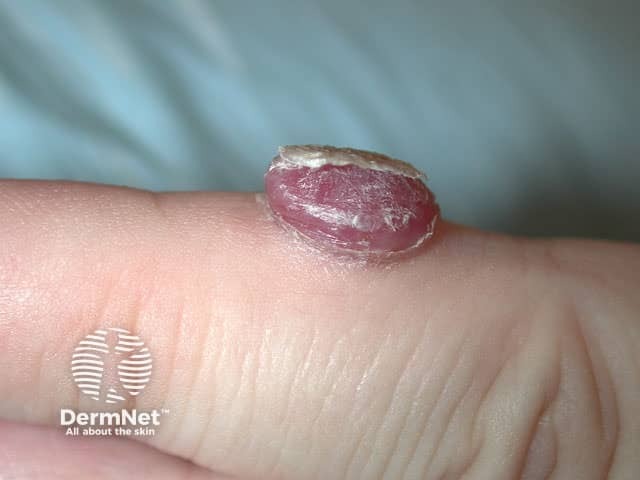
Pyogenic granuloma
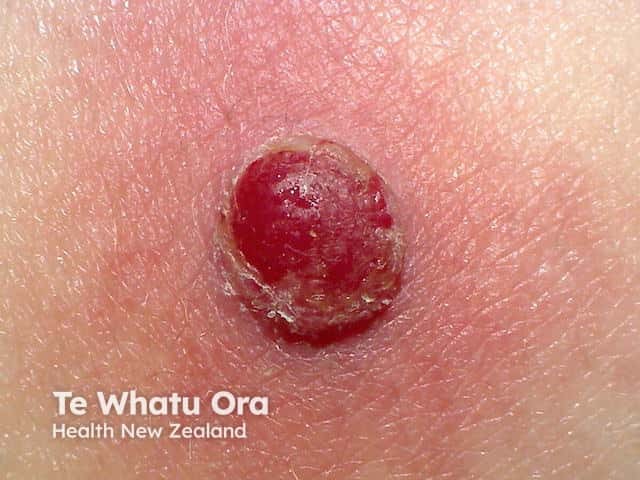
Pyogenic granuloma
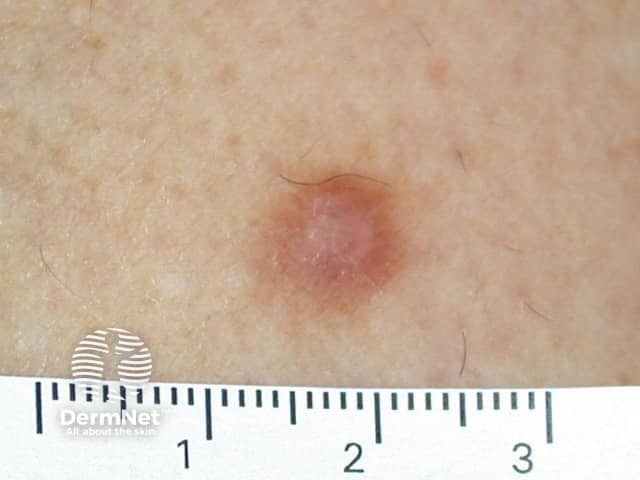
Dermatofibroma is a reactive lesion that presents as one or more firm dermal papules.
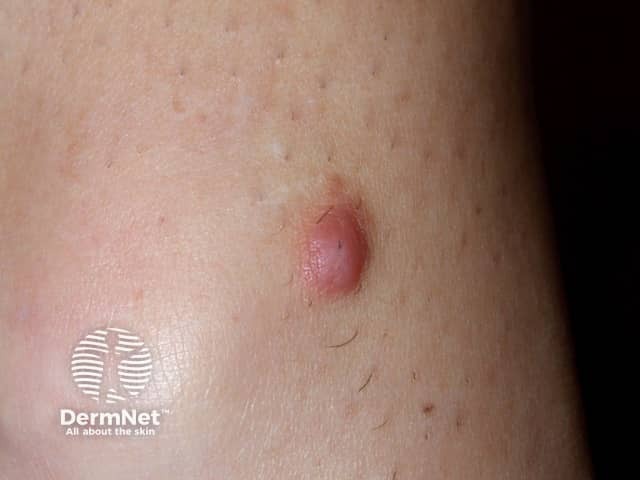
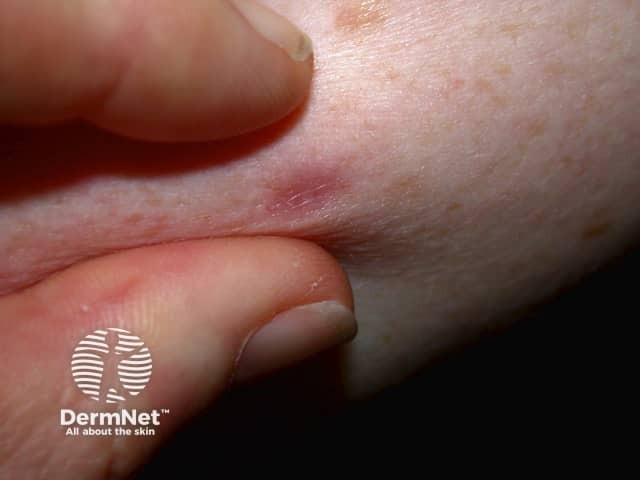
Pinch test
The lipoma is the most common benign soft-tissue tumour.
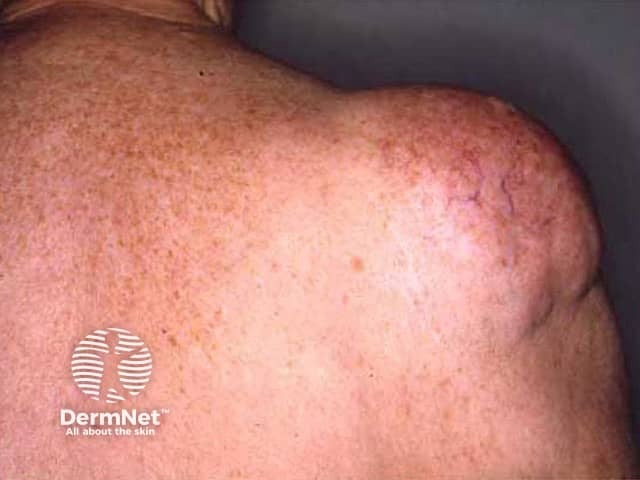
Lipoma
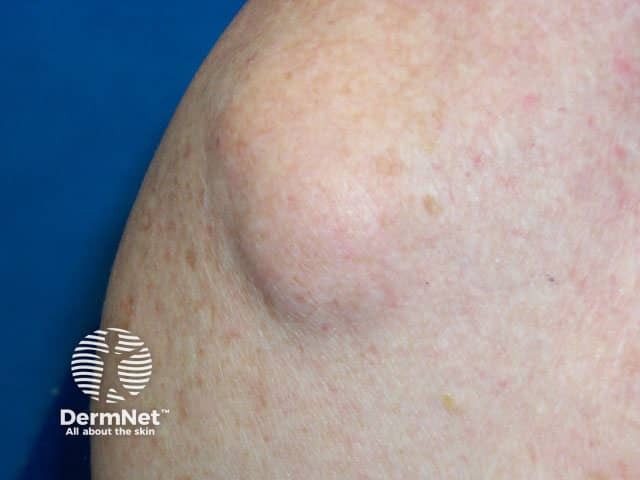
Lipoma
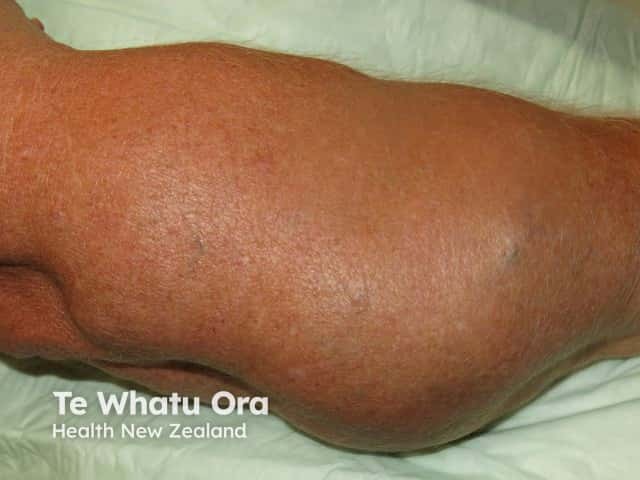
Painful lipomas
The most common type of skin tag is also called acrochordon.
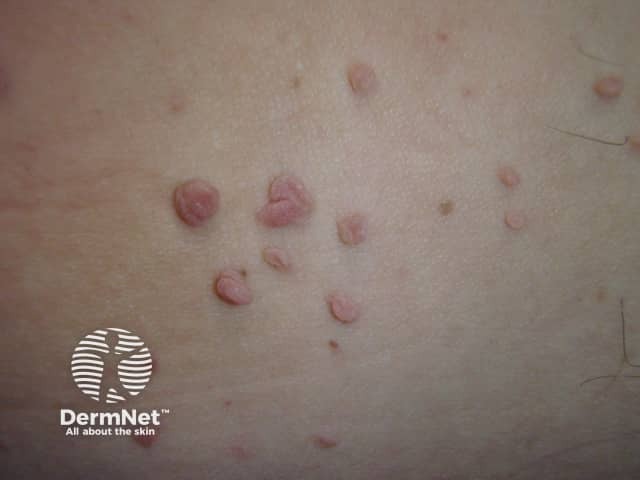
Skin tags
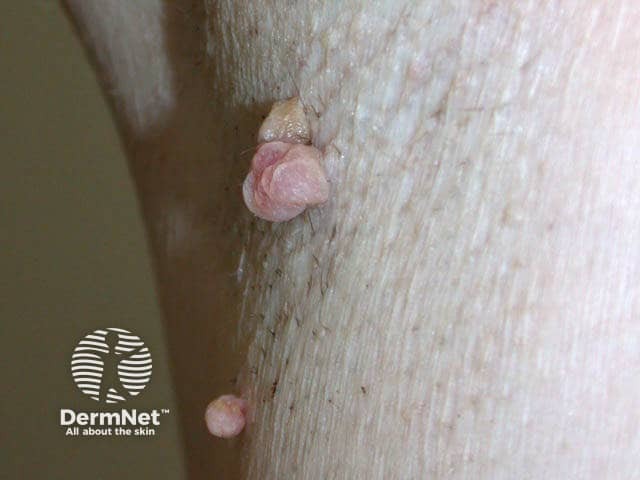
Skin tag
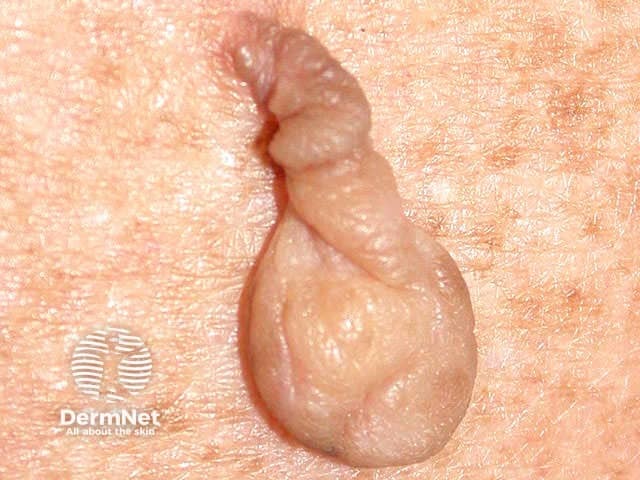
Skin tag