Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Yan Ling Apollonia Tay, Medical Student, University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. March 2020. Reviewed by Dr Louise Reiche, Dermatologist, Palmerston North, New Zealand. Updated June 2020 by Medical Editor: Dr Helen Gordon, Auckland, New Zealand.
Submit your photo of COVID-19-related skin conditions
COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019) is an infection caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2, that can lead to serious respiratory illness and can be fatal.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) declared on 11 March 2020 that the COVID-19 outbreak was officially a pandemic, as COVID-19 had spread rapidly worldwide [1].
Commonly used systemic medications for severe skin conditions include immunomodulators or immunosuppressive drugs. These may include a biological agent, a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD), or a systemic steroid. Dermatological medications are not known to increase the risk of acquiring COVID-19.
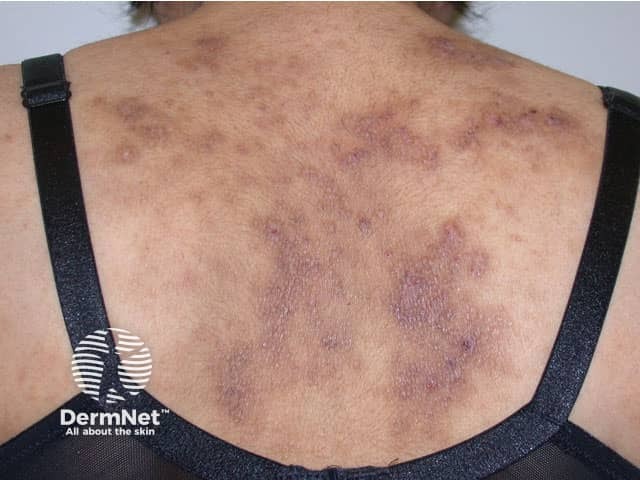
Atopic eczema
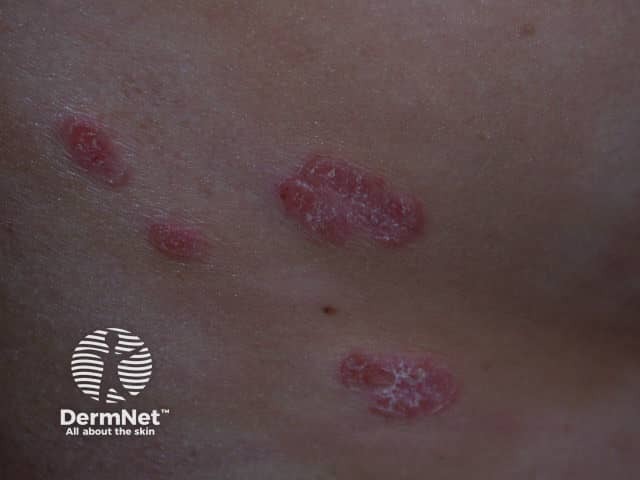
Psoriasis
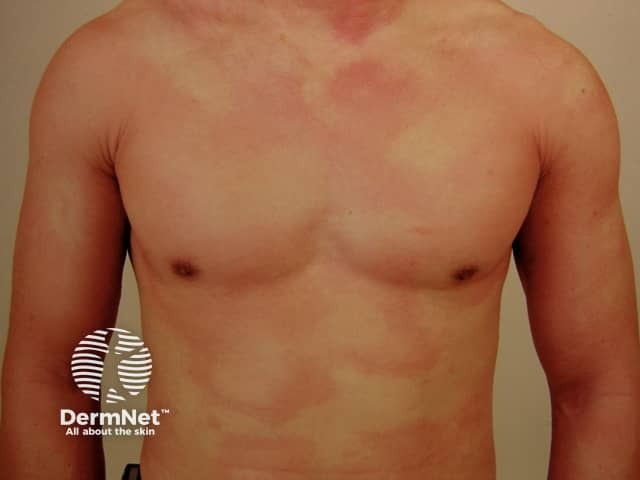
Acute urticaria
If you have tested positive (or are a presumed case) for COVID-19, the biologic medication should be STOPPED for at least four weeks or until you have fully recovered from COVID-19 [3,4]. You should inform any doctor involved in your care that you are on this medication.
If you are currently well, and do not have any other chronic medical conditions [3,4]:
If you have tested positive (or are a presumed case) for COVID-19:
If you have cold or flu-like symptoms [4]:
The influenza vaccine by intramuscular injection is highly recommended for all patients without contraindications. See immunisation in immunosuppressed dermatology patients.