Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Introduction
Demographics
Causes
Clinical features
Complications
Diagnosis
Differential diagnoses
Treatment
Outcome
An incontinence-associated dermatitis is a form of irritant contact dermatitis due to contact with urine and faeces in people who are incontinent of urine or faeces or both (dual incontinence) [1].
Incontinence-associated dermatitis can affect anyone with incontinence of urine, faeces, or both. The reported prevalence varies from 5.6% to 50% with incidence rates between 3.4% and 25%, depending on the setting and population studied [1]. Approximately one-third of patients with faecal incontinence develops incontinence-associated dermatitis [2].
Incontinence-associated dermatitis is due to a combination of chemical and physical irritation of the skin. The presence of urine and faeces causes a rise in pH, which increases the permeability of the skin, affecting barrier function as well as increasing the risk of infection. Friction to the skin causes physical irritation, which results in weakened skin [3].
The clinical findings in incontinence-associated dermatitis are circumscribed redness and swelling of the convexities of genital and anal skin and, in some cases, erosions and blisters (bullae). Depending on position, the distribution of dermatitis can be symmetrical or asymmetrical.
The surrounding skin may have a wet, macerated appearance in the acute phase, and dryness and peeling skin in the chronic phase. Dermatitis may spread to involve the skin folds and in some cases, skin that is not directly in contact with urine and faeces but these areas are always less severely affected.
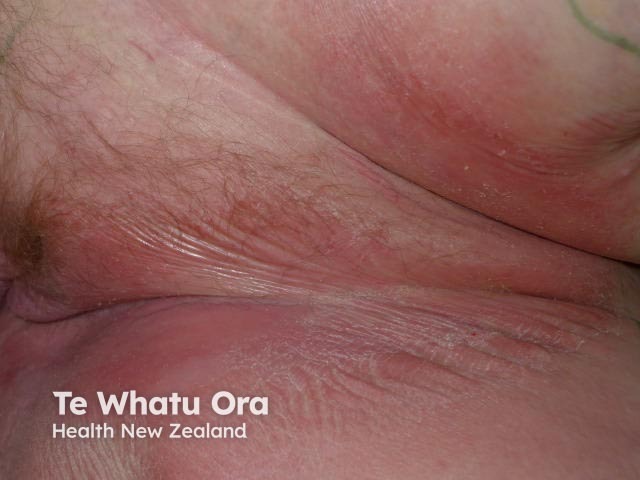
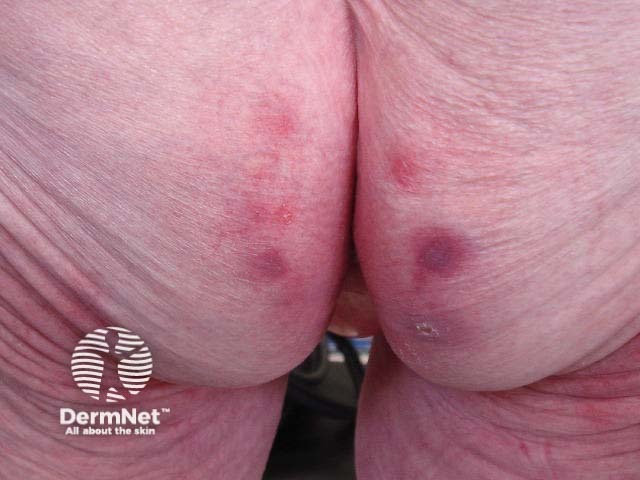
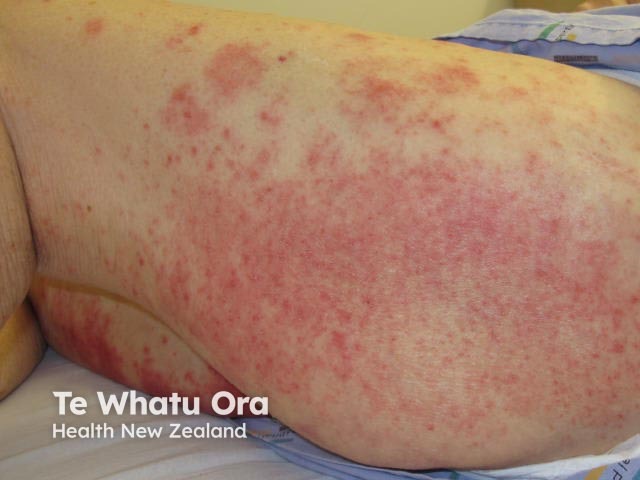
Incontinence-associated dermatitis can cause considerable irritation and discomfort. It can be emotionally upsetting for the patient and caregivers.
There is an increased risk of skin infection with Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus.
Incontinence-associated dermatitis can be complicated by partial and full-thickness pressure ulceration.
Incontinence-associated dermatitis is a clinical diagnosis based on the physical examination findings in people with urine or faecal incontinence.
Incontinence-associated dermatitis should be distinguished from:
Prevent further incontinence-associated dermatitis by careful attention to skin cleansers, regular and liberal applications of a moisturiser, and the use of a barrier cream [1].
The management of incontinence should also be considered and any treatable causes should be addressed.
Treatment of established incontinence-associated dermatitis includes:
There are many over-the-counter preparations for cleansing, moisturising and protecting the skin, but there is not enough evidence to recommend one product over another [4].
Antibiotics and antifungal agents should be used to eradicate confirmed bacterial and fungal skin infections respectively.

Established incontinence-associated dermatitis is difficult to treat and can often recur. Good skin care and management of the incontinence and any associated infection or pressure sores can result in clearance of dermatitis or reduction in its severity.