Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Dr Jenny Chung, House Officer, Department of Dermatology, Auckland City Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand. DermNet Editor In Chief: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell/Maria McGivern. August 2018.
Introduction
Demographics
Causes
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Differential diagnoses
Treatment
Outcome
Pemphigoid nodularis is a rare nodular variant of bullous pemphigoid. There is limited literature on pemphigoid nodularis to date, with only case reports describing the condition. It was first described by Provost et al in 1979 and Yung et al in 1981.
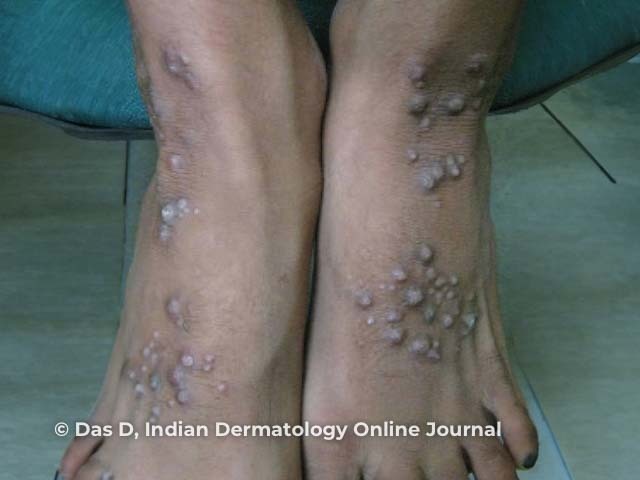
Pemphigoid nodularis
Pemphigoid nodularis is reported to be more common in women and elderly people.
The causes of this nodular type of bullous pemphigoid are unknown. One theory is that the nodules are induced by rubbing and scratching in individuals with subclinical bullous pemphigoid.
Patients with prurigo nodularis (nodular prurigo) may induce pemphigoid antibodies through physical trauma to the skin and basement membrane.
Pemphigoid nodularis presents with hyperkeratotic nodules and blisters, which are usually located on the extremities and trunk.
The nodules are similar to those seen in nodular prurigo. Pruritic papules or confluent plaques have also been reported.
Pemphigoid nodularis requires clinical or histological evidence of both pruritic nodules and blisters.
Histopathological features of pemphigoid nodularis include:
Blood tests may reveal positive indirect immunofluorescence and autoantibody titres to the 180-kD and 230- kD bullous pemphigoid antigens (BP180 and BP230).
Pemphigoid nodularis can appear similar to nodular prurigo and other forms of prurigo. However, nodular prurigo lacks blisters and has no serum or immunofluorescence evidence of IgG to bullous pemphigoid antigens. Histology can be used to differentiate between the two conditions.
The treatment for pemphigoid nodularis can be challenging. Topical steroid therapy alone is inadequate.
Pemphigoid nodularis is treated with the following:
The prognosis of pemphigoid nodularis is uncertain. Older age and/or neurological comorbidities are associated with higher mortality rates.