Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Authors: Harini Rajgopal Bala, Research and Education Fellow; Jennifer Cahill, Dermatologist; Rosemary L Nixon, Dermatologist, Occupational Physician and Director; Occupational Dermatology Research and Education Centre (ODREC), Skin and Cancer Foundation Inc. Melbourne, Australia. November 2016.
Introduction
Causes
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Treatment
Outcome
Periocular dermatitis is a localised form of periorificial dermatitis. It is characterised by small red scaly papules and pustules located around the eye [1].
Periorificial dermatitis includes perioral dermatitis or periocular dermatitis alone, or in association.
The cause of periocular dermatitis is not well understood. It is thought to be due to a combination of environmental and genetic factors [3].
Periocular dermatitis may be related to [3,5]:
Clinical features of periocular dermatitis include:
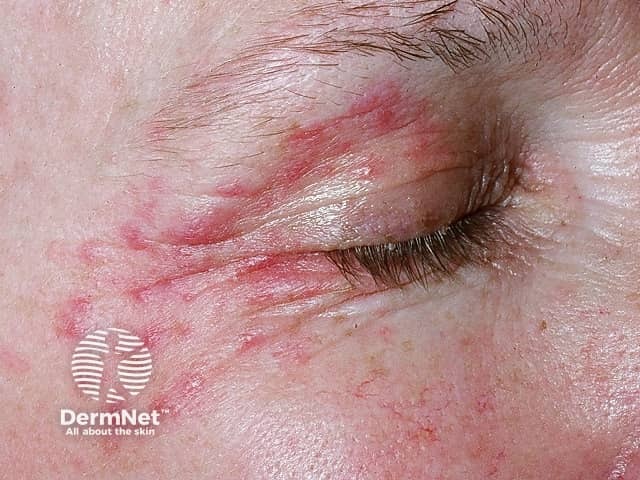
Periocular dermatitis
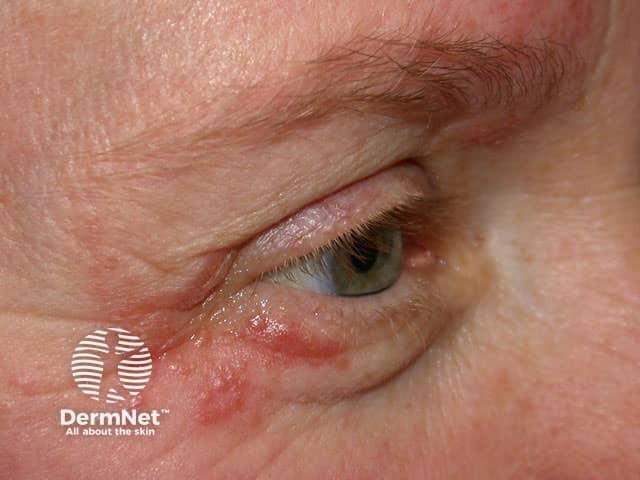
Periocular dermatitis
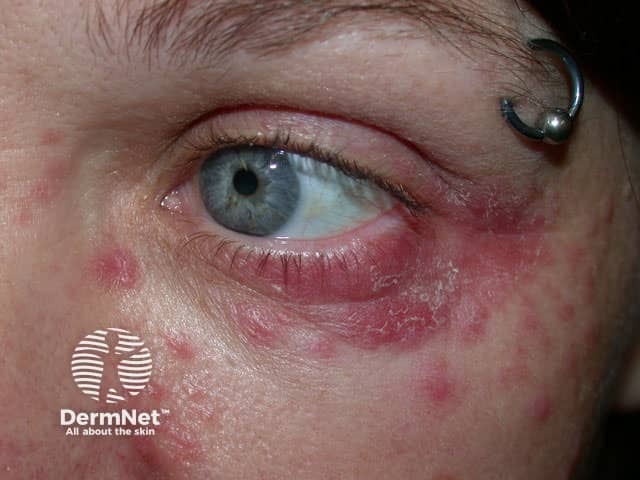
Periocular dermatitis
The clinical presentation of periocular dermatitis is usually typical, and thus it is generally diagnosed on clinical examination [4].
In the unlikely event that a skin biopsy is taken, the histology shows non-specific inflammation, with perifollicular or perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltration [3,4].
Topical therapy may be effective for mild disease [3]. Options include [6]:
Oral therapies may be used alone or in addition to topical treatment for moderate and severe disease. Treatment may be required for up to 3 months.
Periocular dermatitis usually resolves with appropriate management, although it may take some weeks or even months to clear up.
It can be prevented by avoiding applying potent topical corticosteroids and thick face creams around the eye.