Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, 1997. Updated in April 2016.
Background
Who should do a self-skin examination?
When should I examine my skin?
What do skin cancers look like?
Warning signs of skin cancer
What parts of my skin should I check?
When should I see my doctor?
Skin cancer is the most common of all cancers, afflicting perhaps two-thirds of white-skinned New Zealanders and many others throughout the world. Skin cancer is also the easiest cancer to cure if diagnosed and treated early. However, if the skin cancer is allowed to progress, it can result in disfigurement and even death.
Everyone should! It is particularly important for people with the following characteristics to do so.
Skin self-examination can be supplemented by clinical examination by a dermatologist or a general practitioner. In many areas of New Zealand and elsewhere, sophisticated photographic screening systems have been established (mole mapping). Whole-body digital photographs are recorded, together with close-up and dermatoscopic pictures of lesions of concern. These are examined by an expert in dermatoscopy. Whole-body images reveal new lesions, and digital dermatoscopic surveillance at intervals can reveal subtle changes that may indicate the development of melanoma within an existing lesion.
Skin self-examination should be done often enough to become a habit, but not so often as to feel like a bother. For most people an interval of one to three months is ideal. Photographic screening is generally performed annually.
After the first few times, self-examination should take no longer than a few minutes. You will need help in seeing your back, so enrol your partner or a good friend to help.
There are three main types of skin cancer:
There are many other types of skin cancer, but these are rare.
Because each has many different appearances, it is important to know the early warning signs. Look especially for change of any kind. Do not ignore a suspicious spot simply because it does not hurt. Skin cancers may be painless, but dangerous all the same. If you notice one or more of the warning signs, see a doctor right away.
A skin growth that increases in size and appears pearly, translucent, tan brown, black, or multicoloured.
A melanocytic naevus (mole), birthmark or any skin spot that:
A spot or sore that:
In other words, be concerned by a lesion that looks different from your other skin spots. This is sometimes called an ugly duckling—in New Zealand, we often use another term, a black sheep. The good news is that most ugly ducklings turn out to be harmless. Benign melanocytic naevus (moles), freckles and seborrhoeic keratoses can be hard to distinguish from skin cancers at times.
Watch our video on self-examination made in association with Melanoma New Zealand, or check out the self-skin examination guide below.
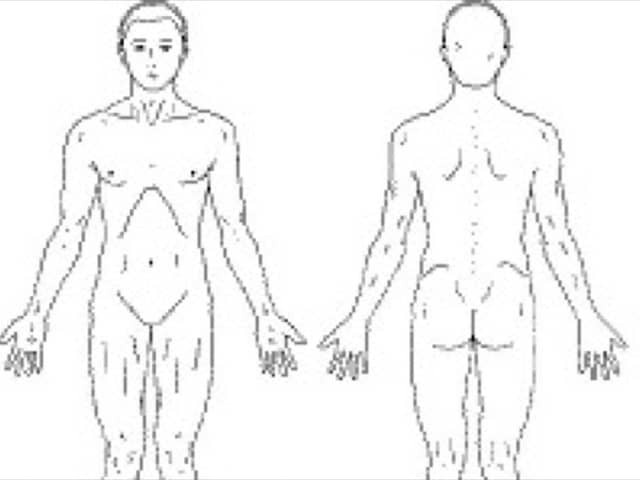
Self examination
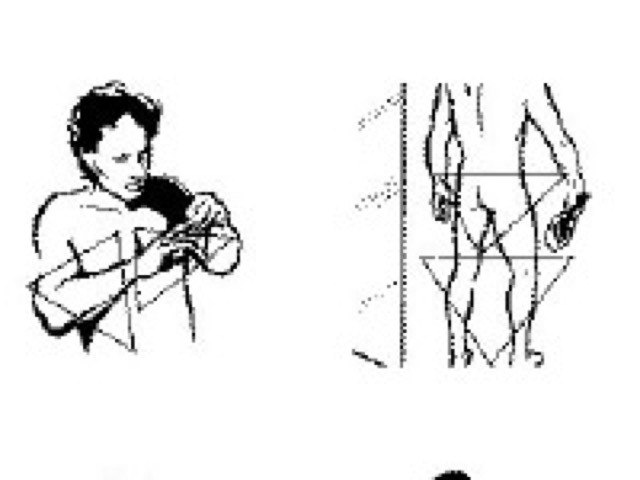
Self examination
Show your doctor anything that concerns you — the earlier the better. Ask for a full skin check. Like most cancers, the earlier you detect skin cancer the simpler the treatment. Because skin cancer is on the outside of your body it is the easiest cancer to see. So even though skin cancer is the commonest cancer, it is also the most curable. Keep your eyes open for any changes, and take a few sensible precautions.