Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer, 2013. Minor revision, 22 February 2014.
Introduction
Causes
Demographics
Signs and symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Outcome
Superficial thrombophlebitis is an inflammation of a superficial vein due to a blood clot and is found just under the skin. It most commonly affects the veins in the leg but can occur in other veins around the body, for example, on the arms, penis and breasts.
The cause of superficial thrombophlebitis is not completely clear but it is believed to be associated with a change in the dynamic balance of haemostasis. In 1846, the German pathologist Virchow showed that damage to a blood vessel wall, abnormal blood flow, or a change in blood constituents causing abnormal blood clotting, could lead to inflammation or formation of blood clots in the veins.
Superficial thrombophlebitis can occur spontaneously and without apparent reason.
Characteristic signs and symptoms of superficial thrombophlebitis include:
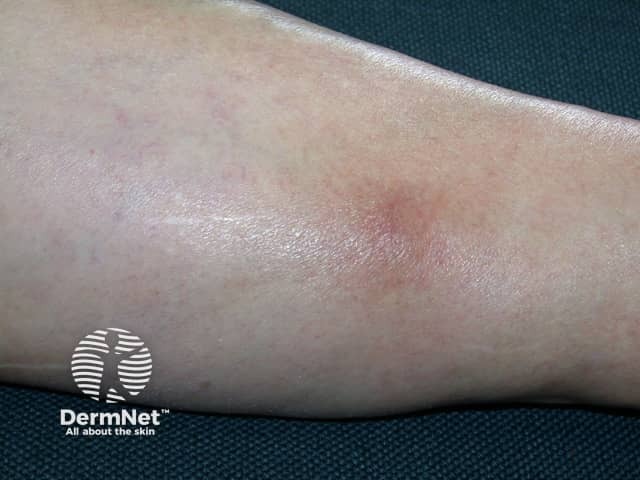
Superficial thrombophlebitis
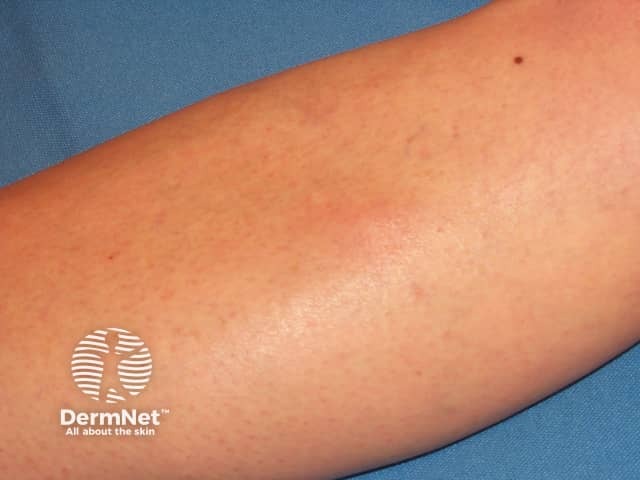
Superficial thrombophlebitis
The visual characteristics of superficial thrombophlebitis are not enough to confirm the diagnosis as several other conditions have similar symptoms. A thorough history and complete physical examination are essential.
If the condition is often recurring or there is the possibility of complications, your doctor may perform other tests, such as blood tests, ultrasound scan and radiographic imaging.
Mild cases of superficial thrombophlebitis may not need any treatment. Usually, symptoms will resolve within 3–4 weeks. You should try to keep up with normal routines and remain active.
In more severe cases the following treatments may be used.
Superficial thrombophlebitis is not usually a serious condition and often settles down and goes away on its own within 2–6 weeks. However, it can be recurrent and persistent and cause significant pain and immobility. In addition, complications may occur if the affected veins become infected or the blood clot moves further up the vein to where the superficial and deep veins join; leading to a more serious condition called deep vein thrombosis (DVT).