Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Diagnosis and testing Inflammation
Author: Dr Ahmed Sadek, Cairo Hospital for Dermatology & Venereology (Al-Haud Al-Marsoud), Egypt. June 2022.
Contributors: Dr Dalia Hossam, Dr Radwa Magdy, Dr Nehal Saied, Dr Noha Hashem, Dr Safaa Yehia Negm, Dr Moshera Saied El Bahrawy, Dr Amira Ragab, Dr Amal Wagih, Dr Haidy El-Hussieny, Dr Mona Ragib, Dr Hala Amer. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. June 2022
Trichoinflamoscopy
Seborrheic dermatitis
Psoriasis
Trichoscopic evaluation of scalp psoriasis
Systemic sclerosis (SSc)
Trichoscopic examination of the forehead area
Dermatomyositis
Trichoscopic findings
The following page covers the features of inflammatory skin disease using trichoscopy.
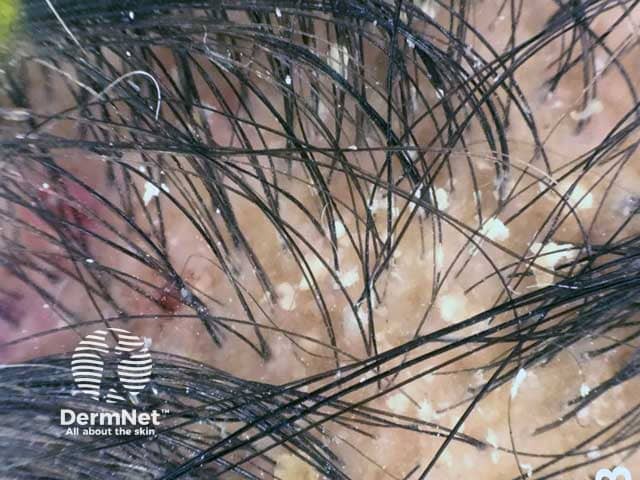
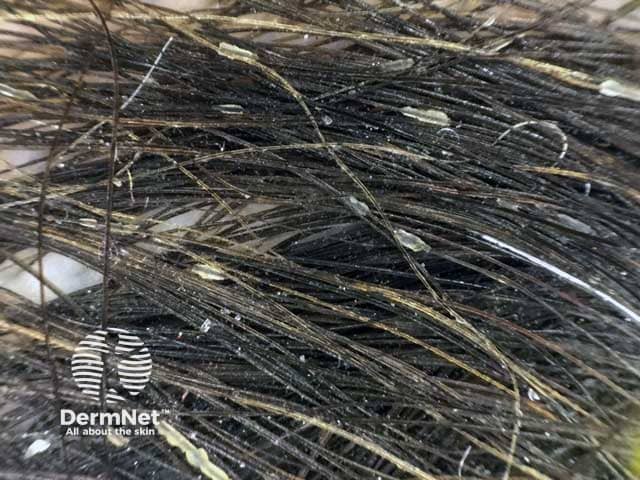
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic relapsing inflammatory skin condition with a predilection for areas rich in sebaceous glands (i.e. the scalp, central face, and anterior chest are most affected). The disorder is characterised by scaling with poorly defined erythematous patches and plaques. Young adults are more frequently affected, and men are affected more than women.
The most frequent trichoscopic findings include:

Dermoscopic image of diffuse yellowish greasy scales in a male patient with seborrhoeic dermatitis
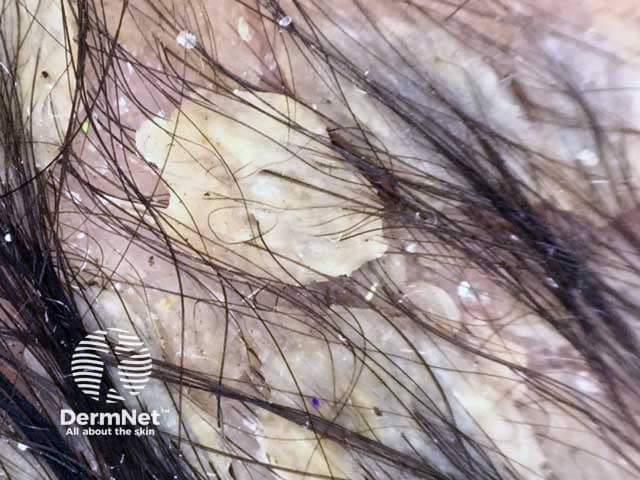
Dermoscopic image of seborrhoeic dermatitis showing adherent yellowish scales and interfollicular oily material on the scalp of a male infant (SD-patient1)

Dermoscopic image of hair casts represented by detached hyperkeratotic and parakeratotic cells of the inner root sheath which surrounds the hair shaft
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory cutaneous disorder with multisystem involvement. The scalp is the most commonly affected site (50–80% of psoriasis patients) and may be the first or only disease manifestation.
Scalp psoriasis is characterised by sharply bordered, erythematous lesions covered by silver or white scales. The lesions often spread over the anterior hairline into the forehead and may also affect the retro-auricular region.
Evaluation of scalp psoriasis is based on the evaluation of vascular alterations.
At low magnifications:
At high magnifications:
Systemic sclerosis is an autoimmune connective tissue disease. Different factors are incorporated in the pathogenesis of the disease including; small vessel vasculopathy, production of autoantibodies, and fibroblast dysfunction.
Clinical manifestations and prognosis are variable according to the degree of cutaneous and systemic organs involvement. Clinical subtypes include limited cutaneous SSc, diffuse cutaneous SSc, and SSc without skin involvement.
Trichoscopic findings include:
Dermatomyositis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterised by proximal myopathy, and cutaneous, cardiac, pulmonary, and gastrointestinal affection. Common cutaneous signs include Gottron's papules, heliotrope rash, mechanic's hand, and poikiloderma.