Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Created 2008.
The first step algorithm for dermoscopy distinguishes melanocytic lesions from non-melanocytic lesions. It is used to evaluate pigmented lesions.
Look for specific features of a melanocytic lesion. If these are absent, look for specific features to diagnose pigmented basal cell carcinoma, seborrhoeic keratosis or haemangioma. Also consider whether the lesion could be a viral wart or dermatofibroma (look for the central white patch). If none of these lesions can be diagnosed, treat the lesion as melanocytic (see above).
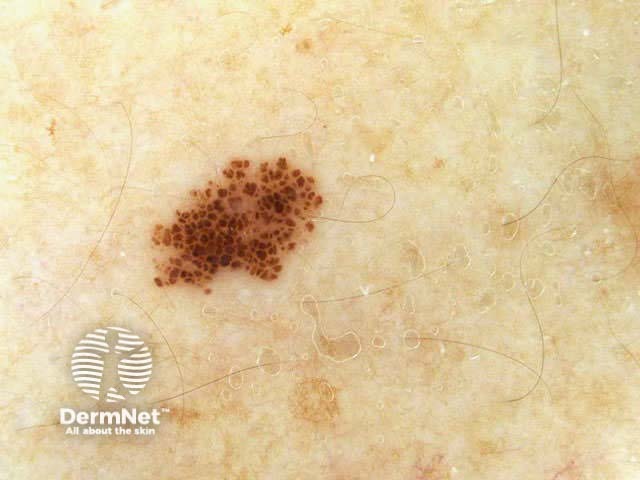
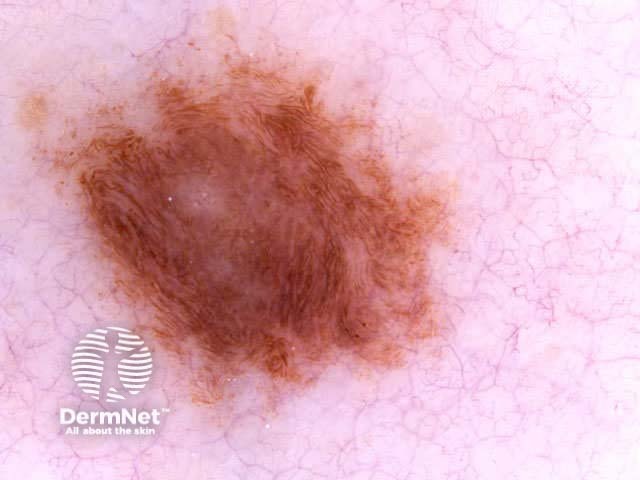
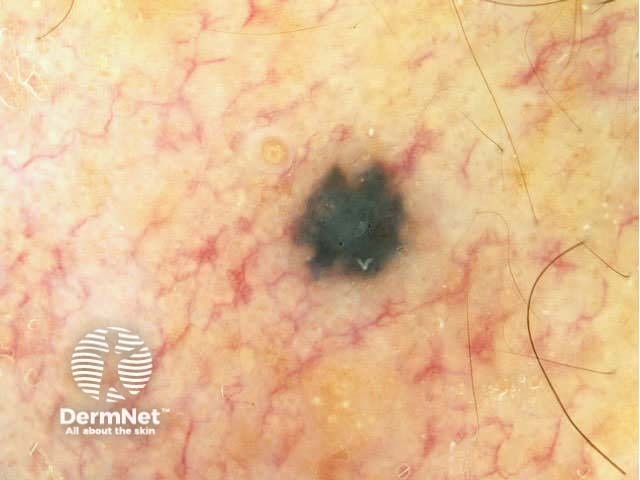
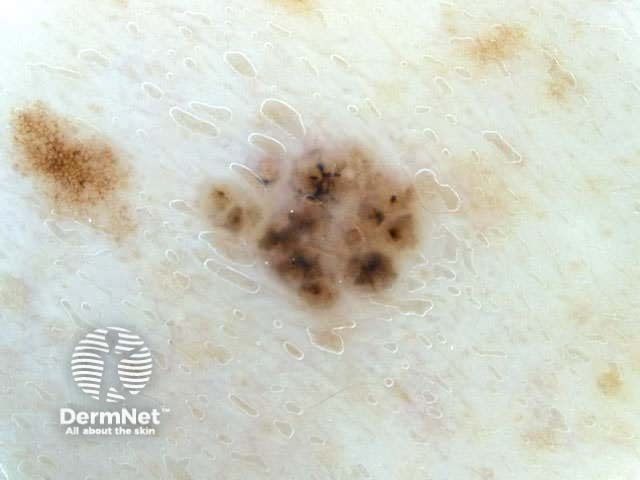
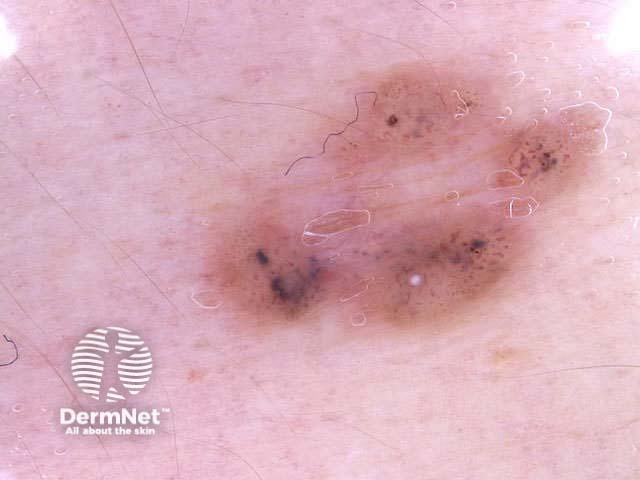
Benign and malignant melanocytic lesions have one or more of the following characteristics:
Pigment network Pseudonetwork Aggregated globules Streaks Homogeneous blue Parallel pattern No listed criteria Multiple features 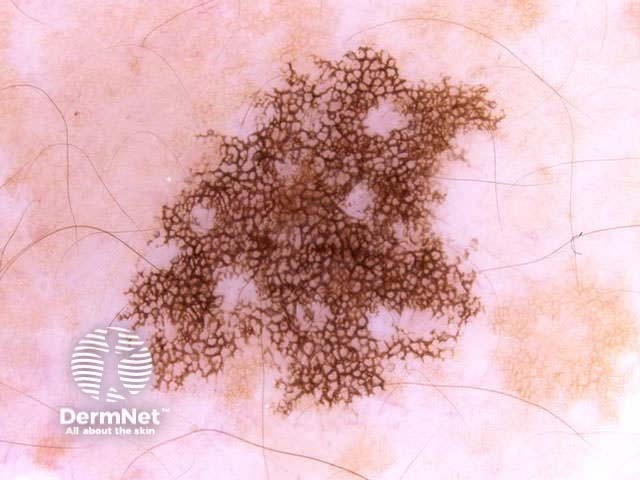
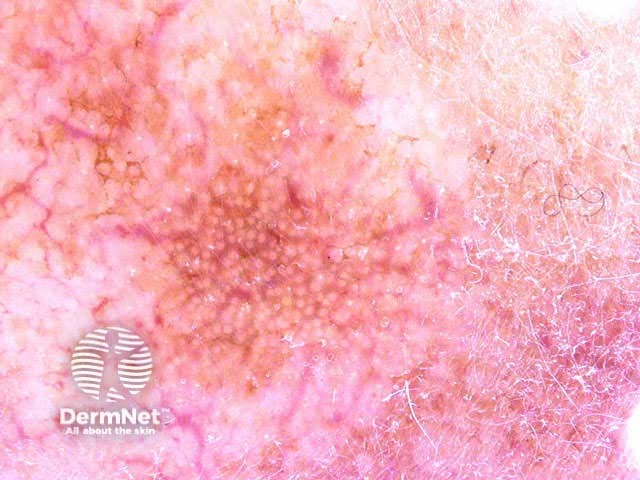

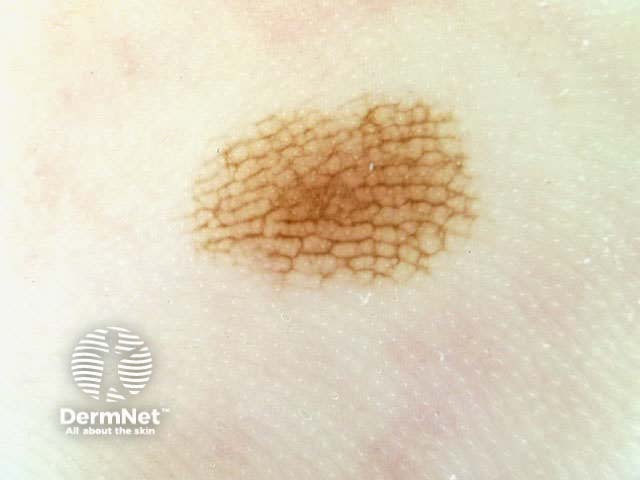
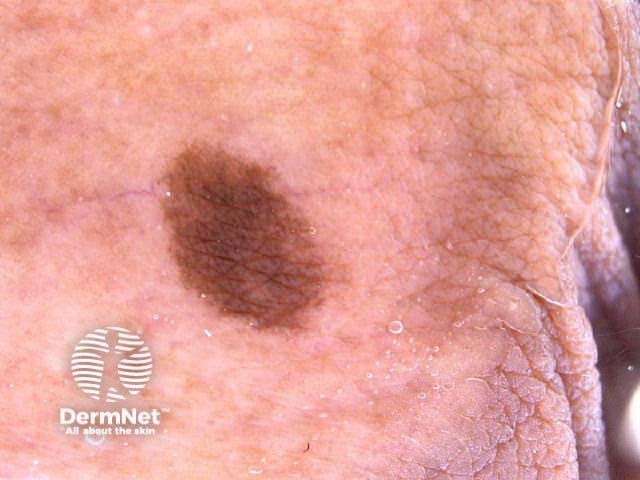
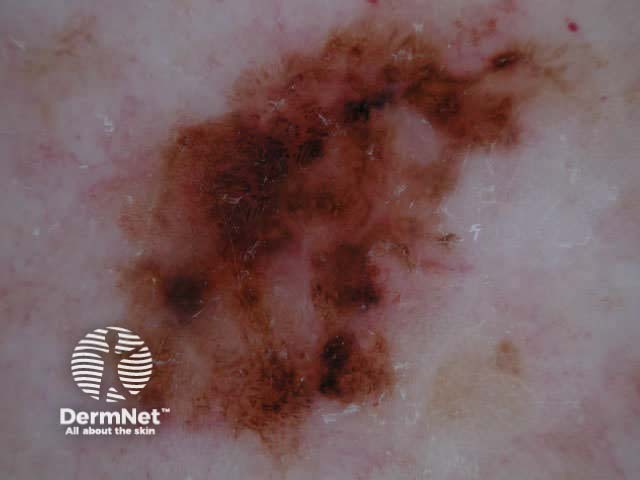
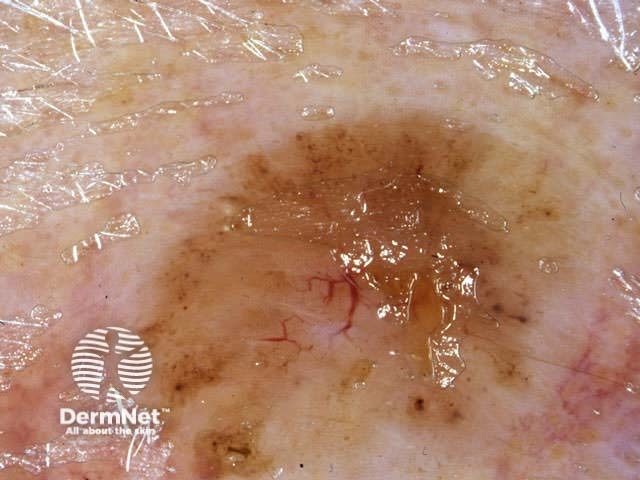
Seborrhoeic keratoses have the following characteristics:
Milia-like cysts Comedo-like openings Fingerprint-like structures Cerebriform pattern 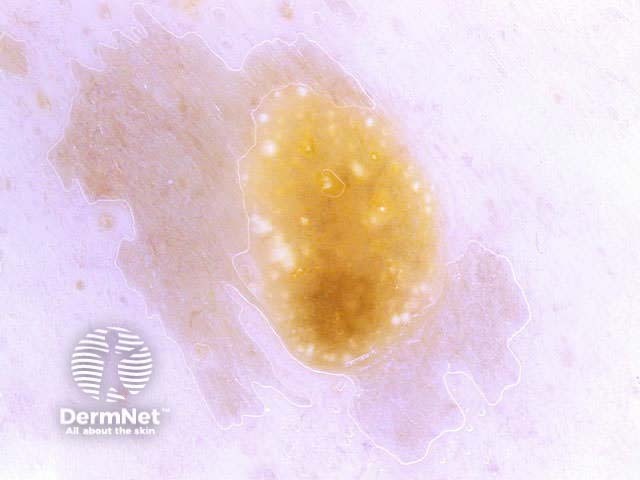
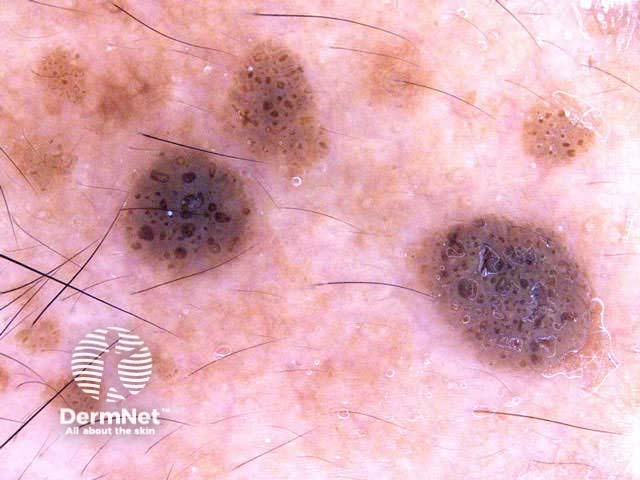
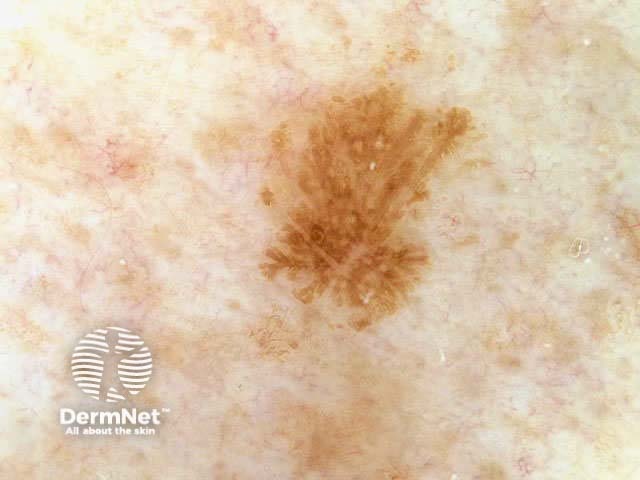
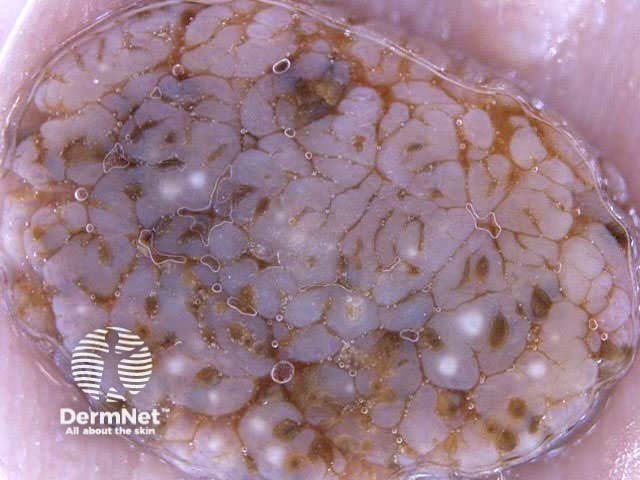
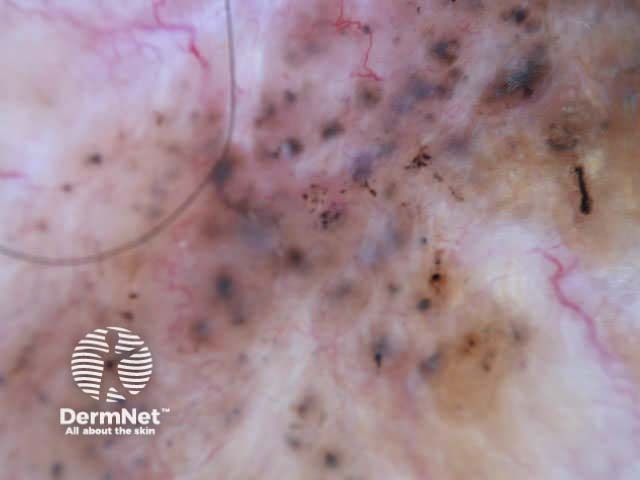
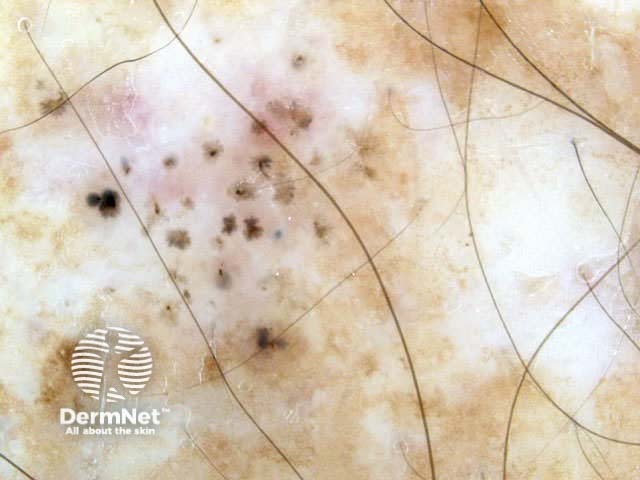
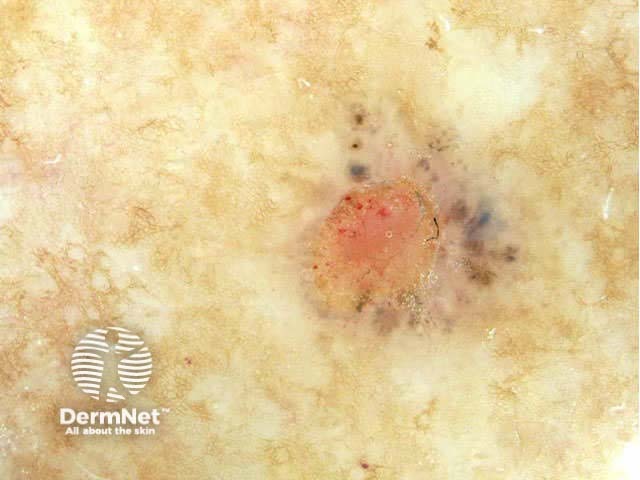
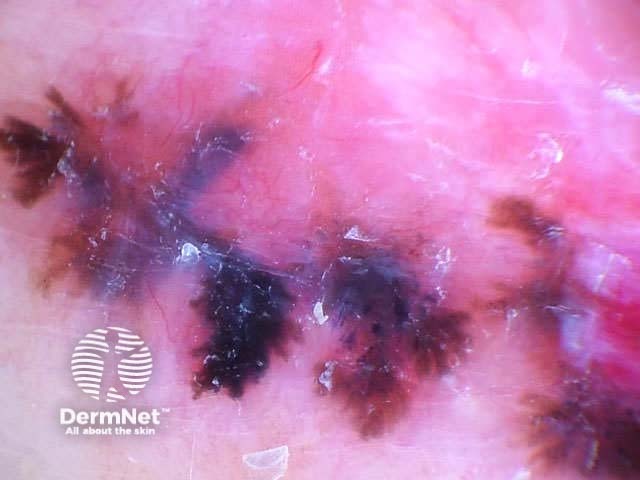
Pigmented basal cell carcinomas have the following characteristics:
Arborising vessels Leaf-like structures Ovoid nests Multiple blue-grey globules Multiple brown globules Spoke-wheel areas Ulceration Bizarre structures 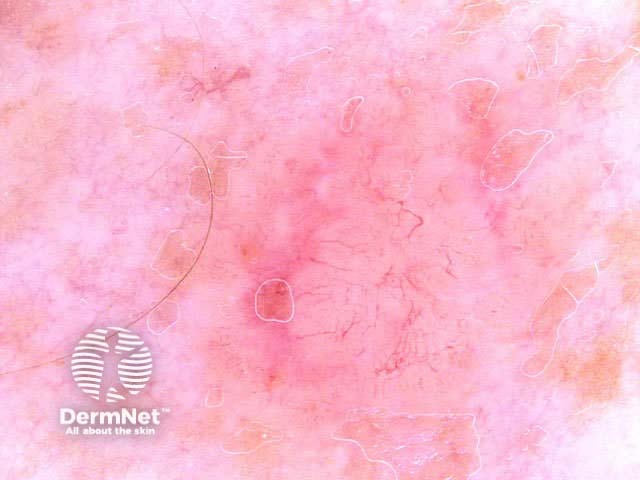
Haemangiomas have the following characteristics:
Red-blue lacunes Red-blue lacunes Homogeneous areas Mixed pattern 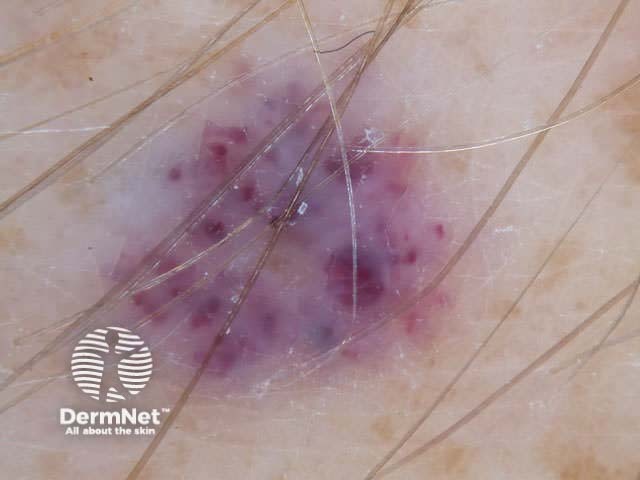
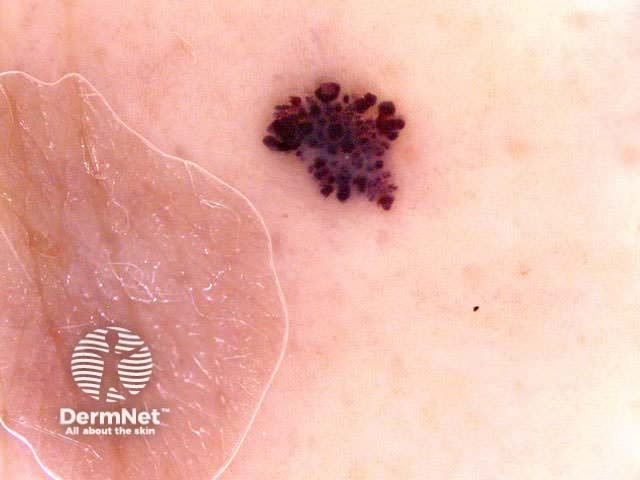
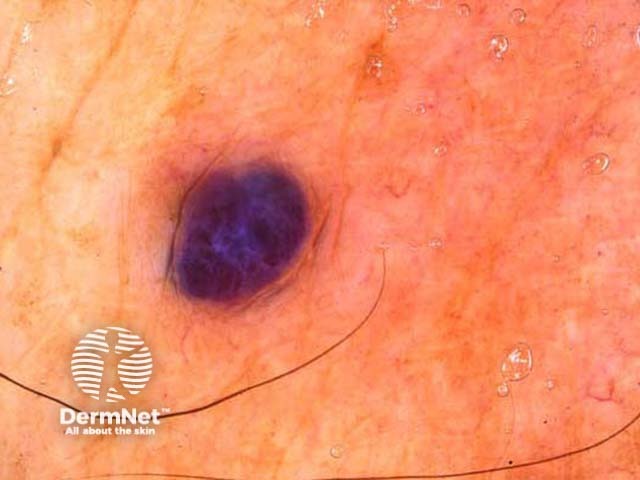
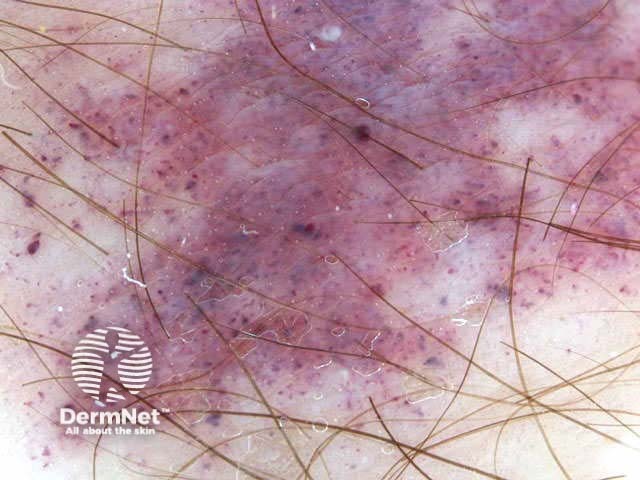
The second step is to distinguish benign melanocytic lesions from malignant melanoma using one of the following methods.
If these algorithms appear too complicated, use the 3-point checklist, which is a safe way to identify malignant pigmented lesions.
Practice identifying melanocytic and non-melanocytic pigmented lesions by dermoscopy.
See the DermNet bookstore.