Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Authors: Dr Alexander Coe, Dermatology Registrar, Canberra Hospital, Canberra, Australia; Dr Catherine Drummond, Dermatologist, Canberra, Australia. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. July 2021
Introduction
Uses
Contraindications
More information
Benefits
Disadvantages
Side effects and risks
Baricitinib is an orally administered first-generation selective inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase receptors JAK 1 and JAK 2 approved for use in some countries for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and atopic dermatitis.
Baricitinib is approved for use in various countries for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy. It can be used in combination with topical steroids and/or topical calcineurin inhibitors. Clinical trials have reported 60% of patients taking 4 mg/d achieve EASI 50 after 16 weeks.
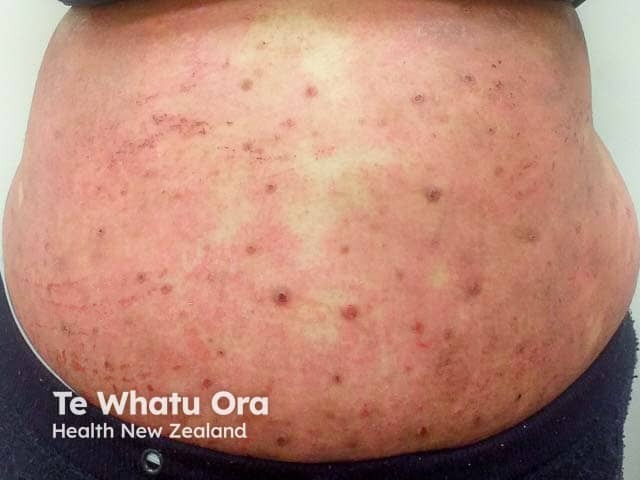
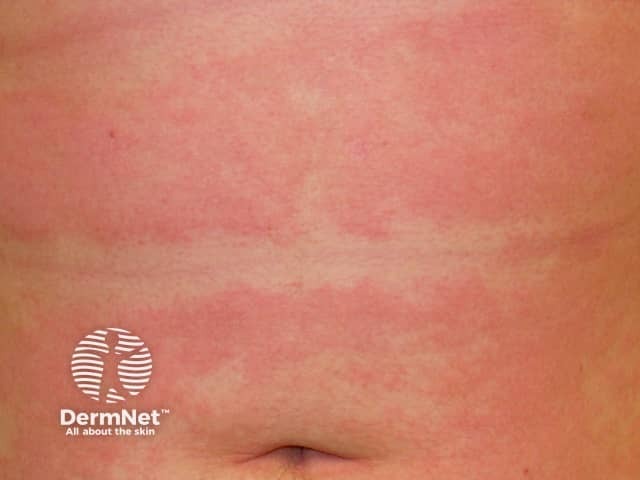
Subacute atopic dermatitis
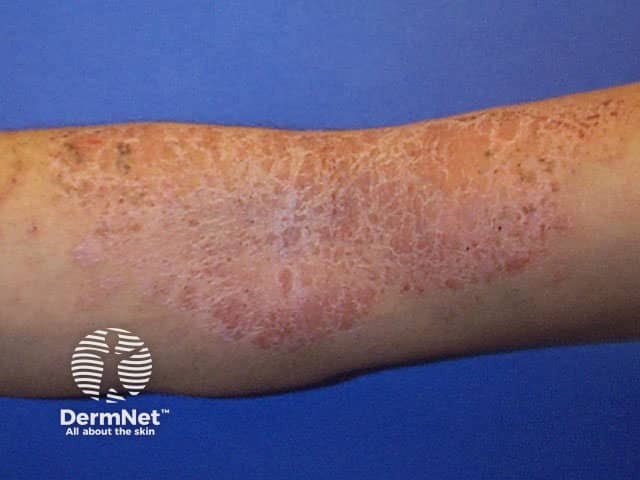
Atopic dermatitis
Clinical trials in progress are demonstrating efficacy in the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis, alopecia areata, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Caution should be used when treating the elderly (>65 years of age), patients with Stage 3 renal impairment, or diabetics.
Baricitinib is a novel small molecule inhibitor of tyrosine kinase receptors. It has anti-inflammatory effects by reducing expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin (IL)-6, IL-12, IL-17, IL-22, IL-23, and interferon-gamma.
Baricitinib is available as 2 mg and 4 mg film-coated tablets which are taken orally with or without food. The usual starting dose for treating atopic dermatitis is 2 mg/d, increasing to 4 mg/d if disease activity is not controlled. Treatment should be ceased after 8 weeks of 4 mg/d if there has been no clinical improvement.
Before starting baricitinib, investigations should include:
Monitoring during baricitinib treatment should include full blood count, liver function tests, and lipids. Treatment should be interrupted if haemoglobin falls below 8 g/dL, lymphocyte count below 500 cells/mm3, neutrophil count below 1000 cells/mm3, or liver transaminases increase.
Baricitinib is generally well-tolerated and clinical trials have extended out to 52 weeks of use.
In 2021, the FDA issued new and updated black box warnings for baricitinib in line with warnings in place for tofacitinib. Although large safety trials have not been conducted with baricitinib, their similar mechanisms of action raise concerns regarding a possible increased risk of serious heart events, blood clots, and death.
Approved datasheets are the official source of information for medicines, including approved uses, doses, and safety information. Check the individual datasheet in your country for information about medicines.
We suggest you refer to your national drug approval agency such as the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory agency (MHRA) / emc, and NZ Medsafe, or a national or state-approved formulary eg, the New Zealand Formulary (NZF) and New Zealand Formulary for Children (NZFC) and the British National Formulary (BNF) and British National Formulary for Children