Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Hydroquinone — extra information
Hydroquinone
Authors: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer, 2005; Updated: Dr Ian Coulson, Consultant Dermatologist, East Lancashire NHS Trust, Lancashire, UK. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. September 2021.
Introduction Demographics Contraindications More information Benefits Disadvantages Side effects and risks
What is hydroquinone?
Hydroquinone is a skin-lightening agent used topically for the treatment of hyperpigmentation.
Who uses hydroquinone?
Hydroquinone is most commonly used in bleaching creams by patients aged 13 years and over with a dark skin type. It can be used, often in combination with other medications, to treat:
- Melasma
- Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation such as subsequent to acne
- Freckles and lentigines
- Poikiloderma of Civatte
- Drug-induced pigmentation due to chemotherapy agents
- Folliculitis barbae and pseudofolliculitis barbae
Hydroquinone may also be used as a pretreatment before fractional laser therapy or chemical peels.
Skin conditions that may be treated with hydroquinone
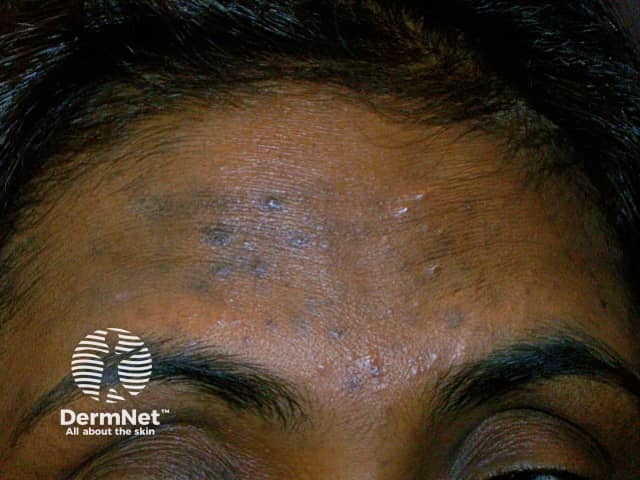
Hyperpigmentation due to acne
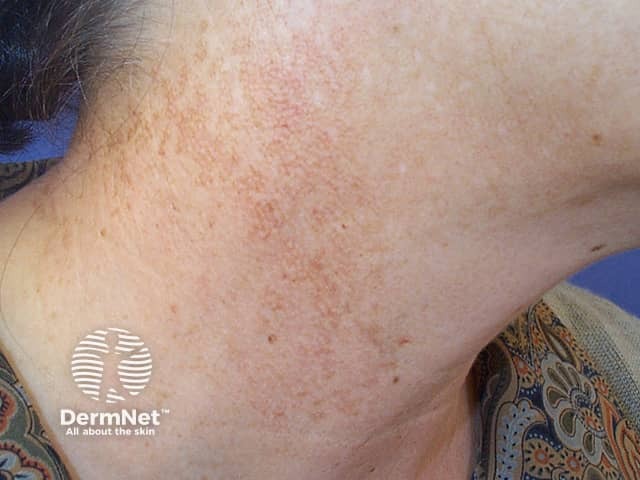
Poikiloderma of Civatte
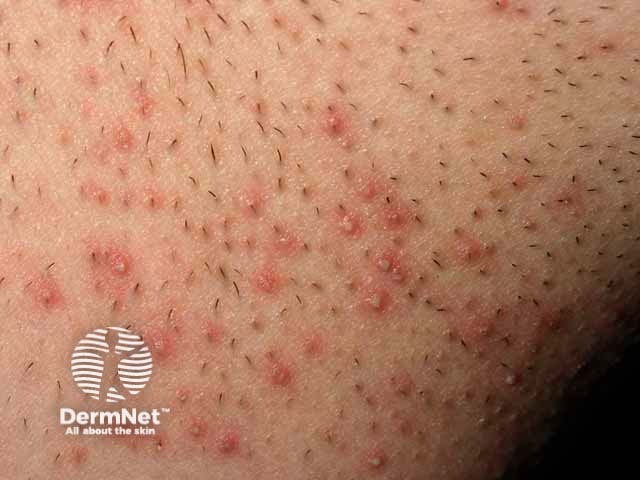
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
What are the contraindications with hydroquinone?
Hydroquinone should not be used by individuals allergic to hydroquinone or any of the excipients in the formulation such as the preservative metabisulphite. [see Contact allergy to preservatives]
Tell me more about hydroquinone.
Hydroquinone is used in a cream or lotion formulation in a concentration of 1-5%. It is often found in a combination formulation with other skin lightening agents such as topical retinoids (to increase efficiency) and low potency topical steroids (to reduce irritancy).
In New Zealand and many other countries, hydroquinone is only available on prescription, and may need to be compounded by the pharmacist.
Hydroquinone must be distinguished from monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone which can cause irreversible pigment loss. [see Depigmentation therapy for vitiligo]
Mechanism of action of hydroquinone
Hydroquinone lightens epidermal, but not dermal, pigmentation by reducing the production of new melanin:
- Reversible inhibition of tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in converting L3,4-diphenylalanine to the skin pigment melanin
- Selective damage to melanocytes and melanosomes.
How to use hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is applied topically just to the hyperpigmented skin only, twice daily for 3 months, after which time many patients maintain their improvement by using it twice each week. If there has been no benefit after 3 months of treatment, then the hydroquinone should be stopped. Management of the underlying cause of the hyperpigmentation is also recommended.
When initiating hydroquinone treatment, it is advisable to:
- Start with a test area about 1 cm in diameter. If there is no irritation or redness within 24 hours, the cream can be used more widely on the affected areas.
- Apply a thin film initially daily and if there is no irritation after one week, the application frequency can be increased to twice a day.
- Do not apply close to the eyes or mouth.
- Do not use any other topical medication, particularly benzoyl peroxide.
- Wait for 10 minutes before applying sunscreen or cosmetics over the hydroquinone.
- Treatment should be discontinued if undue redness, scaling, itch, or weeping occurs.
What are the benefits of hydroquinone?
Hydroquinone is particularly effective for the treatment of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation which is unlikely to recur provided the underlying inflammatory dermatosis is also controlled.
In melasma, 70% of sufferers notice clearance or reduction in pigmentation with twice daily hydroquinone used for three months. This improvement can be maintained in 50% of individuals with twice weekly application.
Response of melasma after three months of hydroquinone
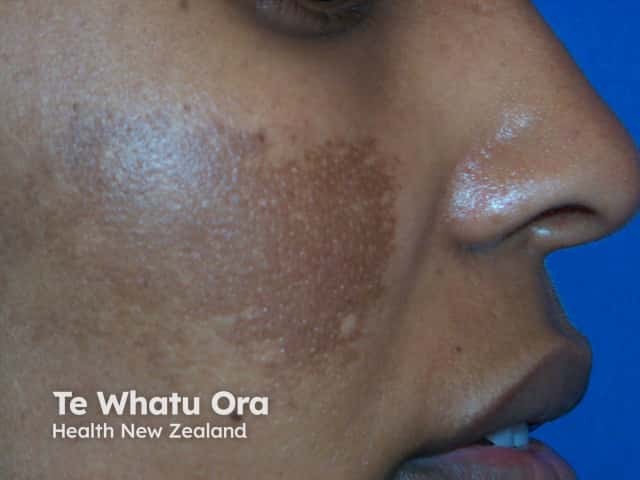
Pre-treatment
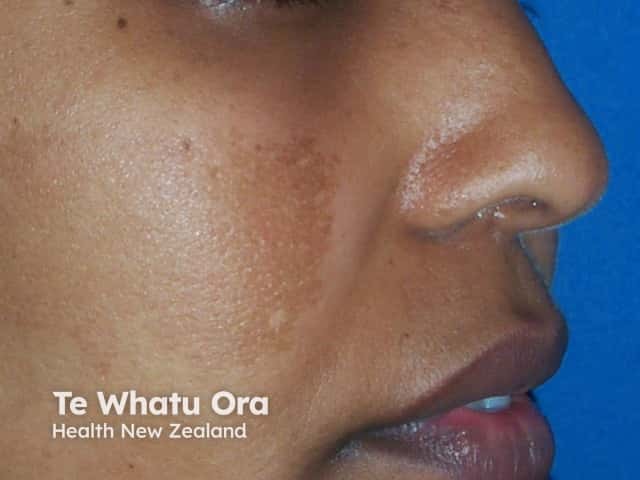
Post-treatment
What are the disadvantages of hydroquinone?
Hydroquinone does not treat pigmentation in the dermis.
Melasma can be resistant to treatment and usually requires combination therapy and multiple therapeutic approaches, of which hydroquinone is one component.
What are the side effects and risks of hydroquinone?
Hydroquinone can cause mild irritant contact dermatitis when used in concentrations above 4%. A short drug holiday and/or application of a topical steroid will usually settle the reaction.
Commercial formulations of hydroquinone contain the preservative metabisulphite, which can cause an allergic reaction.
Concerns have been raised about the safety of hydroquinone in Europe, Japan, and the USA due to:
- High dose oral hydroquinone causing cancer in rats, however after 50 years of topical use there have been no cases of cancer reported in humans
- Exogenous ochronosis due to topical hydroquinone used in high concentrations, multiple times per day, for years.
Other reported cutaneous adverse effects of hydroquinone include:
- Pigmented colloid milium
- Foreign body reaction
- Milia
- Acquired trimethylaminuria
- Nail pigmentation.
The safety of topical hydroquinone has not been established in pregnancy and lactation.
Nail pigmentation due to hydroquinone use
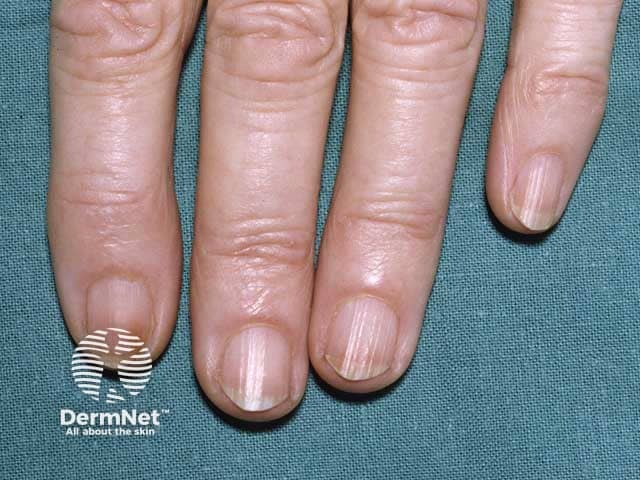
Nail pigmentation due to hydroquinone
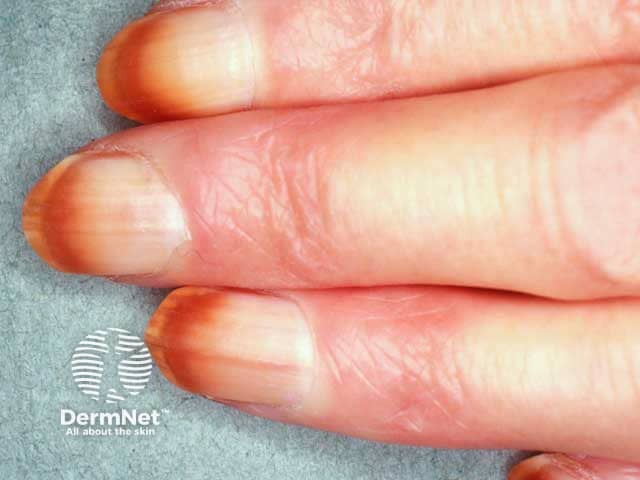
Nail pigmentation due to hydroquinone
Approved datasheets are the official source of information for medicines, including approved uses, doses, and safety information. Check the individual datasheet in your country for information about medicines.
We suggest you refer to your national drug approval agency such as the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory agency (MHRA) / emc, and NZ Medsafe, or a national or state-approved formulary eg, the New Zealand Formulary (NZF) and New Zealand Formulary for Children (NZFC) and the British National Formulary (BNF) and British National Formulary for Children (BNFC).
Bibliography
- Chandra M, Levitt J, Pensabene CA. Hydroquinone therapy for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation secondary to acne: not just prescribable by dermatologists. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012;92(3):232–5. doi:10.2340/00015555-1225. Journal
- McKesey J, Tovar-Garza A, Pandya AG. Melasma treatment: an evidence-based review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(2):173–225. doi:10.1007/s40257-019-00488-w. PubMed
- Saade DS, Maymone MBC, De La Garza H, Secemsky EA, Kennedy KF, Vashi NA. Trends in use of prescription skin lightening creams. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(11):5650. doi:10.3390/ijerph18115650. Journal
- Schwartz C, Jan A, Zito PM. Hydroquinone. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; May 10, 2021. PubMed
- Sofen B, Prado G, Emer J. Melasma and post inflammatory hyperpigmentation: management update and expert opinion. Skin Therapy Lett. 2016;21(1):1–7. Journal
- Tse TW. Hydroquinone for skin lightening: safety profile, duration of use and when should we stop?. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010;21(5):272–5. doi:10.3109/09546630903341945. PubMed
On DermNet
- Acne scarring
- Brown spots and freckles
- Cysteamine cream
- Ethnic dermatology
- Nail cosmetics allergy
- Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation
- Solar lentigo
Other websites
