Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Author: Anoma Ranaweera, Medical Writer, New Zealand. Editor in Chief: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. October 2019.
Introduction - interleukin-17 Introduction - interleukin-17 pathway Protective role of interleukin-17 Skin disease involvement Future indications
Interleukin (IL)-17 refers to a family of proteins that play critical roles against bacterial infections and fungal infections and in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
The IL-17 cytokine family consists of six cytokines (interleukins 17A to 17F) and five receptors (interleukins 17RA to 17RE). The interleukins 17A, 17F, and 17A/F heterodimer ligands share a common receptor subunit (interleukin-17RA) for signalling.
IL-17 is mainly produced by a subset of CD4 cells named Th-17 (T–helper 17) cells. It is mainly secreted by activated CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, while its receptor is found on many cell types.
IL-17 has been classified as a pro-inflammatory cytokine because it induces the expression of mediators of inflammation involved in the proliferation, maturation, and chemotaxis of neutrophils.
Overproduction of interleukins 17A, 17F, and 17A/F is associated with tissue damage and autoimmune diseases such as:
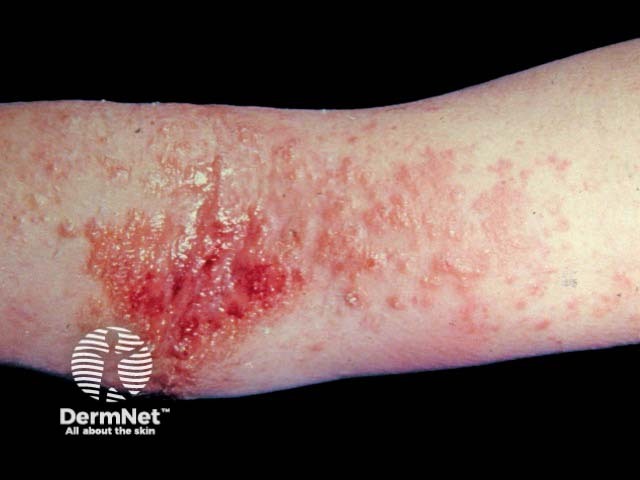
Atopic eczema
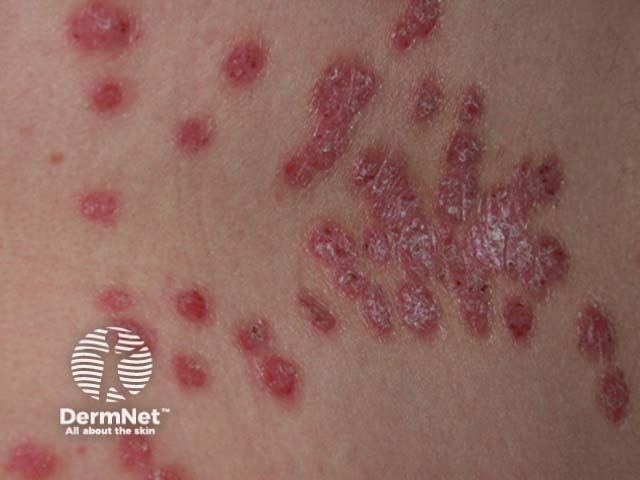
Chronic plaque psoriasis
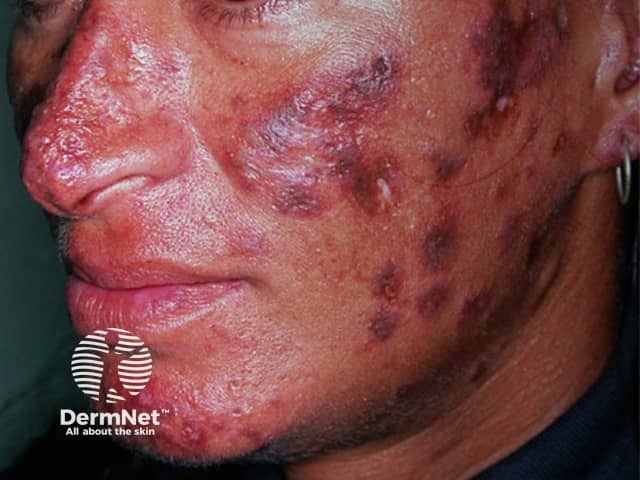
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
The IL-17 family of cytokines play a role in the management of pathogens.
The same cytokines have also been reported to have functions outside the skin, at least trials involving mice. IL-17E has a protective role in CNS inflammation and participates in protective responses against parasites in the intestine [7–9].

Candida intertrigo
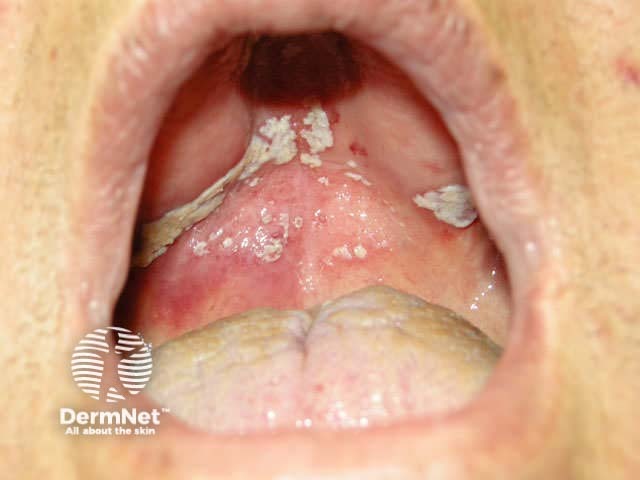
Oral candidiasis
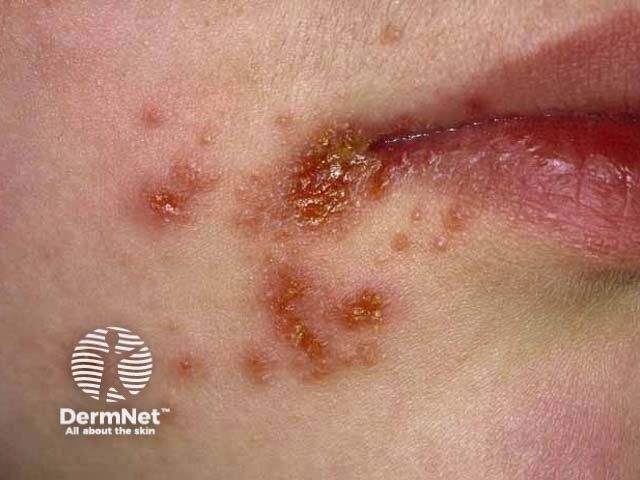
Impetigo
Skin diseases in which interleukin-17 is involved or is thought to be involved are as follows.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by epidermal hyperplasia.
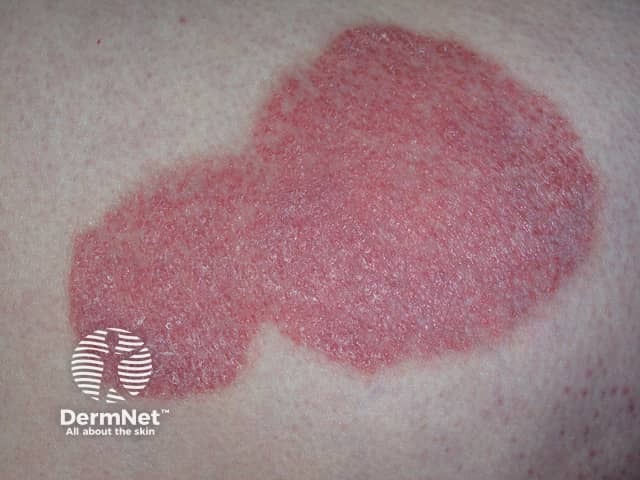
Chronic plaque psoriasis
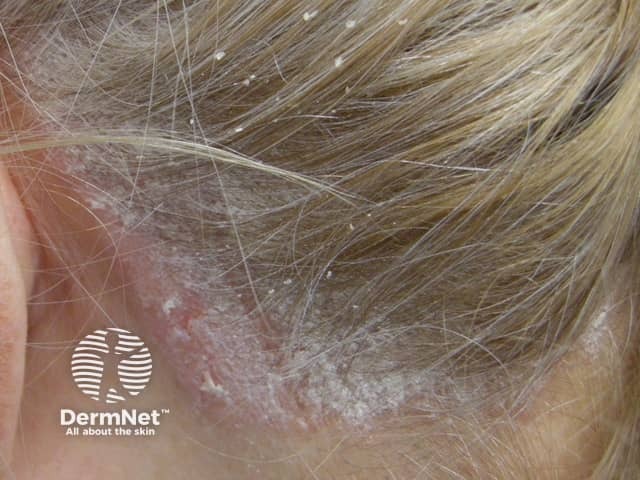
Scalp psoriasis
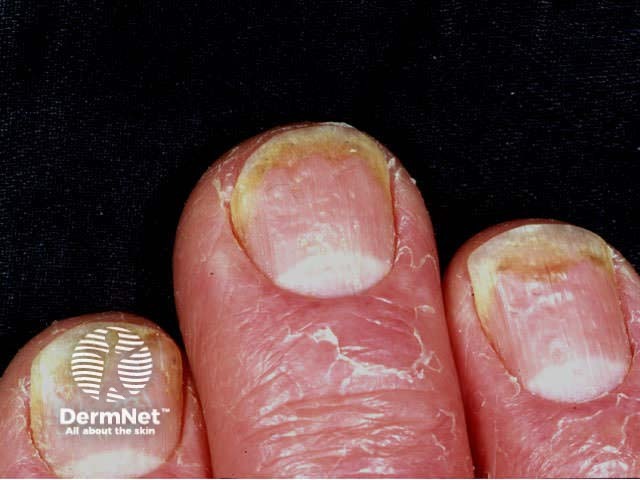
Nail psoriasis
The role of IL-17 is under investigation in various forms of dermatitis.
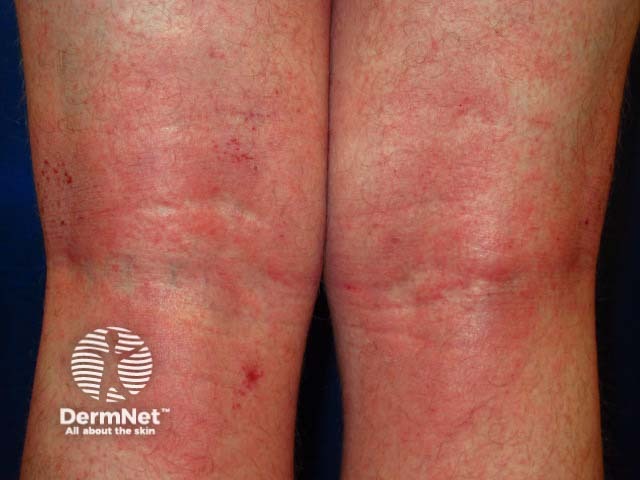
Atopic dermatitis
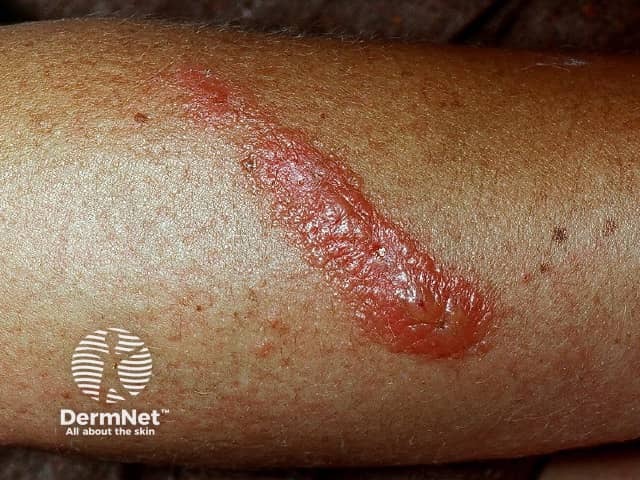
Plant contact dermatitis
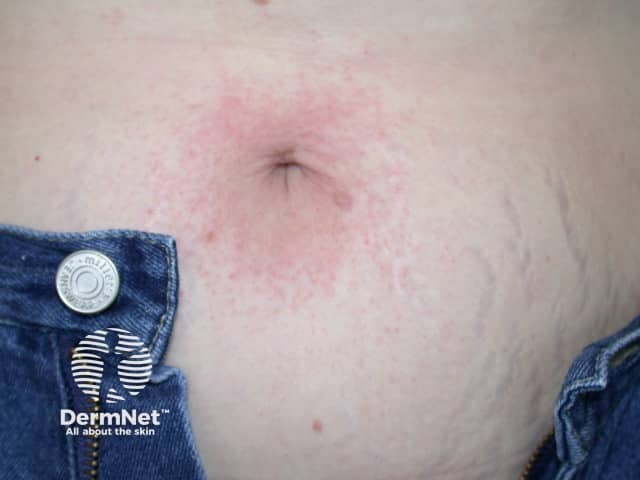
Nickel dermatitis
IL-17 signalling has been associated with the development of skin cancer during chemical carcinogenesis in mouse models.
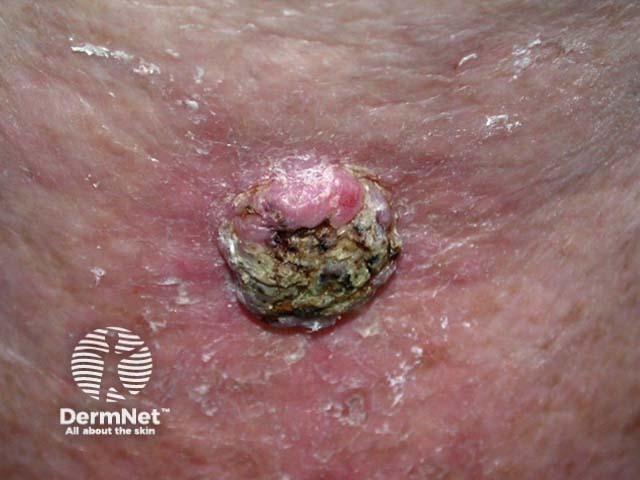
Squamous cell carcinoma of limbs
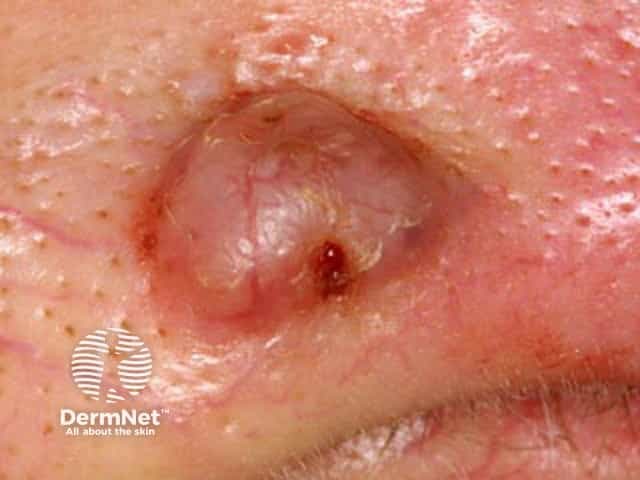
Basal cell carcinoma affecting the nose
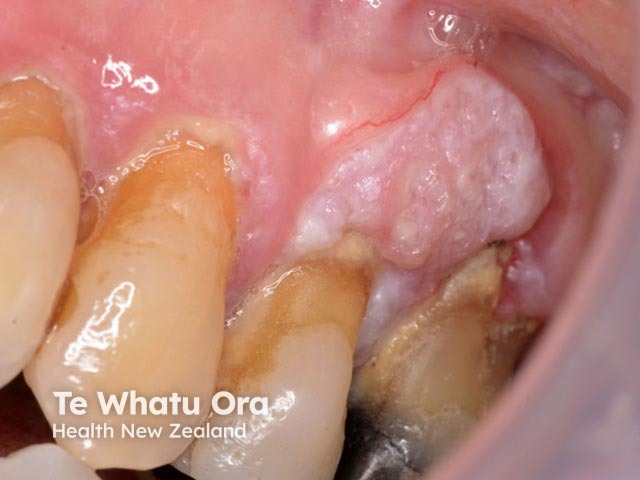
Oral cancer
The proinflammatory properties of IL-17 are protective against infection. A good understanding of the different roles played by the IL-17 cytokines is necessary to design effective drugs relating to pathogenesis and mechanisms of inflammation.